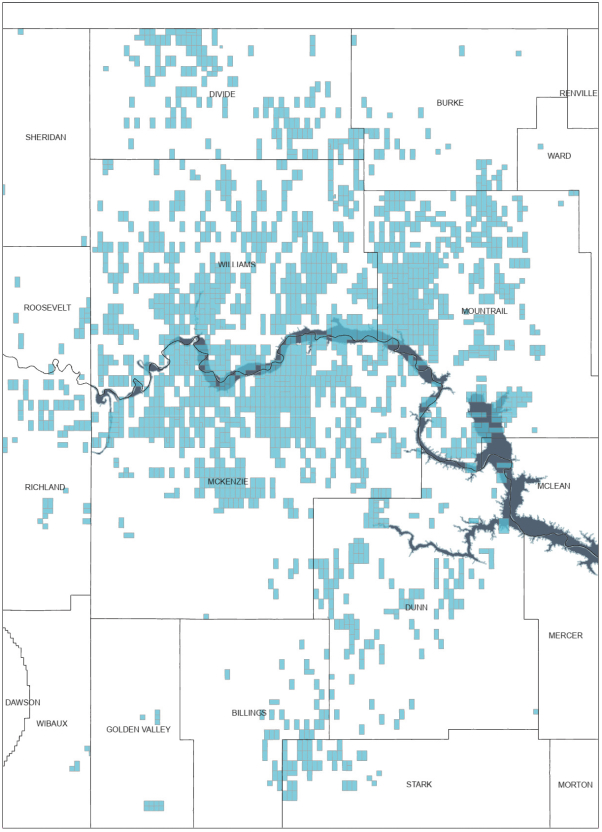
The map below illustrates our acreage position in the Williston Basin as of August 31, 2022.
86
INFORMATION STATEMENT
Vitesse Energy, Inc.
Common Stock
(par value $0.01)
This Information Statement is being sent to you in connection with the spin-off by Jefferies Financial Group Inc., which we refer to as “Jefferies,” of its newly formed indirect majority owned subsidiary, Vitesse Energy, Inc., which we refer to as “Vitesse” or “we.” Prior to the spin-off, Vitesse will acquire all of the issued and outstanding equity interests of Vitesse Energy, LLC, which we refer to as “Vitesse Energy,” and Vitesse Oil, LLC, which we refer to as “Vitesse Oil,” which together represent substantially all of those businesses or investments of Jefferies that acquire, develop, manage and monetize non-operated oil and natural gas working, royalty and mineral interests in the United States, primarily in the Bakken and Three Forks formations in the Williston Basin in North Dakota and Montana. Following Vitesse’s acquisitions of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil and a series of transactions described in this Information Statement, Jefferies will hold approximately 94.37% of the total issued and outstanding Vitesse common stock immediately prior to the spin-off. To effect the spin-off, Jefferies will distribute all of the issued and outstanding shares of Vitesse common stock held by Jefferies to the holders of Jefferies common stock on a pro-rata basis. After the distribution, Jefferies will not own any shares of Vitesse common stock. The distribution of Vitesse common stock is intended to be tax-free to Jefferies shareholders for U.S. federal income tax purposes, except for cash that shareholders receive in lieu of fractional shares and subject to the discussion in the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off—Consequences to Holders of Jefferies Common Stock.” You should consult your own tax advisor as to the tax consequences of the distribution to you, including potential tax consequences under state, local and non-U.S. tax laws.
If you are a record holder of Jefferies common stock as of the close of business on December 27, 2022, which is the record date for the distribution, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock you hold on that date, you will be entitled to receive one share of Vitesse common stock. Jefferies will distribute the shares of Vitesse common stock in book-entry form, which means that we will not issue physical stock certificates. The distribution agent will not distribute any fractional shares of Vitesse common stock. Instead, the distribution agent will aggregate fractional shares into whole shares, sell the whole shares in the open market at prevailing market prices and distribute the aggregate cash proceeds of the sales, net of brokerage fees and other costs, to each holder pro rata (net of any required withholding for taxes applicable to each holder) in lieu of any fractional share to which the holder otherwise would have been entitled to receive in the distribution. As discussed in the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date,” if you sell your shares of Jefferies common stock in the “regular-way” market after the record date and on or before the distribution date, you also will be selling your right to receive shares of Vitesse common stock in connection with the distribution.
The distribution will be effective as of 11:59 p.m., New York City time, on January 13, 2023. Immediately after the distribution becomes effective, Vitesse will be an independent, publicly traded company.
Jefferies shareholders are not required to vote on or take any other action in connection with the spin-off. We are not asking you for a proxy and you are requested not to send us a proxy. Jefferies shareholders will not be required to pay any consideration for the shares of Vitesse common stock they receive in the spin-off, and they will not be required to surrender or exchange their shares of Jefferies common stock or take any other action in connection with the spin-off.
No trading market for Vitesse common stock currently exists. We expect, however, that a limited trading market for Vitesse common stock, commonly known as a “when-issued” trading market, will develop on the third trading day before the distribution date, and we expect “regular-way” trading of Vitesse common stock will begin on the first trading day after the distribution date. We intend to list Vitesse common stock on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “VTS.” Following the distribution, Jefferies will continue to trade on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “JEF.”
Vitesse is an “emerging growth company” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012.
In reviewing this Information Statement, you should carefully consider the matters described in the section entitled “Risk Factors” beginning on page 26 of this Information Statement.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved these securities or determined if this Information Statement is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
This Information Statement is not an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy, any securities.
The date of this Information Statement is January 6, 2023.
This Information Statement was first mailed to Jefferies shareholders on or about January 6, 2023.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| PAGE | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 8 | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 10 | ||||
| 11 | ||||
| 11 | ||||
| 11 | ||||
| 12 | ||||
| 20 | ||||
| 26 | ||||
| 26 | ||||
| 30 | ||||
| 33 | ||||
| 46 | ||||
| 49 | ||||
| 54 | ||||
| 56 | ||||
| 56 | ||||
| 56 | ||||
| 58 | ||||
| 58 | ||||
| 59 | ||||
| 59 | ||||
| Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off |
59 | |||
| 62 | ||||
| 63 | ||||
| 63 | ||||
| 64 | ||||
| 64 | ||||
| 65 | ||||
| 66 | ||||
| 67 | ||||
| 68 | ||||
| 69 | ||||
i
| PAGE | ||||
| 72 | ||||
| 76 | ||||
| 81 | ||||
| 81 | ||||
| 83 | ||||
| 84 | ||||
| 85 | ||||
| 87 | ||||
| 93 | ||||
| 94 | ||||
| 94 | ||||
| 95 | ||||
| 95 | ||||
| 95 | ||||
| 99 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
101 | |||
| 101 | ||||
| 102 | ||||
| 102 | ||||
| 102 | ||||
| 103 | ||||
| 104 | ||||
| 105 | ||||
| 113 | ||||
| 117 | ||||
| 119 | ||||
| 119 | ||||
| 119 | ||||
| 121 | ||||
| 121 | ||||
| 122 | ||||
| 124 | ||||
| 124 | ||||
| 125 | ||||
| 125 | ||||
| 127 | ||||
| 128 | ||||
| 129 | ||||
| 129 | ||||
| 130 | ||||
| 130 | ||||
| 131 | ||||
| 131 | ||||
| 131 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
ii
| PAGE | ||||
| SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT |
135 | |||
| 135 | ||||
| 136 | ||||
| 137 | ||||
| 137 | ||||
| 140 | ||||
| 142 | ||||
| 143 | ||||
| 143 | ||||
| 143 | ||||
| 145 | ||||
| 145 | ||||
| 145 | ||||
| 145 | ||||
| 146 | ||||
| 146 | ||||
| 147 | ||||
| 148 | ||||
| 148 | ||||
| 148 | ||||
| COMPARISON OF RIGHTS OF JEFFERIES SHAREHOLDERS AND VITESSE STOCKHOLDERS |
149 | |||
| 155 | ||||
| F-1 | ||||
iii
In this Information Statement, unless the context otherwise requires:
| ∎ | “3B Energy” refers to 3B Energy, LLC, the holder of a minority of the equity interests in Vitesse Energy prior to the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions and an entity owned by Bob Gerrity, our Chief Executive Officer and a member of our Board, and Brian Cree, our President and Chief Operating Officer; |
| ∎ | “Amended and Restated Bylaws” refers to the bylaws of Vitesse that will be in effect immediately prior to the Distribution Date; |
| ∎ | “Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation” refers to the certificate of incorporation of Vitesse that will be in effect immediately prior to the Distribution Date; |
| ∎ | “AST” refers to American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC; |
| ∎ | “Basin” refers to a large natural depression on the earth’s surface in which sediments generally brought by water accumulate; |
| ∎ | the “Board” refers to our board of directors; |
| ∎ | “Bbl” refers to one stock tank barrel, of 42 U.S. gallons liquid volume, used herein in reference to oil, condensate or NGLs; |
| ∎ | “Boe” refers to barrels of oil equivalent, calculated by converting natural gas to oil equivalent barrels at a ratio of six Mcf of natural gas to one Bbl of oil and at a ratio of one Bbl of NGL to one Bbl of oil; |
| ∎ | “Boe/d” refers to one Boe per day; |
| ∎ | “Btu” refers to a British thermal unit, which is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit; |
| ∎ | “completion” refers to the process of preparing an oil and natural gas wellbore for production through the installation of permanent production equipment, as well as perforation and fracture stimulation to optimize production of oil, natural gas and/or NGLs; |
| ∎ | “condensate” refers to a mixture of hydrocarbons that exists in the gaseous phase at original reservoir temperature and pressure, but that, when produced, is in the liquid phase at surface pressure and temperature; |
| ∎ | “CAA” refers to the Clean Air Act; |
| ∎ | “Cawley” refers to Cawley, Gillespie & Associates, Inc.; |
| ∎ | “CERCLA” refers to the Comprehensive Environmental, Response, Compensation, and Liability Act; |
| ∎ | “CFTC” refers to the Commodities Futures Trading Commission; |
| ∎ | the “Code” refers to the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended; |
| ∎ | “COVID-19” refers to the SARS-CoV-2 novel coronavirus and known variants; |
| ∎ | “CWA” refers to the Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1972; |
| ∎ | “DGCL” refers to the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware; |
| ∎ | “Differential” refers to an adjustment to the price of oil or natural gas from an established spot market price to reflect differences in the quality and/or location of oil or natural gas; |
| ∎ | the “Distribution” refers to the transaction in which Jefferies will distribute to its shareholders all outstanding shares of our common stock held by Jefferies; |
| ∎ | the “Distribution Date” refers to the date on which the Distribution occurs; |
| ∎ | the “Dodd-Frank Act” refers to the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act; |
| ∎ | the “DOI” refers to the Department of the Interior; |
| ∎ | “dry hole” refers to a well found to be incapable of producing oil and natural gas in sufficient quantities to justify completion; |
| ∎ | the “EPA” refers to the Environmental Protection Agency; |
| ∎ | the “ESA” refers to the Endangered Species Act; |
| ∎ | “ESG” refers to environmental, social and governance; |
| ∎ | “Exchange Act” refers to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; |
iv
| ∎ | “Existing Revolving Credit Facility” refers to Vitesse Energy’s Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of April 29, 2022, as amended from time to time, among Vitesse Energy, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto; |
| ∎ | “FERC” refers to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission; |
| ∎ | “FTC” refers to the Federal Trade Commission; |
| ∎ | “GAAP” refers to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States; |
| ∎ | “Gerrity Bakken” refers to Gerrity Bakken, LLC, the holder of a minority of the equity interests in Vitesse Oil and an entity owned by Bob Gerrity, our Chief Executive Officer and a member of our Board; |
| ∎ | “GHGs” refer to greenhouse gases; |
| ∎ | “gross acres” refers to the total acres in which a working interest is owned; |
| ∎ | “gross wells” refers to the total wells in which a working interest is owned; |
| ∎ | “IPOs” refer to initial public offerings; |
| ∎ | “IRS” refers to the Internal Revenue Service; |
| ∎ | “IRS Ruling” refers to a private letter ruling being sought by Jefferies from the IRS; |
| ∎ | “Jefferies” refers to Jefferies Financial Group Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries other than, for all periods following the Spin-Off, Vitesse, unless the context requires otherwise; |
| ∎ | “Jefferies Board” refers to Jefferies’ board of directors; |
| ∎ | “Jefferies Capital Partners” refers to Jefferies Capital Partners V L.P. and Jefferies SBI USA Fund L.P., collectively, the holders of a majority of the equity interests in Vitesse Oil and entities in which Jefferies holds an indirect limited partner interest; |
| ∎ | “Jefferies Parties” refers to Jefferies and certain of its affiliates; |
| ∎ | “MBbls” refers to one thousand barrels of oil or NGLs; |
| ∎ | “MBoe” refers to one thousand barrels of oil equivalent; |
| ∎ | “Mcf” refers to one thousand cubic feet of natural gas; |
| ∎ | “MMBoe” refers to one million barrels of oil equivalent; |
| ∎ | “MMBtu” refers to one million British thermal units; |
| ∎ | “MMcf” refers to one million cubic feet of natural gas; |
| ∎ | “net acres” refers to the sum of the fractional working interests owned in gross acres (e.g., a 10% working interest in a lease covering 1,280 gross acres is equivalent to 128 net acres); |
| ∎ | “net wells” refers to wells that are deemed to exist when the sum of fractional ownership working interests in gross wells equals one; |
| ∎ | “NEPA” refers to the National Environmental Policy Act; |
| ∎ | “New Revolving Credit Facility” refers to Vitesse’s Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, as amended from time to time, which is expected to be among Vitesse, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto and which is expected to be in effect at the time of the completion of the Spin-Off; |
| ∎ | “NGLs” refer to natural gas liquids; |
| ∎ | “NSPS” refers to New Source Performance Standards; |
| ∎ | “NYBCL” refers to the New York Business Corporation Law; |
| ∎ | “NYMEX” refers to the New York Mercantile Exchange; |
| ∎ | “NYSE” refers to the New York Stock Exchange; |
| ∎ | “OPEC” refers to the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries; |
| ∎ | “OPA” refers to the Oil Pollution Act of 1990; |
| ∎ | “OTC” refers to the over-the-counter market; |
| ∎ | “PDP” or “proved developed producing” refers to proved reserves that can be expected to be recovered through existing wells with existing equipment and operating methods; |
| ∎ | “PDNP” or “proved developed non-producing” refers to proved reserves that are developed behind pipe and are expected to be recovered from zones in existing wells that will require additional completion work or future recompletion prior to the start of production; |
v
| ∎ | “PHMSA” refers to the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration; |
| ∎ | “possible reserves” refers to the additional reserves which analysis of geoscience and engineering data suggest are less likely to be recoverable than probable reserves; |
| ∎ | “Pre-Spin-Off Transactions” refers to the series of transactions, including Vitesse’s acquisitions of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil, described under “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions”; |
| ∎ | “probable reserves” refers to the additional reserves which analysis of geoscience and engineering data indicate are less likely to be recovered than proved reserves but which, together with proved reserves, are as likely as not to be recovered; |
| ∎ | “productive well” refers to a well that is found to be capable of producing oil and natural gas in sufficient quantities such that proceeds from the sale of the production exceed production expenses and taxes; |
| ∎ | “proved developed reserves” refers to proved reserves that can be expected to be recovered through existing wells with existing equipment and operating methods or in which the cost of new equipment or operating methods is relatively minor compared to the cost of a new well; |
| ∎ | “proved reserves” refers to the quantities of oil and natural gas, which, by analysis of geoscience and engineering data, can be estimated with reasonable certainty to be economically producible, from a given date forward, from known reservoirs, and under existing economic conditions, operating methods, and government regulations, prior to the time at which contracts providing the right to operate expire, unless evidence indicates that renewal is reasonably certain, regardless of whether deterministic or probabilistic methods are used for the estimation. The project to extract the hydrocarbons must have commenced or the operator must be reasonably certain that it will commence the project within a reasonable time; |
| ∎ | “PUD” or “proved undeveloped” refers to proved reserves that are expected to be recovered from new wells on undrilled acreage, or from existing wells where a relatively major expenditure is required for development. Reserves on undrilled acreage are limited to those drilling units offsetting productive units that are reasonably certain of production when drilled. Undrilled locations can be classified as having undeveloped reserves only if a development plan has been adopted indicating that they are scheduled to be drilled within five years unless specific circumstances justify a longer time. Under no circumstances shall estimates of proved undeveloped reserves be attributable to any acreage for which an application of fluid injection or other improved recovery technique is contemplated, unless such techniques have been proved effective by actual projects in the same reservoir or an analogous reservoir, or by other evidence using reliable technology establishing reasonable certainty: |
| ∎ | “RCRA” refers the Federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act; |
| ∎ | “Record Date” refers to December 27, 2022; |
| ∎ | “reserves” refers to estimated remaining quantities of oil and gas and related substances anticipated to be economically producible, as of a given date, by application of development projects to known accumulations. In addition, there must exist, or there must be a reasonable expectation that there will exist, the legal right to produce or a revenue interest in the production, installed means of delivering oil and gas or related substances to market, and all permits and financing required to implement the project; |
| ∎ | “SDWA” refers to the Safe Drinking Water Act; |
| ∎ | “SEC” refers to the Securities and Exchange Commission; |
| ∎ | “Securities Act” refers to Securities Act of 1933; |
| ∎ | “Stockholder Nominee” refers to a candidate for the Board who is nominated by stockholders pursuant to the requirements of our Amended and Restated Bylaws; |
| ∎ | “SOFR” refers to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate; |
| ∎ | the “Spin-Off” refers to our separation from Jefferies and the creation of an independent, publicly traded company, Vitesse, through (1) the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions and (2) the Distribution; |
| ∎ | “Standardized Measure” refers to discounted future net cash flows estimated by applying year-end SEC prices (based on the 12-month unweighted arithmetic average of the first-day-of-the-month oil and natural gas prices for such year-end period) to the estimated future production of year-end proved reserves. Future cash flows are reduced by estimated future production and development costs, including asset retirement obligations, based on year-end costs to determine pre-tax cash inflows. Future income taxes, if applicable, are computed by applying the statutory tax rate to the excess of pre-tax cash flows over our tax basis in the oil and natural gas properties. Future net cash flows after income taxes are discounted using a 10% annual discount rate; |
vi
| ∎ | “Treasury Regulations” refers to final, temporary, and (to the extent they can be relied upon) proposed regulations under the Code, as promulgated from time to time (including corresponding provisions and succeeding provisions); |
| ∎ | “Two-stream basis” refers to the reporting of production or reserve volumes of oil and wet natural gas, where the NGLs have not been removed from the natural gas stream, and the economic value of the NGLs is included in the wellhead natural gas price; |
| ∎ | “USRPHC” refers to United States real property holding corporation; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse,” “we,” “our” and “us” (1) when used in the past tense, refer to Vitesse Energy and do not give effect to the consummation of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, and (2) when used in the present tense or future tense, refer to Vitesse Energy, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries and give effect to the consummation of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, in each case unless the context requires otherwise; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse Energy” refers to Vitesse Energy, LLC and its consolidated subsidiaries; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse Energy Finance” refers to Vitesse Energy Finance LLC, the holder of a majority of the equity interests in Vitesse Energy prior to the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions and an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Jefferies; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse Energy MIUs” refers to management incentive units with respect to Vitesse Energy; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse Oil” refers to Vitesse Oil, LLC; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse Oil MIUs” refers to management incentive units with respect to Vitesse Oil; |
| ∎ | “Vitesse Oil Revolving Credit Facility” refers to Vitesse Oil’s Credit Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2015, as amended from time to time, among Vitesse Oil, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto; |
| ∎ | “VOCs” refers to volatile organic compounds; |
| ∎ | “WOTUS” refers to the waters of the United States; and |
| ∎ | “WTI” refers to West Texas Intermediate. |
vii
PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL AND OPERATING DATA
Unless otherwise indicated, the historical financial information presented in this Information Statement is that of our predecessor, Vitesse Energy. The pro forma condensed combined financial information in this Information Statement is derived from the audited consolidated financial statements and unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements of Vitesse Energy included elsewhere in this Information Statement, which we refer to as the “Audited Consolidated Financial Statements” and the “Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements,” respectively. The pro forma condensed combined financial information reflects, among other things, the consummation of the Spin-Off, including the acquisition of Vitesse Oil.
In addition, unless otherwise indicated, the reserve and operational data presented in this Information Statement is with respect to all of the assets of Vitesse Energy prior to giving effect to the Spin-Off.
This Information Statement includes information concerning our industry and the markets in which we operate that is based on information from public filings, internal company sources, various third-party sources and management estimates. Management’s estimates regarding Vitesse’s position, share and industry size are derived from publicly available information and our internal research, and are based on assumptions we made upon reviewing such data and our knowledge of such industry and markets, which we believe to be reasonable. While we are not aware of any misstatements regarding any industry data presented in this Information Statement and believe such data to be accurate, we have not independently verified any data obtained from third-party sources and cannot assure you of the accuracy or completeness of such data. Such data involve uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed in the section entitled “Risk Factors.”
We own or have rights to various trademarks, logos, service marks and trade names that we use in connection with the operation of our business. We also own or have the rights to copyrights that protect the content of our products. Solely for convenience, the trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights referred to in this Information Statement are listed without the ™, ® or © symbols, but such references do not constitute a waiver of any rights that might be associated with the respective trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights included or referred to in this Information Statement.
viii
This summary highlights selected information from this Information Statement and provides an overview of our company, our separation from Jefferies and Jefferies’ distribution of our common stock to its shareholders. For a more complete understanding of our business and the Spin-Off, you should read the entire Information Statement carefully, particularly the discussion of “Risk Factors” and the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements and the notes thereto included in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
Vitesse is an independent energy company engaged in the acquisition, development, and production of non-operated oil and natural gas properties in the United States that are generally operated by leading oil companies and are primarily in the Bakken and Three Forks formations in the Williston Basin of North Dakota and Montana. We also have properties in the Central Rockies, including the Denver-Julesburg Basin and the Powder River Basin. Since our inception in 2014, we have built a strong and diversified asset base through a combination of property acquisitions, development activities and the implementation of proprietary platforms and processes utilizing our extensive data resources. We believe the location and concentration of our assets in some of North America’s leading unconventional oil and natural gas resource plays, along with our technical and data capabilities, will continue to provide us with acquisition and development opportunities that will result in significant incremental long-term value.
Vitesse has historically created value by acquiring non-operated minority working and mineral interests in oil and natural gas properties, comprising producing wells, near-term development opportunities and undeveloped acreage, and partnering with premier operators with significant experience in developing and producing oil and natural gas in our core areas. Over the past eight years, we have executed on our technical, data driven, and financially disciplined acquisition and development strategy to build our core position in the Williston Basin and Central Rockies and grow our oil and natural gas production. During that time, we have focused on limiting our downside by maintaining conservative acquisition guidelines, limiting our debt leverage and opportunistically locking in future prices for a portion of our oil production. As a result, we have been able to preserve value when many independent energy companies were forced into financial recapitalizations and restructurings when commodity prices declined significantly in 2014, 2018 and 2020.
With the current higher oil and natural gas price environment, we are focused on using free cash flow to maintain a strong balance sheet, provide growing returns of capital to our stockholders, and grow our oil and natural gas production by developing our extensive inventory of drilling locations, as well as acquiring both producing wells and new development opportunities.
We owned an average working interest of 2.6% in 5,203 gross (133.9 net) productive wells and royalty interests in an additional 998 productive wells as of August 31, 2022. We engage in oil and natural gas well development by participating on a proportionate basis alongside third-party interests in wells drilled and completed in spacing units that include our acreage. As of August 31, 2022, we owned a working interest in a further 253 gross (6.5 net) wells that were being drilled or completed, and an additional 413 gross (8.5 net) wells that had been permitted for development by our operating partners. We rely on our operators to propose, permit and initiate the drilling and completion of wells. We assess each drilling and completion opportunity on a case-by-case basis and participate in wells that are expected to meet a desired return based upon estimates of recoverable oil and natural gas reserves, anticipated oil and natural gas prices, the expertise of the operator, and the anticipated completed well cost, as well as other factors.
Our non-operated business model provides us with inherent flexibility regarding the cadence of capital deployment and the agility to allocate a portion of our cash flow to the drilling and completion opportunities that we believe will achieve the highest rate of return. We work with more than 35 experienced operators that provide technical insights and opportunities for additional acquisitions and continued development. In
1
addition, our business model allows us to not be burdened with various contractual arrangements with respect to minimum drilling obligations, and we can minimize exploratory, upfront leasing and infrastructure costs customarily incurred by operators.
Our operators generally market and sell the oil and natural gas extracted from our wells on their behalf and on our behalf. In addition, these operators coordinate the transportation of oil and natural gas production from wells in which we participate to appropriate pipelines or rail transport facilities pursuant to arrangements that such operators negotiate and maintain with various parties purchasing such production. The price at which our production is sold generally ties to a market spot price, and the Differential between the market spot price and our realized sales price represents the imbedded transportation and marketing costs of moving the oil and natural gas from the wellhead to the refinery or processing plant. The Differential will fluctuate based on availability of pipeline, rail and other transportation methods.
Vitesse is led by a dedicated management team with extensive experience in the energy industry. Our management team includes Bob Gerrity, our Chief Executive Officer, a successful industry leader who was the founder and chief executive officer of Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation, which pioneered low-cost “reserve manufacturing” in the Wattenberg field of Colorado during the 1990s. Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation was one of the most active operators in the United States following its IPO in 1990, at times running more than 15 active drilling rigs and completing as many as 500 wells per year. Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation merged with Snyder Oil Corporation to form Patina Oil & Gas Corporation in 1996, which was merged with Noble Energy, Inc. in 2005. Today, these former assets comprise a material portion of Chevron Corporation’s position in the Denver-Julesburg Basin.
Leveraging his prior experience and acknowledging the trend in advances in shale drilling and completion technologies, Mr. Gerrity believed the shale industry would transition to a reserve manufacturing phase marked by well-capitalized and efficient low-cost operators. In 2013, Mr. Gerrity and Brian Cree, our President and Chief Operating Officer, began to seek out non-operated lease and mineral interests with development opportunities in areas of the Williston Basin that were in the core of the field and operated by premier industry leaders, at which time an affiliate of Jefferies made an initial investment in Vitesse Oil to partially fund the acquisition of non-operated working and mineral interests primarily in undeveloped oil and natural gas assets. In 2014, Messrs. Gerrity and Cree began to see a growing number of acquisition and development opportunities in the Williston Basin, and Jefferies made a direct investment in Vitesse to support larger scale acquisition and development efforts. Since that time, Vitesse has completed over 120 acquisitions totaling approximately $520 million and deployed over a further $400 million in the development of oil and natural gas properties.
Vitesse Oil, which will be acquired by Vitesse as part of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, is an independent energy company also engaged in the acquisition, development and production of non-operated oil and natural gas properties in the Williston Basin of North Dakota. As of August 31, 2022, Vitesse Oil had 2,515 net acres in the Williston Basin and owned working interests in approximately 871 gross (7.8 net) productive wells and royalty interests in an additional 120 productive wells, with average production of 816 Boe per day during the month ended August 31, 2022. In addition, Vitesse Oil had 73 gross (0.3 net) wells that were being drilled or completed, and an additional 83 gross (0.3 net) wells that had been permitted for future development by its operators as of August 31, 2022. Based on year-end SEC prices, as of December 31, 2021, Vitesse Oil had approximately 4,107 MBoe of estimated proved reserves located primarily in the core of the Williston Basin, and average production of 641 Boe per day for the year ended December 31, 2021. For information concerning Vitesse Oil, see “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Statements.”
Our business strategy going forward is focused on creating long-term stockholder value through the acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas assets at attractive rates of return, while maintaining a strong
2
and conservative balance sheet and distributing a portion of our free cash flow to our stockholders in the form of a regular cash dividend on a quarterly basis. The key elements of our business strategy include the following:
| ∎ | Dividends to Stockholders. Our business plan focuses on building a diversified, low-leverage, free cash flow generating business that can deliver regular cash dividends to our stockholders. We made cash distributions to our members totaling $25.0 million during 2019, $0.0 during 2020, $12.0 million during 2021, and $42.0 million during the nine months ended August 31, 2022. In addition to the aforementioned cash distribution payments, Jefferies retained close to $25.0 million in hedging gain proceeds that were attributable to derivatives associated with our oil production during 2019 and 2020, further demonstrating our commitment to generating value for our investors. Following the Distribution, we expect that Vitesse will initially pay quarterly cash dividends and dividend equivalents totaling approximately $66.0 million per fiscal year. Such dividend equivalents will be paid pursuant to awards granted under the VTS LTIP (as defined in the section entitled “Executive Compensation— Vitesse Energy, Inc. Long-Term Incentive Plan”) and the Transitional Plan (as defined in the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Transitional Equity Award Adjustment Plan”). |
| ∎ | Growth through Value-Enhancing Acquisitions. We have been a consolidator and clearing house of non-operated working interests in various leading oil and natural gas shale plays in the United States, and we will continue that strategy and potentially pursue operated asset packages and other acquisition strategies going forward. Our near-term drilling acquisition strategy is centered around building a strong presence in our core basins by acquiring smaller non-operated lease and wellbore positions with direct exposure to near-term drilling activity. By virtue of their smaller footprint, these targeted acquisitions have been completed at a significant discount to the prices paid for contiguous acreage positions typically sought by larger producers and operators of oil and natural gas wells. Acquisitions such as these have been a significant driver of increasing our production. Over the last eight years, we have closed approximately 120 discrete acquisitions totaling more than $520 million, and we intend to continue these activities, while at the same time evaluating and pursuing larger asset packages in both our current area of operations and other areas. We believe our disciplined acquisition strategy can responsibly add production, cash flow and scale to existing operations. |
| ∎ | Built to Last. From our inception, we have focused on creating a durable organization that generates strong financial returns and sustainable free cash flow through commodity cycles. Rather than primarily acquiring producing reserves, we have focused our efforts on acquiring an attractive inventory of undeveloped drilling locations that afford us flexibility in the face of oil and natural gas price fluctuations and taking advantage of technical improvements and cost reductions over time, supporting the sustainable generation of free cash flow. Our management team fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement, constantly looking for ways to improve our operations and technical and data analysis, and strengthen our organizational agility and adaptability. |
| ∎ | Risk Diversification. We seek to diversify our capital and operational risk through participation in a large number of oil and natural gas wells with multiple operators across multiple basins. We seek to diversify our risk by operator, formation, value concentration and commodity (oil and natural gas). As of August 31, 2022, we owned an average working interest of 2.6% in 5,203 gross (133.9 net) productive wells and royalty interests in an additional 998 productive wells, with more than 35 experienced operators that provide development and production activities on our oil and natural gas properties. We believe we can further diversify our risk over time with acquisitions in additional basins, focusing on accretive acquisitions of high-quality assets with experienced operators in the most prolific basins in the United States. During the nine months ended August 31, 2022, our average production was 10,048 Boe per day, consisting of approximately 8,910 Boe per day in the Williston Basin and 1,138 Boe per day in the Central Rockies. During the month ended August 31, 2022, our average production was 10,898 Boe per day, consisting of approximately 9,462 Boe per day in the Williston Basin and 1,436 Boe per day in the Central Rockies. |
3
| ∎ | Strong Balance Sheet and Financial Flexibility. We maintain financial strength and flexibility through the prudent management of our balance sheet and free cash flow. During 2020, 2021, and the first nine months of 2022 we were free cash flow positive and reduced our outstanding debt from $104.0 million at November 30, 2019 to $68.0 million at November 30, 2021 and to $66.0 million at August 31, 2022. Following the Spin-Off, we intend to maintain conservative indebtedness and a simple capital structure consisting only of our New Revolving Credit Facility and common stock. We intend to maintain the flexibility to manage our free cash flow by continuing to adhere to a target Net Debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (last twelve months) of less than 1.0. As of August 31, 2022, our Net Debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (last twelve months) was 0.4. For the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, we generated net income and Adjusted EBITDA of $81.2 million and $158.0 million, respectively. From our inception in 2014 through August 31, 2022, we generated approximately $144.0 million of net income during a volatile commodity price environment. For definitions and reconciliations of Net Debt and Adjusted EBITDA to their most directly comparable financial measures in accordance with GAAP, see “Selected Historical Financial Data—Non-GAAP Financial Information.” |
| ∎ | Hedging Strategy. To reduce our exposure to the volatility of oil prices and protect our ability to pay distributions, we have entered into hedging derivative instruments for a portion of our expected oil production, which have included swaps, collars, puts and other structures. We historically have bought oil futures both on an opportunistic basis when WTI prices have allowed us to lock in attractive rates of return on our asset base and upon acquisitions of larger producing assets to protect returns. We currently do not hedge natural gas production due to the mismatch between our operators’ pricing formulas and settlement mechanics on natural gas hedges. Our current hedged position mitigates our exposure to volatile oil prices, with approximately 30% of our expected oil production hedged through November 30, 2024 at attractive prices. However, in the past, based on then-existing market conditions, we have hedged significantly higher percentages of our actual oil production. For further information see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk—Commodity Price Risk.” |
| ∎ | Responsible Stewards. We are committed to ESG initiatives and seek a culture of improvement in ESG practices. We work to provide safe, reliable and affordable energy in a responsible manner by partnering with responsible operators in our core areas, while being cognizant of the broader energy transition. The key tenets of our ESG philosophy are to identify opportunities to reduce our environmental impact, improve safety, invest in our employees, and support the communities in which we live and work while improving transparency and accountability. At the time of the Distribution, our Board will be majority independent and composed of experienced professionals with a strong background in the energy industry and more broadly in business. |
We believe that we will be able to successfully execute our business strategies because of the following competitive strengths:
| ∎ | Every Decision is a Financial Decision. Our business culture encourages employees to think like owners and to make decisions with a long-term perspective. We have developed a systematic approach of responsibly reviewing acquisition and development opportunities. As part of our efforts to maximize returns, we have established a capital allocation framework with the objective of allocating capital to acquisitions and development of oil and natural gas properties to drive sustainability and growth in free cash flow, the repayment of debt and stockholder dividends. This framework entails disciplined investment in capital expenditures and acquisitions, allowing us to distribute a significant portion of our cash flow to our stockholders. We also retain flexibility with respect to share repurchases, subject to approval from our Board and as conditions warrant. We will continue to evaluate and pursue profitable and accretive acquisition and consolidation opportunities that enhance stockholder value and build scale. As opportunities arise, we intend to identify and acquire additional acreage and producing assets to supplement our existing operations. |
4
| ∎ | Data and Technology Driven. Our proprietary data-driven approach allows for rapid multi-disciplinary evaluation to determine the most attractive acquisition and development opportunities. We created customized data systems (vLuminis) that are integrated, centralized and utilized by our employees so that decisions are based on a common base of information. We maintain real-time business intelligence dashboards to monitor operators, rigs, well performance, drilling and completion costs and production results. This data informs model forecasts, type curves and decisions about acquisition and development opportunities. We maintain responsive, basin-wide models that are updated in real time and incorporate historical data by operator and region. These models, along with our proprietary systems and platforms, provide necessary inputs and evaluation metrics, which allow us to make informed investment decisions based on forecasted production, operating expenses, type curves, drilling inventory, cash flow and other operational and financial outputs. As a result, we have the capability to process multiple opportunities quickly with the current team in place. |
| ∎ | Experienced Management and Industry Relationships. Vitesse’s management team has developed deep and longstanding relationships with many of our operators, other working interest and mineral owners, investment banks, acquisition and divestiture companies and investors. A majority of our evaluated and executed acquisitions and transactions are self-sourced. We have become a preferred non-operator to some of the largest companies operating in the Williston Basin and Central Rockies given our track record of evaluating and acquiring non-operated oil and natural gas working interests, and being a responsible financial partner. As a result, we see broad deal flow from single wellbore near-term development acquisition opportunities to packages consisting of both producing and undeveloped assets worth hundreds of millions of dollars. Our management team has an over 30-year track record of creating value together at both private and public oil and natural gas companies. |
| ∎ | Proactive Asset Management Philosophy. Our experienced team of landmen and accountants review acquired assets to unlock incremental value. Many assets we acquire have title defects or other land related issues where deep analysis and consistent, quality diligence adds value in many areas, including increased working interest ownership and working capital management. Our long-term view provides the time to solve issues and find additional well interests to increase the velocity of overall returns. This is enabled by strong departmental relationships with operators and accurate data management. |
Industry Trends Impacting Our Business
Commodity prices are the most significant factor impacting our acquisition and divestiture strategy, as well as the decisions of our operators in conducting their operations. Prices for oil and natural gas can be highly volatile. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic and efforts to mitigate the spread of the disease, combined with OPEC actions in early 2020, led to spot and future prices of oil and natural gas falling to historic lows during the second quarter of 2020 and remaining depressed through much of 2020. Our operators in the Williston Basin responded by significantly decreasing drilling and completion activity, and by shutting in or curtailing production from a significant number of producing wells. Commodity prices, however, quickly reached pre-pandemic levels in the second half of 2021, and during the first nine months of 2022 only further accelerated upward, in part as a result of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine may have further global economic consequences, including disruptions of the global energy markets and the amplification of inflation and supply chain constraints, partially due to sanctions by the European Union, the United Kingdom and the United States on imports of oil and gas from Russia. On October 5, 2022, OPEC also announced a 2 MMBbl/d reduction in production quotas, the organization’s largest cut since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
As a result of such commodity price volatility, which we expect to continue for the remainder of 2022 and into 2023, our earnings and operating cash flows can vary substantially, and are subject to external factors over which the company has no control. While we do hedge a substantial portion of our production, we are still significantly subject to movements in commodity prices. Such volatility can make it difficult to predict future effects on our company and the decisions of our operators. Factors that we expect will continue to impact commodity prices include product demand connected with global economic conditions, industry production
5
and inventory levels, the United States Department of Energy’s future planned repurchases (or additional possible releases) of oil from the strategic petroleum reserve, technology advancements, production quotas or other actions imposed by OPEC countries, actions of regulators, and regional supply interruptions or fears thereof that may be caused by military conflicts (including invasion), civil unrest, pandemic or political uncertainty. Any of the foregoing can have a substantial impact on the prices of oil and natural gas, which in turn impacts the decision of our operators to drill and extract resources. Despite such commodity price volatility, we expect that our cash flow from operations and borrowing availability under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility or New Revolving Credit Facility, as applicable, will allow us to meet our liquidity needs for the next twelve months.
Our principal executive offices are located at 9200 E Mineral Ave, Suite 200, Centennial, Colorado 80112. Our current office space consists of approximately 15,000 square feet of leased space. We believe our current office space is sufficient to meet our needs and that additional office space can be obtained if necessary.
Ownership of Vitesse common stock is subject to numerous risks, including risks relating to the Spin-Off. The following list of risk factors is not exhaustive. Please read the information in the section entitled “Risk Factors” for a more thorough description of these and other risks.
Risks Relating to the Spin-Off
| ∎ | If the Distribution is not a tax-free transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes, Jefferies and recipients of shares of Vitesse common stock could be subject to significant tax liability, and Vitesse could have an indemnification obligation to Jefferies. |
| ∎ | We intend to agree to numerous restrictions to preserve the non-recognition treatment of the Distribution, which may reduce our strategic and operating flexibility. |
| ∎ | We may be unable to achieve the expected benefits from the Spin-Off, following which we will be subject to new reporting requirements, incur increased costs, and certain members of management and directors may face conflicts of interest. |
| ∎ | Our acquisitions of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil may require consents or approvals, which could harm our business and financial performance if not obtained. |
| ∎ | Until the Distribution occurs, the Jefferies Board may change the terms of the Spin-Off in ways that may be unfavorable to us. |
| ∎ | If you do not want to receive our common stock in the Distribution, your sole recourse will be to divest yourself of your Jefferies common stock. |
Risks Relating to Our Common Stock
| ∎ | No market for our common stock currently exists. Following the Spin-Off, an active trading market may not develop or be sustained, and our stock price may fluctuate significantly. |
| ∎ | Although we expect to pay dividends, we cannot provide assurance that we will pay dividends on our common stock, and our indebtedness may limit our ability to pay dividends on our common stock. |
| ∎ | Certain provisions in our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, Amended and Restated Bylaws and Delaware law may discourage takeovers. |
| ∎ | The rights associated with our common stock will differ from the rights associated with Jefferies common stock. |
| ∎ | Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will designate the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings, potentially limiting our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes. |
6
Risks Relating to Our Business
| ∎ | Our business may be affected by volatile or extended declines in oil and natural gas prices. |
| ∎ | We have incurred net losses in the past, in part due to fluctuations in oil and gas prices, and we may incur such losses again in the future. |
| ∎ | Our estimated proved reserves may prove to be inaccurate. |
| ∎ | Seasonal weather conditions may adversely affect our operators’ ability to conduct drilling and completion activities and to sell oil and natural gas for periods of time. |
| ∎ | Our business relies on third parties, such as our operators, and depends on transportation and processing facilities and other assets that are owned by third parties. |
| ∎ | The majority of our producing properties are located in the Williston Basin, making us vulnerable to risks associated with operating in one major geographic area. |
| ∎ | We may be materially adversely affected by the negative global and economic impact resulting from the military conflict in Ukraine, other geopolitical tensions, ongoing risks from COVID-19, cybersecurity threats, and inflation related costs. |
| ∎ | Asset retirement costs may be difficult to predict and may be substantial. Unplanned costs could divert resources from other projects. |
| ∎ | Increased attention to ESG matters, fuel conservation measures and related governmental initiatives, technological advances and negative shift in market perception towards the oil and natural gas industry could reduce demand for oil and natural gas. |
Risks Relating to Our Indebtedness
| ∎ | Any significant reduction in our borrowing base under our New Revolving Credit Facility may negatively impact our financial results or restrict our business and financing activities. |
| ∎ | We may not be able to generate enough cash flow to meet our current or potential future debt obligations or to pay dividends to our stockholders. |
| ∎ | Variable rate indebtedness could subject us to interest rate risk, which could cause our debt service obligations to increase significantly. |
| ∎ | Our business plan requires the expenditure of significant capital, which we may be unable to obtain on favorable terms or at all. |
Risks Relating to Legal and Regulatory Matters
| ∎ | New federal rules and regulations could restrict our ability to acquire federal leases and/or impose more onerous permitting and other costly environmental, health and safety requirements. |
| ∎ | Certain U.S. federal income tax deductions currently available with respect to oil and natural gas development may be eliminated as a result of future legislation. |
| ∎ | Legislative and regulatory developments could have an adverse effect on our ability to use derivative instruments to reduce the effect of volatile oil and natural gas price, interest rate and other risks associated with our business. |
| ∎ | Our business is subject to complex federal, state, and local laws, as well as other laws and regulations that could adversely affect the cost, manner or feasibility of doing business. |
| ∎ | Federal and state legislative and regulatory initiatives relating to climate change, hydraulic fracturing and reducing gas flaring could result in increased costs and additional operating restrictions or delays. |
We expect the following transactions, among others, to be consummated prior to the completion of the Spin-Off (which we refer to as the “Pre-Spin-Off Transactions”):
| ∎ | Vitesse was incorporated on August 5, 2022; |
| ∎ | 3B Energy will transfer all of its Vitesse Energy equity interests to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for prior loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to 3B Energy; |
7
| ∎ | Each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will transfer all of their vested Vitesse Energy MIUs to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for prior loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree; |
| ∎ | Vitesse Energy Finance and the remaining holders of vested Vitesse Energy MIUs will transfer all of their Vitesse Energy equity interests to Vitesse in exchange for newly issued shares of Vitesse common stock; |
| ∎ | Jefferies Capital Partners and Gerrity Bakken will transfer all of their Vitesse Oil equity interests to Vitesse in exchange for newly issued shares of Vitesse common stock; |
| ∎ | Through a series of distributions, all of the Vitesse common stock held by Vitesse Energy Finance will ultimately become held directly by Jefferies; |
| ∎ | Through a series of distributions, a portion of the Vitesse common stock held by Jefferies Capital Partners will ultimately become held directly by Jefferies; and |
| ∎ | Vitesse will enter into the New Revolving Credit Facility, which will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, and will use a portion of the proceeds from borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility to repay in full and terminate the Vitesse Oil Revolving Credit Facility. Borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility will remain outstanding as borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility. |
Pursuant to the above described transactions, Jefferies will directly hold approximately 94.37% of the total issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately prior to the Distribution. For more information, see “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions” and “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons.”
On July 19, 2022, Jefferies announced plans for the complete legal and structural separation of Vitesse from Jefferies.
To effect the separation, first, Jefferies and Jefferies Capital Partners, among others, will undertake the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions described under the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions.” Jefferies will subsequently distribute all of Vitesse’s outstanding common stock held by Jefferies, representing 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock immediately prior to the Distribution, to Jefferies shareholders, and Vitesse will become an independent, publicly traded company. After the Distribution, Jefferies will not own any shares of our common stock.
Prior to completion of the Spin-Off, we intend to enter into a Separation and Distribution Agreement and a Tax Matters Agreement with Jefferies related to the Spin-Off. These agreements will govern the relationship between Jefferies and us up to and after completion of the Spin-Off. See the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions” for more detail. No approval of Jefferies shareholders is required in connection with the Spin-Off, and Jefferies shareholders will not have any appraisal rights in connection with the Spin-Off.
Completion of the Spin-Off is subject to the satisfaction, or the waiver by the Jefferies Board, of a number of conditions. If the Jefferies Board waives any condition prior to the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, and the result of such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will file an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement accordingly. In the event that the Jefferies Board waives a condition after this Registration Statement becomes effective and such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will communicate such change to Jefferies shareholders by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change.
In addition, Jefferies has the right not to complete the Spin-Off if, at any time, the Jefferies Board determines, in its sole and absolute discretion, that the Spin-Off is not in the best interests of Jefferies or its shareholders, or is otherwise not advisable. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, Jefferies and Vitesse will have incurred significant costs related to the Spin-Off, including fees for consultants, financial and legal advisors, accountants and auditors, that will not be recouped. Total one-time transaction costs associated with the Spin-Off are preliminarily estimated to range from $14 million to $16 million if the Spin-Off is completed. If
8
the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, the one-time transaction costs will generally be limited to the transaction costs incurred for services rendered as of the date the Spin-Off is abandoned, which will be less than the ranges noted above. Our management has devoted significant time to manage the Spin-Off process, which has decreased the time they have had to manage the business of Vitesse. See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Conditions to the Spin-Off” for more detail.
In 2017, Jefferies announced that its primary business initiative would be to become a focused financial services company with clear drive and direction, concentrating on investment banking and capital markets and alternative asset management. Since that time, Jefferies has strategically and opportunistically monetized a significant portion of its merchant banking portfolio and realigned its internal structure to achieve those goals. Jefferies has continued to make clear that it would continue to liquidate its merchant banking portfolio, with the intention of selling the businesses and investments comprising the portfolio to third parties, distributing the businesses and investments comprising the portfolio to shareholders or transferring the balance of the businesses and investments comprising the portfolio to its asset management reportable segment. As they contemplated the Spin-Off, the Jefferies Board and management determined that positioning Vitesse as an independent publicly traded company would further Jefferies’ long-term goals and enhance stockholder value.
A wide variety of factors were considered by the Jefferies Board in evaluating the Spin-Off. Among other things, the Jefferies Board considered several potential benefits of the Spin-Off, including:
| ∎ | Strategic goals. Following the Spin-Off, Jefferies will be one step closer to its previously announced goal of liquidating its merchant banking portfolio and focusing solely on financial services. |
| ∎ | Maximizing shareholder value and choice. Jefferies shareholders should benefit from both the benefits to be reaped as Jefferies further reduces its merchant banking portfolio and further dedicates its management’s focus on financial services and from the potential for value enhancement that might be achieved in a stand-alone, publicly traded Vitesse. Jefferies believes the Spin-Off will help unlock the value in Vitesse that may not be clear to investors while it remains part of Jefferies. Those investors looking for a pure play company that is focused on creating long-term stockholder value through the profitable acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas assets will be able to invest directly in Vitesse, which should result in greater alignment between the interests of each company’s stockholder base and the characteristics of its respective business, capital structure and financial results. |
| ∎ | Separate capital structures and allocation flexibility. The Spin-Off will enable each of Jefferies and Vitesse to leverage its distinct profile and cash flow characteristics to optimize its capital structure and capital allocation strategy. The Spin-Off will permit each company to allocate its financial resources to meet the unique needs of its own businesses, which will allow each company to intensify its focus on its distinct strategic priorities and individual business risk and return profiles. |
The Jefferies Board also considered several potentially negative factors in evaluating the Spin-Off. Notwithstanding these potentially negative factors, the anticipated effects of which are not reasonably determinable, and considering the factors discussed above, the Jefferies Board determined that the Spin-Off provided the best opportunity to achieve the above benefits and enhance stockholder value. Neither Jefferies nor Vitesse can assure you that, following the Spin-Off, any of the benefits described above or otherwise will be realized to the extent anticipated or at all. For additional information, see the sections entitled “Risk Factors” and “The Spin-Off—Reasons for the Spin-Off.”
Emerging Growth Company Status
Vitesse is an “emerging growth company” as defined by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012. We will continue to be an emerging growth company until the earliest to occur of the following:
| ∎ | the last day of the fiscal year in which our total annual gross revenues first meet or exceed $1.235 billion (as adjusted for inflation); |
9
| ∎ | the date on which we have, during the prior three-year period, issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt; |
| ∎ | the last day of the fiscal year in which we (1) have an aggregate worldwide market value of common stock held by non-affiliates of $700 million or more (measured at the end of each fiscal year) as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter and (2) have been a reporting company under the Exchange Act for at least one year (and filed at least one annual report under the Exchange Act); or |
| ∎ | the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of our common stock pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act. |
For as long as we are an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including, but not limited to, not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, exemption from new or revised financial accounting standards applicable to public companies until such standards are also applicable to private companies, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports, proxy statements and registration statements, and exemptions from the requirement of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval on golden parachute compensation not previously approved. We may choose to take advantage of some or all of these reduced burdens. For example, we have taken advantage of the reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this Information Statement. For as long as we take advantage of the reduced reporting obligations, the information we provide stockholders may be different from information provided by other public companies. In addition, it is possible that some investors will find our common stock less attractive as a result of these elections, which may result in a less active trading market for our common stock and higher volatility in our stock price.
In addition, we intend to take advantage of the extended transition period that allows an emerging growth company to delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. Our election to use the extended transition period permitted by this election may make it difficult to compare our financial statements to those of non-emerging growth companies and other emerging growth companies that have opted out of the extended transition period and who will comply with new or revised financial accounting standards.
Vitesse Energy has a secured Existing Revolving Credit Facility with Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and a syndicate of banks, as lenders. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility will mature on April 29, 2026. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility permits borrowing on a revolving credit basis with availability equal to the least of (1) the current aggregate elected commitments of $170 million, (2) the current borrowing base of $200 million and (3) the maximum credit amount of $500 million. The aggregate elected commitments of the lenders under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility may be increased up to a maximum credit amount of $500 million, subject to the satisfaction of certain customary conditions, including the willingness of the existing lenders to increase their commitments or of new lenders to provide additional commitments. In connection with the closing of the Existing Revolving Credit Facility in April 2022, the borrowing base was set at $200 million. Our borrowing base under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility is subject to regular, semi-annual redeterminations on or about April 1 and October 1 of each year based on, among other things, the value of our proved oil and natural gas reserves, as determined by the lenders in their discretion. As of August 31, 2022, under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility we had outstanding borrowings of $66.0 million and $104.0 million of available borrowing capacity. At our option, borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on SOFR (“Term SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the administrative agent’s prime rate, the federal funds rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day Term SOFR rate plus 1.0%), plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to Term SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the current commitment utilization percentage. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility is guaranteed by all of our subsidiaries and is collateralized by a first priority lien on substantially all assets of Vitesse Energy and its subsidiaries, including a first priority lien on properties
10
representing a minimum of 85% of the proved reserve value of our oil and natural gas properties. For further information, see the section entitled “Description of our Indebtedness—Existing Revolving Credit Facility.”
Vitesse intends to enter into the secured New Revolving Credit Facility in connection with the Spin-Off. The New Revolving Credit Facility will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility of Vitesse Energy. Vitesse expects to enter into the New Revolving Credit Facility with Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and a syndicate of banks, as lenders. The New Revolving Credit Facility will mature on April 29, 2026. The New Revolving Credit Facility is expected to permit borrowing on a revolving credit basis with availability equal to the least of (1) the anticipated aggregate elected commitments of $170 million, (2) the anticipated borrowing base of $265 million and (3) the maximum credit amount of $500 million. It is anticipated that the aggregate elected commitments of the lenders under the New Revolving Credit Facility may be increased up to a maximum credit amount of $500 million, subject to the satisfaction of certain customary conditions, including the willingness of the existing lenders to increase their commitments or of new lenders to provide additional commitments. The borrowing base under the New Revolving Credit Agreement is expected to be redetermined in a manner consistent with the Existing Revolving Credit Agreement. We anticipate that borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility will bear interest at rates consistent with the Existing Revolving Credit Agreement. The New Revolving Credit Facility will continue to be guaranteed by all of our subsidiaries and will continue be collateralized by a first priority lien on substantially all assets of Vitesse and its subsidiaries, including a first priority lien on properties representing a minimum of 85% of the total present value of our proved oil and natural gas properties. For further information, see the section entitled “Description of our Indebtedness—New Revolving Credit Facility.” The summaries above do not purport to be complete and you are encouraged to read the Existing Revolving Credit Facility and the form of the New Revolving Credit Facility, which are filed as exhibits to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is part, for greater detail with respect to these agreements.
We are a Delaware corporation. Our principal executive offices are located at 9200 E. Mineral Ave. Suite 200, Centennial, Colorado 80112. Our telephone number is (720) 361-2500. Our website address is www.vitesse-vts.com. Information contained on, or connected to, our website or Jefferies’ website does not and will not constitute part of this Information Statement or the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, or any other filings with, or any information furnished or submitted to, the SEC.
Reasons for Furnishing This Information Statement
We are furnishing this Information Statement solely to provide information to Jefferies shareholders who will receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. Jefferies shareholders are not required to vote on the Distribution. Therefore, you are not being asked for a proxy and you are not required to send a proxy to Jefferies. You do not need to pay any consideration, exchange or surrender your existing shares of Jefferies common stock or take any other action to receive your shares of Vitesse common stock. You should not construe this Information Statement as an inducement or encouragement to buy, hold or sell any of our securities or any securities of Jefferies. We believe that the information contained in this Information Statement is accurate as of the date set forth on the cover. Changes to the information contained in this Information Statement may occur after that date, and neither we nor Jefferies undertakes any obligation to update the information except in the normal course of our and Jefferies’ respective public disclosure obligations and practices.
In preparation for the Spin-Off, on November 30, 2022, the Vitesse Board resolved to change Vitesse’s fiscal year end from November 30 (the fiscal year end of Jefferies) to December 31. As a result, Vitesse’s fiscal year end is now December 31. Vitesse expects that the first periodic report it will file following the Spin-Off pursuant to its obligations under the Exchange Act will be its Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022.
11
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT THE SPIN-OFF
The following provides only a summary of certain information regarding the Spin-Off. You should read this Information Statement in its entirety for a more detailed description of the matters described below.
| Q: | Why am I receiving this Information Statement? |
| A: | Jefferies is making this Information Statement available to you because you are a holder of shares of Jefferies common stock. If you are a holder of shares of Jefferies common stock as of the Record Date, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock that you hold as of the Record Date, you will be entitled to receive one share of Vitesse common stock. This Information Statement will help you understand how the Spin-Off will affect your post-Distribution ownership in Jefferies and Vitesse. |
| Q: | What is the Spin-Off? |
| A: | The Spin-Off is the method by which we will separate from Jefferies. In the Spin-Off, Jefferies will distribute to its shareholders all the outstanding shares of our common stock held by Jefferies, which we refer to as the “Distribution.” Following the Spin-Off, we will be an independent, publicly traded company, and Jefferies will not retain any ownership interest in us. Jefferies will continue as an independent, publicly traded company primarily focused on its investment banking and capital markets and asset management businesses. |
| Q: | Will the number of Jefferies shares I own change as a result of the Spin-Off? |
| A: | No, the number of shares of Jefferies common stock you own will not change as a result of the Spin-Off. |
| Q: | What are the reasons for the Spin-Off? |
| A: | A wide variety of factors were considered by the Jefferies Board in evaluating the Spin-Off. Among other things, the Jefferies Board considered several potential benefits of the Spin-Off, including: |
| ∎ | Strategic goals. Following the Spin-Off, Jefferies will be one step closer to its previously announced goal of liquidating its merchant banking portfolio and focusing solely on financial services. |
| ∎ | Maximizing shareholder value and choice. Jefferies shareholders should benefit from both the benefits to be reaped as Jefferies further reduces its merchant banking portfolio and further dedicates its management’s focus on financial services and from the potential for value enhancement that might be achieved in a stand-alone, publicly traded Vitesse. Jefferies believes the Spin-Off will help unlock the value in Vitesse that may not be clear to investors while it remains part of Jefferies. Those investors looking for a pure play company that is focused on creating long-term stockholder value through profitable acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas assets will be able to invest directly in Vitesse, which should result in greater alignment between the interests of each company’s stockholder base and the characteristics of its respective business, capital structure and financial results. |
| ∎ | Separate capital structures and allocation flexibility. The Spin-Off will enable each of Jefferies and Vitesse to leverage its distinct profile and cash flow characteristics to optimize its capital structure and capital allocation strategy. The Spin-Off will permit each company to allocate its financial resources to meet the unique needs of its own businesses, which will allow each company to intensify its focus on its distinct strategic priorities and individual business risk and return profiles. |
The Jefferies Board also considered several potentially negative factors in evaluating the Spin-Off. Notwithstanding these negative factors, the anticipated effects of which are not reasonably determinable, and considering the factors discussed above, the Jefferies Board determined that the Spin-Off provided the best opportunity to achieve the above benefits and enhance stockholder value. Neither Jefferies nor Vitesse can assure you that, following the Spin-Off, any of the benefits described above or otherwise will be realized to the extent anticipated or at all. For additional information, see the sections entitled “Risk Factors” and “The Spin-Off—Reasons for the Spin-Off.”
12
| Q: | Why is the separation of Vitesse structured as a spin-off? |
| A: | Jefferies believes that a distribution of our shares to holders of Jefferies common stock, which Jefferies intends to be tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes, is the most efficient way to separate our business from Jefferies in a manner that will achieve the above benefits. |
| Q: | What will I receive in the Distribution in respect of my shares of Jefferies common stock? |
| A: | As a holder of Jefferies common stock, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock you hold on the Record Date, you will receive a distribution of one share of Vitesse common stock. The distribution agent will distribute only whole shares of our common stock in the Spin-Off. See “—How will fractional shares be treated in the Distribution?” for more information on the treatment of the fractional shares you may be entitled to receive in the Distribution. Your proportionate interest in Jefferies will not change as a result of the Spin-Off. |
| Q: | What is being distributed in the Distribution? |
| A: | Jefferies will distribute approximately 26,614,467 shares of our common stock in the Distribution, based on the approximately 226,134,603 shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding as of December 16, 2022. The actual number of shares of our common stock that Jefferies will distribute will depend on the total number of shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on the Record Date. The shares of our common stock that Jefferies distributes will constitute all of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock held by Jefferies immediately prior to the Distribution, representing approximately 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock immediately prior to the Distribution. For more information on the shares being distributed in the Distribution, see the section entitled “Description of Our Capital Stock—Common Stock.” |
| Q: | What is the record date for the Distribution? |
| A: | Jefferies will determine record ownership as of the close of business on December 27, 2022, which we refer to as the “Record Date.” |
| Q: | When will the Distribution occur? |
| A: | The Distribution will be effective as of 11:59 p.m., New York City time, on January 13, 2023. On or shortly after the Distribution Date, the whole shares of our common stock will be credited in book-entry accounts for Jefferies shareholders entitled to receive the shares in the Distribution. See “—How will Jefferies distribute shares of our common stock?” for more information on how to access your book-entry account or your bank, brokerage or other account holding the Vitesse common stock you receive in the Distribution on and following the Distribution Date. |
| Q: | What do I have to do to participate in the Distribution? |
| A: | All holders of Jefferies common stock as of the Record Date will participate in the Distribution. You are not required to take any action in order to participate, but we urge you to read this Information Statement carefully. Holders of Jefferies common stock on the Record Date will not need to pay any cash or deliver any other consideration, including any shares of Jefferies common stock, in order to receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. In addition, no shareholder approval of the Distribution is required. We are not asking you for a vote and request that you do not send us a proxy card. |
| Q: | If I am a holder of Jefferies convertible preferred stock that is convertible into Jefferies common stock, will I be entitled to receive Vitesse shares in the Distribution? |
| A: | Holders of Jefferies convertible preferred stock will not be entitled to participate in the Distribution unless they convert such securities into Jefferies common stock prior to the Record Date. Jefferies expects that, as a result of the Distribution, the conversion price of its convertible preferred stock will be adjusted in accordance with Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation. |
13
| Q: | If I sell my shares of Jefferies common stock on or before the Distribution Date, will I still be entitled to receive shares of Vitesse common stock in the Distribution? |
| A: | If you sell your shares of Jefferies common stock before the Record Date, you will not be entitled to receive shares of Vitesse common stock in the Distribution. If you hold shares of Jefferies common stock on the Record Date and decide to sell them on or before the Distribution Date, you may be able to choose to sell your Jefferies common stock with or without your entitlement to the Vitesse common stock to be distributed in the Spin-Off. You are encouraged to consult with your bank, broker or other nominee, as applicable, and your financial advisor regarding your options and the specific implications of selling your shares of Jefferies common stock prior to or on the Distribution Date. See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date” for more information. |
| Q: | Is the completion of the Spin-Off subject to the satisfaction or waiver of any conditions? |
| A: | Yes, the completion of the Spin-Off is subject to the satisfaction, or the Jefferies Board’s waiver, of the following conditions: |
| ∎ | the Jefferies Board shall have authorized and approved the applicable Pre-Spin-Off Transactions (as described in the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions”) and Distribution and not withdrawn such authorization and approval, and shall have declared the dividend of our common stock to Jefferies shareholders; |
| ∎ | the ancillary agreements contemplated by the Separation and Distribution Agreement, including the Tax Matters Agreement, shall have been executed by each party to those agreements; |
| ∎ | our common stock shall have been accepted for listing on the NYSE or another national securities exchange approved by Jefferies, subject to official notice of issuance; |
| ∎ | the SEC shall have declared effective our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, under the Exchange Act, and no stop order suspending the effectiveness of the Registration Statement shall be in effect and no proceedings for that purpose shall be pending before or threatened by the SEC; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have received the IRS Ruling, substantially to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have received the written opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, which shall remain in full force and effect, subject to the limitations specified therein and the accuracy of and compliance with certain representations, warranties and covenants, to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code; |
| ∎ | the Jefferies Board shall have received one or more opinions (which have not been withdrawn or adversely modified) in customary form from one or more nationally recognized valuation, appraisal or accounting firms or investment banks as to the solvency and financial viability of Jefferies prior to the Spin-Off and each of Jefferies and Vitesse after the consummation of the Spin-Off; |
| ∎ | the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions shall have been completed; |
| ∎ | no order, injunction or decree issued by any governmental authority of competent jurisdiction or other legal restraint or prohibition preventing consummation of the Distribution shall be in effect, and no other event outside the control of Jefferies shall have occurred or failed to occur that prevents the consummation of the Distribution; |
| ∎ | no other events or developments shall have occurred prior to the Distribution Date that, in the judgment of the Jefferies Board, would result in the Distribution having a material adverse effect on Jefferies or its shareholders; |
14
| ∎ | prior to the Distribution Date, notice of Internet availability of this Information Statement or this Information Statement shall have been mailed to the holders of Jefferies common stock as of the Record Date; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have duly elected the individuals listed as members of our post-Distribution Board in this Information Statement, and such individuals shall be the members of our Board, immediately after the Distribution; provided, however, that to the extent required by any law or requirement of the NYSE or any other national securities exchange, as applicable, the existing directors shall appoint one independent director prior to the date on which “when-issued” trading of our common stock begins and this independent director shall begin his or her term prior to the Distribution and shall serve on our Audit Committee, Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee and Compensation Committee; and |
| ∎ | immediately prior to the Distribution Date, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws, each in substantially the form filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, shall be in effect. |
Jefferies and Vitesse cannot assure you that any or all of these conditions will be met, or that the Distribution will be consummated even if all of the conditions are met. Jefferies may at any time prior to the Distribution Date decide to abandon the Distribution or modify or change the terms of the Distribution. The IRS Ruling and the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP are intended to provide support that the intended tax-free treatment of the Distribution will be respected. Were Jefferies to waive the requirement of receipt of either or both of the IRS Ruling or the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, there would be less comfort that the intended tax-free treatment of the Distribution will be respected. Such waiver would be deemed to be material to Jefferies shareholders, and therefore Jefferies would communicate such change to shareholders by, depending on the timing of the waiver, either filing an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement or filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change. Were the Distribution treated as a taxable transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (1) Jefferies generally would be subject to tax as if it sold the Vitesse common stock in a transaction taxable to Jefferies, which could result in a material tax liability, and (2) Jefferies shareholders who are U.S. Holders generally would be, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, treated as receiving a distribution in an amount equal to the fair market value of our common stock received, which could result in a material tax liability for those U.S. Holders. For more information, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.”
If the Jefferies Board waives any condition prior to the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, and the result of such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will file an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement accordingly. In the event that the Jefferies Board waives a condition after this Registration Statement becomes effective and such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will communicate such change to Jefferies shareholders by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change. For a complete discussion of all of the conditions to the Distribution, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Conditions to the Spin-Off.”
| Q: | Can Jefferies decide to cancel the Distribution even if all the conditions have been satisfied? |
| A: | Yes. The Jefferies Board may, in its sole discretion and at any time prior to the Distribution Date, decide to terminate or abandon the Distribution even if all the conditions to the Distribution have been satisfied if the Jefferies Board determines that the Distribution is not in the best interests of Jefferies or its shareholders or is otherwise not advisable. For a more detailed description, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Conditions to the Spin-Off.” |
| Q: | How will Jefferies distribute shares of our common stock? |
| A: | Registered shareholders: If you own your shares of Jefferies common stock directly through Jefferies’ transfer agent, AST, you are a registered shareholder. In this case, the distribution agent will credit the whole shares of our common stock you receive in the Distribution by way of direct registration in book-entry form to a new account with our transfer agent. Registration in book-entry form refers to a method of recording share ownership where no physical stock certificates are issued to shareholders, as is the case in |
15
| the Distribution. You will be able to access information regarding your book-entry account holding the Vitesse shares at: www.astfinancial.com or by calling (800) 937-5449. |
“Street name” or beneficial shareholders: If you own your shares of Jefferies common stock beneficially through a bank, broker or other nominee, your bank, broker or other nominee will credit your account with the whole shares of our common stock you receive in the Distribution on or shortly after the Distribution Date. Please contact your bank, broker or other nominee for further information about your account.
We will not issue any physical stock certificates to any stockholders, even if requested. See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—When and How You Will Receive Vitesse Shares” for a more detailed explanation.
| Q: | How will fractional shares be treated in the Distribution? |
| A: | The distribution agent will not distribute any fractional shares of our common stock in connection with the Spin-Off. Instead, the distribution agent will aggregate all fractional shares into whole shares and sell the whole shares in the open market at prevailing market prices on behalf of Jefferies shareholders entitled to receive a fractional share. The distribution agent will then distribute the aggregate cash proceeds of the sales, net of brokerage fees and other costs, pro rata to these holders (net of any required withholding for taxes applicable to each holder). See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Treatment of Fractional Shares” for a more detailed explanation of the treatment of fractional shares. The distribution agent will, in its sole discretion, without any influence by Jefferies or us, determine when, how, through which broker-dealer and at what price to sell the whole shares of Vitesse common stock. The distribution agent is not, and any broker-dealer used by the distribution agent will not be, an affiliate of either Jefferies or us. |
| Q: | What are the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to me of the Distribution? |
| A: | It is a condition to the completion of the Distribution that Jefferies receives (1) the IRS Ruling and (2) an opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, each substantially to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code. Accordingly, assuming the Distribution so qualifies for U.S. federal income tax purposes, no gain or loss will be recognized by, or be includible in the income of, a U.S. Holder (as defined in the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off”) as a result of the Distribution, except with respect to any cash received by Jefferies shareholders in lieu of fractional shares. Jefferies has received the IRS Ruling. |
We urge you to consult your tax advisor as to the specific tax consequences of the Distribution to you, including the effect of any U.S. federal, state, local or foreign tax laws and of changes in applicable tax laws. See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off” for more information regarding the potential tax consequences to you of the Spin-Off.
| Q: | How will I determine the tax basis I will have in the shares of stock I receive in the Spin-Off? |
| A: | Generally, your aggregate basis in the stock you hold in Jefferies and the shares of our common stock received in the Spin-Off (including any fractional shares to which you otherwise would be entitled) will equal the aggregate basis of Jefferies common stock held by you immediately before the Distribution. This aggregate basis should be allocated between your Jefferies common stock and our common stock you receive in the Spin-Off (including any fractional shares to which you otherwise would be entitled) in proportion to the relative fair market values of each immediately after the Distribution. You should consult your tax advisor about how this allocation will work in your situation (including a situation where you have purchased Jefferies shares at different times or for different amounts) and regarding any particular consequences of the Spin-Off to you, including the application of state, local and non-U.S. tax laws. The material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Spin-Off are described in more detail under “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.” |
16
| Q: | Does Vitesse intend to pay cash dividends? |
| A: | Following the Distribution, we expect that Vitesse will initially pay quarterly cash dividends and dividend equivalents totaling approximately $66.0 million per fiscal year. Notwithstanding this current expectation, the timing, declaration, amount of and payment of any dividends will be within the discretion of the Board and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our operating subsidiaries, covenants associated with certain of our debt service obligations, legal requirements or limitations, industry practice, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board. Moreover, if as expected we determine to initially pay a dividend following the Distribution, there can be no assurance that we will continue to pay dividends in the same amounts or at all thereafter. We have not adopted, and do not currently expect to adopt, a separate written dividend policy to reflect our Board’s policy. See the section entitled “Dividend Policy” for more information. |
| Q: | What indebtedness will Vitesse have in place prior to or at the time of the Distribution? |
| A: | We intend to enter into the New Revolving Credit Facility in connection with the Spin-Off. The New Revolving Credit Facility will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility of Vitesse Energy. |
| Q: | How will Vitesse common stock trade? |
| A: | Currently, there is no public market for our common stock. We intend to list our common stock on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “VTS.” |
We anticipate that trading in our common stock will begin on a “when-issued” basis on the third trading day before the Distribution Date and will continue up to and including the Distribution Date. “When-issued” trading in the context of a spin-off refers to a sale or purchase made conditionally on or before the Distribution Date because the securities of the spun-off entity have not yet been distributed. “When-issued” trades generally settle within two trading days after the Distribution Date. On the first trading day following the Distribution Date, any “when-issued” trading of our common stock will end and “regular-way” trading will begin. “Regular-way” trading refers to trading after the security has been distributed and typically involves a trade that settles on the second full trading day following the date of the trade. See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date” for more information. We cannot predict the trading prices for our common stock before, on or after the Distribution Date.
| Q: | What will happen to the listing of Jefferies common stock? |
| A: | Jefferies common stock will continue to trade on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “JEF” after the Distribution. |
| Q: | Will the Spin-Off affect the trading price of my Jefferies common stock? |
| A: | We expect the trading price of shares of Jefferies common stock immediately following the Distribution to be lower than the trading price immediately prior to the Distribution because the trading price will no longer reflect the value of Vitesse Energy. Furthermore, until the market has fully analyzed the value of Jefferies without Vitesse Energy, the trading price of shares of Jefferies common stock may fluctuate and result in a higher volatility in stock price. There can be no assurance that, following the Distribution, the combined trading prices of the Jefferies common stock and the Vitesse common stock will equal or exceed what the trading price of Jefferies common stock would have been in the absence of the Spin-Off. |
It is possible that after the Spin-Off, the combined equity value of Jefferies and Vitesse will be less than Jefferies’ equity value before the Spin-Off.
17
| Q: | What will Vitesse’s relationship be with Jefferies following the Spin-Off? |
| A: | Following the Distribution, Vitesse and Jefferies will be separate companies with separate management teams and separate boards of directors and Jefferies will not own any shares of our common stock. Vitesse will enter into a Separation and Distribution Agreement and a Tax Matters Agreement with Jefferies to effect the separation and provide a framework for the relationship between Vitesse and Jefferies after the Spin-Off, and will enter into certain other agreements. These agreements will, among other things, govern the relationship between Vitesse and Jefferies following the Spin-Off. For additional information regarding the Separation and Distribution Agreement and Tax Matters Agreement, see the sections entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to the Spin-Off” and “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.” |
| Q: | Who will manage Vitesse following the Spin-Off? |
| A: | Vitesse will be led by Bob Gerrity, who will serve as Vitesse’s Chief Executive Officer, Brian Cree, who will serve as Vitesse’s President, and David Macosko, who will serve as Vitesse’s Chief Financial Officer. For more information regarding Vitesse’s directors and management, see the section entitled “Management.” |
| Q: | Do I have appraisal rights in connection with the Spin-Off? |
| A: | No. Holders of Jefferies common stock are not entitled to appraisal rights in connection with the Spin-Off. |
| Q: | Who is the transfer agent and registrar for Vitesse common stock? |
| A: | American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC. |
| Q: | Are there risks associated with owning shares of Vitesse common stock? |
| A: | Yes. Our business faces both general and specific risks and uncertainties. Our business also faces risks relating to the Spin-Off. Following the Spin-Off, we will also face risks associated with being an independent, publicly traded company. Accordingly, you should read carefully the information set forth in the section entitled “Risk Factors.” |
| Q: | What if I hold my shares through a broker, bank or other nominee? |
| A: | Jefferies shareholders who hold their shares through a broker, bank or other nominee will have their brokerage account credited with shares of Vitesse common stock. For additional information, those shareholders are encouraged to contact their broker, bank or nominee directly. |
| Q: | What if I have stock certificates reflecting my shares of Jefferies common stock? Should I send them to the transfer agent or to Jefferies? |
| A: | No. You should not send your stock certificates to the transfer agent or to Jefferies. You should retain your Jefferies stock certificates. |
| Q: | Where can I get more information? |
| A: | If you have any questions relating to the mechanics of the Distribution, you should contact the distribution agent at: |
American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC 6201 15th Ave
Brooklyn, NY 11219
Telephone: (800) 937-5449
Corporate website: www.astfinancial.com
18
Before the Spin-Off, if you have any questions relating to the Spin-Off, you should contact Jefferies at:
Investor Relations
Jefferies Financial Group Inc.
520 Madison Avenue
New York, New York 10022
Attn: Jonathan Freedman
Phone: (212) 778-8913
After the Spin-Off, if you have any questions relating to Vitesse, you should contact us at:
Investor Relations
Vitesse Energy, Inc.
9200 E. Mineral Ave. Suite 200
Centennial, Colorado 80112
Attn: Ben Messier
Phone: (720) 532-8232
A link to our investor relations website and additional contact information will be made available at www.vitesse-vts.com. Information contained on, or connected to, our website does not and will not constitute part of this Information Statement or the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, or any other filings with, or any information furnished or submitted to, the SEC.
19
| Distributing Company |
Jefferies Financial Group Inc., a New York corporation. After the Distribution, Jefferies will not own any shares of our common stock. |
| Distributed Company |
Vitesse Energy, Inc., a newly formed Delaware corporation and an indirect majority owned subsidiary of Jefferies. At the time of the Distribution, we will hold, directly or through our subsidiaries, the assets and liabilities of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil. After the Spin-Off, we will be an independent, publicly traded company. |
| Distributed Securities |
Jefferies will distribute all of the shares of our common stock held by Jefferies, representing approximately 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock immediately prior to the Distribution. Based on the approximately 226,134,603 shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on December 16, 2022, and applying the distribution ratio pursuant to which, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock, one share of Vitesse common stock will be distributed, approximately 26,614,467 shares of Vitesse common stock will be distributed. |
| Record Date |
The Record Date is the close of business on December 27, 2022 |
| Distribution Date |
The Distribution Date is January 13, 2023. |
| Distribution Ratio |
For every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock each Jefferies shareholder holds on the Record Date, they will receive one share of our common stock. The distribution agent will distribute only whole shares of our common stock in the Spin-Off. See the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Treatment of Fractional Shares” for more detail. Please note that if you sell your shares of Jefferies common stock on or before the Distribution Date, the buyer of those shares may in some circumstances be entitled to receive the shares of our common stock to be distributed in respect of the Jefferies shares that you sold. For more information, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date.” |
| The Distribution |
On the Distribution Date, Jefferies will release the shares of our common stock to the distribution agent to distribute to Jefferies shareholders. Jefferies will distribute our shares in book-entry form and thus we will not issue any physical stock certificates. You will not be required to make any payment, surrender or exchange your shares of Jefferies common stock or take any other action to receive your shares of our common stock. |
| Fractional Shares |
The distribution agent will not distribute any fractional shares of our common stock to Jefferies shareholders. Instead, the distribution agent will first aggregate fractional shares into whole shares, then sell the whole shares in the open market at prevailing market prices on behalf of Jefferies shareholders entitled to receive a fractional share, and finally distribute the aggregate cash proceeds of the sales, net of brokerage fees and other costs, pro rata to these holders (net of any required withholding for taxes applicable to each holder). If |
20
| you receive cash in lieu of fractional shares, you will not be entitled to any interest on the payments. The cash you receive in lieu of fractional shares generally will, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, be taxable as described under the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.” |
| Conditions to the Spin-Off |
Completion of the Spin-Off is subject to the satisfaction, or the waiver of the Jefferies Board, of the following conditions: |
| ∎ | the Jefferies Board shall have authorized and approved the applicable Pre-Spin-Off Transactions (as described in the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions”) and Distribution and not withdrawn such authorization and approval, and shall have declared the dividend of our common stock to Jefferies shareholders; |
| ∎ | the ancillary agreements contemplated by the Separation and Distribution Agreement, including the Tax Matters Agreement, shall have been executed by each party to those agreements; |
| ∎ | our common stock shall have been accepted for listing on the NYSE or another national securities exchange approved by Jefferies, subject to official notice of issuance; |
| ∎ | the SEC shall have declared effective our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, under the Exchange Act, and no stop order suspending the effectiveness of the Registration Statement shall be in effect and no proceedings for that purpose shall be pending before or threatened by the SEC; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have received the IRS Ruling, substantially to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have received the written opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, which shall remain in full force and effect, subject to the limitations specified therein and the accuracy of and compliance with certain representations, warranties and covenants, to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code; |
| ∎ | the Jefferies Board shall have received one or more opinions (which have not been withdrawn or adversely modified) in customary form from one or more nationally recognized valuation, appraisal or accounting firms or investment banks as to the solvency and financial viability of Jefferies prior to the Spin-Off and each of Jefferies and Vitesse after the consummation of the Spin-Off; |
21
| ∎ | the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions shall have been completed; |
| ∎ | no order, injunction or decree issued by any governmental authority of competent jurisdiction or other legal restraint or prohibition preventing consummation of the Distribution shall be in effect, and no other event outside the control of Jefferies shall have occurred or failed to occur that prevents the consummation of the Distribution; |
| ∎ | no other events or developments shall have occurred prior to the Distribution Date that, in the judgment of the Jefferies Board, would result in the Distribution having a material adverse effect on Jefferies or its shareholders; |
| ∎ | prior to the Distribution Date, notice of Internet availability of this Information Statement or this Information Statement shall have been mailed to the holders of Jefferies common stock as of the Record Date; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have duly elected the individuals listed as members of our post-Distribution Board in this Information Statement, and such individuals shall be the members of our Board, immediately after the Distribution; provided, however, that to the extent required by any law or requirement of the NYSE or any other national securities exchange, as applicable, the existing directors shall appoint one independent director prior to the date on which “when-issued” trading of our common stock begins and this independent director shall begin his or her term prior to the Distribution and shall serve on our Audit Committee, Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee and Compensation Committee; and |
| ∎ | immediately prior to the Distribution Date, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws, each in substantially the form filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, shall be in effect. |
| The fulfillment of the foregoing conditions will not create any obligation on the part of Jefferies to complete the Spin-Off. We are not aware of any material U.S. federal, foreign or state regulatory requirements with which we must comply, other than SEC rules and regulations, or any material approvals that we must obtain, other than the approval for listing of our common stock and the SEC’s declaration of the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, in connection with the Distribution. |
The IRS Ruling and the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP are intended to provide support that the intended tax-free treatment of the Distribution will be respected. Were Jefferies to waive the requirement of receipt of either or both of the IRS Ruling or the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, there would be less comfort that the intended tax-free treatment of the Distribution will be respected. Such waiver would be deemed to be material to Jefferies shareholders, and therefore Jefferies would communicate such change to shareholders by, depending on the timing of the waiver, either filing an amendment to
22
the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement or filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change. Were the Distribution treated as a taxable transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (1) Jefferies generally would be subject to tax as if it sold the Vitesse common stock in a transaction taxable to Jefferies, which could result in a material tax liability, and (2) Jefferies shareholders who are U.S. Holders generally would be, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, treated as receiving a distribution in an amount equal to the fair market value of our common stock received, which could result in a material tax liability for those U.S. Holders. For more information, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.”
If the Jefferies Board waives any condition prior to the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, and the result of such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will file an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement accordingly. In the event that the Jefferies Board waives a condition after this Registration Statement becomes effective and such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will communicate such change to Jefferies shareholders by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change. For a complete discussion of all of the conditions to the Distribution, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Conditions to the Spin-Off.”
| In addition, Jefferies has the right not to complete the Spin-Off if, at any time, the Jefferies Board determines, in its sole and absolute discretion, that the Spin-Off is not in the best interests of Jefferies or its shareholders, or is otherwise not advisable. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, Jefferies and Vitesse will have incurred significant costs related to the Spin-Off, including fees for consultants, financial and legal advisors, accountants and auditors, that will not be recouped. Total one-time transaction costs associated with the Spin-Off are preliminarily estimated to range from $14 million to $16 million if the Spin-Off is completed. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, the one-time transaction costs will generally be limited to the transaction costs incurred for services rendered as of the date the Spin-Off is abandoned, which will be less than the ranges noted above. Our management has devoted significant time to manage the Spin-Off process, which has decreased the time they have had to manage the business of Vitesse. |
| Trading Market and Ticker Symbol |
We intend to file an application to list our common stock on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “VTS.” We anticipate that, on the third trading day before the Distribution Date, trading of shares of our common stock will begin on a “when-issued” basis and will continue up to and including the Distribution Date, and we expect that “regular-way” trading of our common stock will begin the first trading day after the Distribution Date. |
| We also anticipate that, on the third trading day before the Distribution Date, there will be two markets in Jefferies common stock: (1) a “regular-way” market on which shares of Jefferies |
23
| common stock will trade with an entitlement for the purchaser of Jefferies common stock to receive shares of our common stock to be distributed in the Distribution, and (2) an “ex-distribution” market on which shares of Jefferies common stock will trade without an entitlement for the purchaser of Jefferies common stock to receive shares of our common stock. For more information, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date.” |
| Material Tax Consequences to Jefferies Shareholders |
It is a condition to the completion of the Distribution that Jefferies receives (1) the IRS Ruling and (2) an opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, each substantially to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code. Accordingly, assuming the Distribution so qualifies for U.S. federal income tax purposes, no gain or loss will be recognized by, or be includible in the income of, a U.S. Holder (as defined in the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off”) as a result of the Distribution, except with respect to any cash received by Jefferies shareholders in lieu of fractional shares. Jefferies has received the IRS Ruling. |
| We urge you to consult your tax advisor as to the specific tax consequences of the Distribution to you, including the effect of any U.S. federal, state, local or foreign tax laws and of changes in applicable tax laws. |
| Relationship with Jefferies After the Spin-Off |
We intend to enter into several agreements with Jefferies related to the Spin-Off, which will govern the relationship between Jefferies and us up to and after completion of the Spin-Off and allocate between Jefferies and us various assets, liabilities, rights and obligations. These agreements include: |
| ∎ | a Separation and Distribution Agreement that will set forth Jefferies’ and our agreements regarding the principal actions that both parties will take in connection with the Spin-Off and aspects of our relationship following the Spin-Off; and |
| ∎ | a Tax Matters Agreement that will govern the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of Jefferies and us after the Spin-Off with respect to all tax matters and will include restrictions to preserve the tax-free status of the Distribution. |
| In addition to the above agreements, we are also currently party to, or intend to enter into, various other agreements with Jefferies and its subsidiaries, and we do not consider these agreements to be material to Jefferies and its subsidiaries. We describe these arrangements in greater detail under the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions” and describe some of the risks of these arrangements under the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to the Spin-Off.” |
24
| Dividend Policy |
Following the Distribution, we expect that Vitesse will initially pay quarterly cash dividends and dividend equivalents totaling approximately $66.0 million per fiscal year. Notwithstanding this current expectation, the timing, declaration, amount of and payment of any dividends will be within the discretion of our Board and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our operating subsidiaries, covenants associated with certain of our debt service obligations, legal requirements or limitations, industry practice, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board. Moreover, if as expected we determine to initially pay a dividend following the Distribution, there can be no assurance that we will continue to pay dividends in the same amounts or at all thereafter. We pay dividends out of distributable cash flow, which we define as Adjusted EBITDA less interest expense and cash taxes. During the year ended November 30, 2021, we generated Adjusted EBITDA of $102.3 million, and during the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, we generated Adjusted EBITDA of $158.0 million. Historically, we have used our distributable cash flow for multiple purposes, including capital expenditures (which includes acquisitions), repayment of debt and payment of distributions. Due to our strategy to grow oil and natural gas production levels during 2021 and 2022, we incurred levels of capital expenditures above a maintenance level. Given the amount of these capital expenditures and the discretionary amount of debt repaid, we would not have been able to pay a $66.0 million distribution during the year ended November 30, 2021. However, going forward, we expect to prioritize the dividend while sustaining production through maintenance capital expenditures. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil paid cash distributions totaling $59.0 million. We have not adopted, and do not currently expect to adopt, a separate written dividend policy to reflect our Board’s policy. See the section entitled “Dividend Policy” for more information. |
| Transfer Agent |
American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC. |
| Risk Factors |
Our business faces both general and specific risks and uncertainties. Our business also faces risks relating to the Spin-Off. Following the Spin-Off, we will also face risks associated with being an independent, publicly traded company. Accordingly, you should read carefully the information set forth under the section entitled “Risk Factors.” |
25
You should carefully consider the following risks and other information in this Information Statement. The following risks have generally been separated into five groups: risks relating to the Spin-Off, risks relating to our common stock, risks relating to our business, risks relating to our indebtedness and risks relating to legal and regulatory matters. If any of the following events actually occur, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected, the trading price of our common stock could decline and you could lose all or part of your investment. Additional risks and uncertainties that we do not presently know about or currently believe are not material may also adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Relating to the Spin-Off
If the Distribution does not qualify as a transaction that is tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes, Jefferies and holders of Jefferies common stock who receive shares of Vitesse common stock in connection with the Spin-Off could be subject to significant tax liability.
Completion of the Spin-Off is conditioned on Jefferies’ receipt of (1) the IRS Ruling and (2) an opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, each substantially to the effect that, subject to the limitations specified therein and the accuracy of and compliance with certain representations, warranties and covenants, the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code. Jefferies has received the IRS Ruling.
Although the IRS Ruling is generally binding on the IRS, the continuing validity of the IRS Ruling is subject to the accuracy of the factual representations made in the ruling request. In addition, Jefferies expects to obtain an opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP as described above. In rendering its opinion, Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP will rely on (1) customary representations and covenants made by Jefferies and Vitesse and (2) specified assumptions, including an assumption regarding the completion of the Distribution and certain related transactions in the manner contemplated by the transaction agreements. If any of those representations, covenants or assumptions are inaccurate, Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP may not be able to provide the opinion and the tax consequences of the Distribution and certain related transactions could differ from those described in this Information Statement. An opinion of counsel neither binds the IRS nor precludes the IRS or the courts from adopting a contrary position. Accordingly, notwithstanding the receipt of the IRS Ruling and the anticipated receipt of the tax opinion, there can be no assurance that the IRS or a court will not take a contrary position and the consequences of the Distribution and certain related transactions to Jefferies and the holders of Jefferies common stock could be materially different from, and worse than, the U.S. federal income tax consequences described in this Information Statement.
If it were determined that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, did not qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution did not qualify as a distribution to which Section 355 of the Code applies, Jefferies would generally be subject to tax as if it sold the Vitesse common stock in a transaction taxable to Jefferies, which could result in a material tax liability. In addition, Jefferies shareholders who are U.S. Holders would generally, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, be treated as receiving a distribution in an amount equal to the fair market value of our common stock received, which could result in a material tax liability.
For more information, see below and the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.”
We intend to agree to numerous restrictions to preserve the non-recognition treatment of the Distribution, which may reduce our strategic and operating flexibility.
We intend to agree in the Tax Matters Agreement to covenants and indemnification obligations that address compliance with Section 355(e) of the Code. These covenants and indemnification obligations may limit our ability to pursue strategic transactions or engage in new businesses or other transactions that may otherwise maximize the value of our business, and might discourage or delay a strategic transaction that our stockholders may consider favorable, including share repurchases, stock issuances, certain asset dispositions and other strategic transactions.
26
To preserve the tax-free treatment of the Distribution, and in addition to our indemnity obligations described above, the Tax Matters Agreement will restrict us, for the two-year period following the Distribution, except in specific circumstances, from: (1) entering into any transaction pursuant to which all or a specified portion of our stock would be acquired, whether by merger or otherwise, (2) issuing equity securities in a manner that could reasonably be expected to have adverse consequences under Section 355(e) of the Code, (3) repurchasing shares of our stock other than in certain open-market transactions, (4) ceasing to actively conduct certain of our businesses or (5) taking or failing to take any other action that prevents the Distribution and certain related transactions from qualifying as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code. For more information, see the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.”
We could have an indemnification obligation to Jefferies in certain circumstances if the Distribution were determined not to qualify for tax-free treatment for U.S. federal tax purposes, or in certain other circumstances, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We intend to enter into a Tax Matters Agreement with Jefferies. The terms of the Tax Matters Agreement will require us to indemnify Jefferies and certain related parties for certain taxes and losses that (i) result primarily from, individually or in the aggregate, the breach of certain representations and warranties made by us (including in connection with the receipt by Jefferies of the IRS Ruling or the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP regarding the tax treatment of the Distribution) or covenants made by us (applicable to actions or failures to act by us and our subsidiaries following the completion of the Distribution), (ii) are attributable to actions we take following the Distribution and result from the failure of the transfer of the Vitesse Energy equity interests to Vitesse, together with the Distribution, to qualify as (a) a reorganization described in Section 355(a) and Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code, (b) a transaction in which the stock distributed thereby is “qualified property” for purposes of Sections 355(c) and 361(c) of the Code, or (c) a transaction in which Jefferies, Vitesse and the holders of Jefferies common stock recognize no income or gain for U.S. federal income tax purposes pursuant to Sections 355, 361 and 1032 of the Code, including, as a result of the application of Section 355(e) of the Code to the Distribution as a result of a 50% or greater change in ownership as described below, or (iii) are attributable to taxes with respect to Vitesse Energy or Vitesse Oil for tax periods or portions thereof ending before the Distribution, including as may arise on audit.
Even if the Distribution were otherwise to qualify as a tax-free transaction under Section 368(a)(1)(D) and Section 355 of the Code, the Distribution would be taxable to Jefferies (but not to Jefferies’ shareholders) pursuant to Section 355(e) of the Code if there were a 50% or greater change in beneficial ownership of either Jefferies or Vitesse as part of a plan or series of related transactions that included the Distribution. For this purpose, any acquisitions of Jefferies or our common stock during the four-year period beginning on the date that begins two years before the date of the Distribution are presumed to be part of such a plan, although we or Jefferies may rebut that presumption. The U.S. federal income tax rules for determining whether there has been a 50% or greater change in beneficial ownership of Jefferies and Vitesse, and the period during which that change is measured, are complex and include the aggregation and attribution rules of Section 355(e)(4)(C) of the Code. The Distribution itself does not give rise to a change in beneficial ownership, and public trading of the stock of Jefferies or Vitesse by small stockholders does not give rise to a change in beneficial ownership, but many other transactions could do so. Such transactions may include (but are not limited to) acquisitions by Vitesse or Jefferies using its own stock, the merger or consolidation of Vitesse or Jefferies with or into another company, redemptions, recapitalizations, stock dividends, and sales or issuances of stock.
Any such indemnification obligation could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. For more information, see the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.”
We may be unable to achieve some or all of the benefits that we expect to achieve from the Spin-Off, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We believe that, as an independent, publicly traded company, we will be able to, among other things, more effectively articulate a clear investment proposition to attract a long-term investor base suited to our business, growth profile and capital allocation priorities.
27
However, we may not achieve the anticipated benefits from the Spin-Off for a variety of reasons, including, among other things:
| ∎ | the Spin-Off will require significant amounts of management’s time and effort, which may divert our management’s attention from operating and growing our business; |
| ∎ | following the Spin-Off, we may be more susceptible to market fluctuations, the risk of takeover by third parties and other adverse events because our business will be less diversified than Jefferies’ businesses prior to the Spin-Off; |
| ∎ | the Spin-Off may require us to incur significant costs, including accounting, tax, legal and other professional services costs, recruiting and relocation costs associated with hiring key senior management personnel who are new to our company, costs to retain key management personnel, tax costs and costs to shared systems and other unforeseen dis-synergy costs; and |
| ∎ | under the terms of the Tax Matters Agreement that we will enter into with Jefferies, we will be restricted from taking certain actions that could cause the Spin-Off or other related transactions to fail to qualify as a tax-free transaction and these restrictions may limit us for a period of time from pursuing certain strategic transactions and equity issuances or engaging in other transactions that might increase the value of our business. |
If we fail to achieve some or all of the benefits that we expect to achieve as an independent company, or do not achieve them in the time we expect, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Our management and accounting systems may not be adequately prepared to meet the reporting and other requirements to which we will become subject following the Spin-Off, and we will incur increased costs as a result of being an independent publicly traded company.
As an independent public company, we will separately become subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the Dodd-Frank Act and will be required to prepare our financial statements according to the rules and regulations required by the SEC. These reporting and other obligations will place significant demands on our management and on administrative and operational resources. Moreover, to comply with these requirements, we anticipate that we will need to implement additional financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures, and may need to hire additional accounting and finance staff. We expect to incur additional annual expenses related to these requirements. If we are unable to upgrade our financial and management controls, reporting systems, information technology and procedures in a timely and effective fashion, our ability to comply with our financial reporting requirements and other rules that apply to reporting companies under the Exchange Act could be impaired. We also expect to incur additional expenses in order to obtain new director and officer liability insurance.
Other significant changes may occur in our cost structure, management, financing and business operations as a result of operating as an independent publicly traded company. As such, our historical financial data may not be indicative of our future performance as an independent, publicly traded company. For additional information about our past financial performance and the basis of presentation of our financial statements, see the sections entitled “Selected Historical Financial Data,” “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Statements” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our historical consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
Federal and state fraudulent transfer laws and New York and Delaware corporate law may permit a court to void the Distribution and related transactions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In connection with the Distribution, Jefferies intends to undertake the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions which, along with the Distribution, may be subject to challenge under federal and state fraudulent conveyance and transfer laws as well as under New York or Delaware corporate law. Under applicable laws, any transaction, contribution or distribution contemplated as part of the Distribution could be voided as a fraudulent transfer or conveyance if, among other things, the transferor received less than reasonably equivalent value or fair consideration in return and the transferor was insolvent or rendered insolvent by reason of the transfer.
28
We cannot be certain as to the standards a court would use to determine whether any entity involved in the Distribution was insolvent at the relevant time. In general, however, a court would look at various facts and circumstances related to the entity in question, including evaluation of whether:
| ∎ | the sum of its debts, including contingent and unliquidated liabilities, was greater than the fair saleable value of all of its assets; |
| ∎ | the present fair saleable value of its assets was less than the amount that would be required to pay its probable liability on its existing debts, including contingent liabilities, as they become absolute and mature; or |
| ∎ | it could pay its debts as they become due. |
If a court were to find that any transaction, contribution or distribution involved in the Distribution was a fraudulent transfer or conveyance, the court could void the transaction, contribution or distribution. In addition, the Distribution could also be voided if a court were to find that it is not a legal distribution or dividend under New York or Delaware corporate law. The resulting complications, costs and expenses of either finding could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
After the Spin-Off, certain members of management and directors may face actual or potential conflicts of interest.
After the Spin-Off, certain members of the management and directors of each of Jefferies and Vitesse may own common stock in both companies and Ms. Linda Adamany and Messrs. Brian Friedman and Joseph Steinberg, each of whom will be a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off, will also continue to serve on the Jefferies Board, and may be required to recuse themselves from deliberations relating to arrangements between us and Jefferies in the future. This ownership and directorship overlap could create, or appear to create, potential conflicts of interest when the management and directors of one company face decisions that could have different implications for themselves and the other company. For example, potential conflicts of interest could arise in connection with the resolution of any dispute regarding the terms of the agreements governing the separation and our relationship with Jefferies thereafter. These agreements include the Separation and Distribution Agreement, the Tax Matters Agreement and any commercial or service agreements between the parties or their affiliates. Potential conflicts of interest may also arise out of any commercial arrangements that we or Jefferies may enter into in the future. For more information, see the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons.”
Our acquisitions of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil may require the consents or approvals of, or provide other rights to, third parties and governmental authorities. If such consents or approvals are not obtained, we may not be entitled to the benefit of certain contracts, permits and other assets and rights, which could increase our expenses or otherwise harm our business and financial performance.
In connection with our acquisitions of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil, the transfer of certain contracts, permits and other assets and rights may require consents or approvals of third parties or governmental authorities or provide other rights to third parties. Some parties may use consent requirements or other rights to terminate contracts or obtain more favorable contractual terms from us, which, for example, could take the form of price increases, require us to expend additional resources in order to obtain the services or assets previously provided under the contract, or require us to make arrangements with new third parties or obtain letters of credit or other forms of credit support. If we do not obtain required consents or approvals, we may be unable to obtain the benefits, permits, assets and contractual commitments that we intended to acquire in connection with our acquisitions of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil, and we may be required to seek alternative arrangements to obtain services and assets which may be more costly and of lower quality. The termination, modification, replacement or replication of these contracts or permits or the failure to timely complete the transfer or separation of these contracts or permits could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Until the Distribution occurs, the Jefferies Board may change the terms of the Spin-Off in ways that may be unfavorable to us.
Until the Distribution occurs, we will continue to be a subsidiary of Jefferies. Accordingly, Jefferies has the discretion to determine and change the terms of the Spin-Off, including the establishment of the Record Date and the Distribution Date, and these changes could be unfavorable to us. In addition, the Jefferies Board may decide not to proceed with the Spin-Off at any time prior to the Distribution.
29
No vote of Jefferies shareholders is required in connection with the Spin-Off. As a result, if the Spin-Off occurs and you do not want to receive our common stock in the Distribution, your sole recourse will be to divest yourself of your Jefferies common stock prior to the Record Date or in the “regular-way” trading market during the period prior to the Distribution.
No vote of Jefferies shareholders is required in connection with the Spin-Off. Accordingly, if the Distribution occurs and you do not want to receive our common stock in the Distribution, your only recourse will be to divest yourself of your Jefferies common stock prior to the Record Date or in the “regular-way” trading market during the period prior to the Distribution.
Risks Relating to Our Common Stock
No market for our common stock currently exists and an active trading market may not develop or be sustained after the Spin-Off. Following the Spin-Off our stock price may fluctuate significantly.
There is currently no public market for our common stock. We intend to apply to list our common stock on the NYSE. We anticipate that before the Distribution Date, trading of shares of our common stock will begin on a “when-issued” basis and this trading will continue up to and including the Distribution Date. However, an active trading market for our common stock may not develop as a result of the Spin-Off or may not be sustained in the future. The lack of an active market may make it more difficult for stockholders to sell our shares and could lead to our share price being depressed or volatile.
We cannot predict the prices at which our common stock may trade after the Spin-Off. The market price of our common stock may fluctuate widely, depending on many factors, some of which may be beyond our control, including:
| ∎ | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our business, financial condition and results of operations due to factors related to our business; |
| ∎ | competition in the oil and natural gas industry and our ability to compete successfully; |
| ∎ | success or failure of our business strategies; |
| ∎ | our ability to retain and recruit qualified personnel; |
| ∎ | our quarterly or annual earnings, or those of other companies in our industry; |
| ∎ | our level of indebtedness, our ability to make payments on or service our indebtedness and our ability to obtain financing as needed; |
| ∎ | announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions or dispositions; |
| ∎ | changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles; |
| ∎ | the failure of securities analysts to cover our common stock after the Spin-Off; |
| ∎ | changes in earnings estimates by securities analysts or our ability to meet those estimates; |
| ∎ | the operating and stock price performance of other comparable companies; |
| ∎ | investor perception of our company and the oil and natural gas industry; |
| ∎ | overall market fluctuations, including the cyclical nature of the oil and natural gas market; |
| ∎ | results from any material litigation or government investigation; |
| ∎ | changes in laws and regulations (including tax laws and regulations) affecting our business; and |
| ∎ | general economic conditions, credit and capital market conditions and other external factors. |
Furthermore, our business profile and market capitalization may not fit the investment objectives of some Jefferies shareholders and, as a result, these Jefferies shareholders may sell their shares of our common stock after the Distribution. See “—Substantial sales of our common stock may occur in connection with the Spin-Off, which could cause our stock price to decline.” Low trading volume for our stock may occur if, among other reasons, an active trading market does not develop. This would amplify the effect of the above factors on our stock price volatility.
Substantial sales of our common stock may occur in connection with the Spin-Off, which could cause our stock price to decline.
Jefferies shareholders receiving shares of our common stock in the Distribution generally may sell those shares immediately in the public market. It is likely that some Jefferies shareholders, including some of its larger
30
shareholders, will sell their shares of our common stock received in the Distribution if, for reasons such as our business profile or market capitalization as an independent company, we do not fit their investment objectives, or, in the case of index funds, we are not a participant in the index in which they are investing. The sales of significant amounts of our common stock or the perception in the market that this will occur may decrease the market price of our common stock.
Vitesse is an emerging growth company and the information we provide stockholders may be different from information provided by other public companies, which may result in a less active trading market for our common stock and higher volatility in our stock price.
Vitesse is an “emerging growth company” as defined by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012. We will continue to be an emerging growth company until the earliest to occur of the following:
| ∎ | the last day of the fiscal year in which our total annual gross revenues first meet or exceed $1.235 billion (as adjusted for inflation); |
| ∎ | the date on which we have, during the prior three-year period, issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt; |
| ∎ | the last day of the fiscal year in which we (1) have an aggregate worldwide market value of common stock held by non-affiliates of $700 million or more (measured at the end of each fiscal year) as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter and (2) have been a reporting company under the Exchange Act for at least one year (and filed at least one annual report under the Exchange Act); or |
| ∎ | the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of our common stock pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act. |
For as long as we are an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including, but not limited to:
| ∎ | not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002; |
| ∎ | exemption from new or revised financial accounting standards applicable to public companies until such standards are also applicable to private companies; |
| ∎ | reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports, proxy statements and registration statements; and |
| ∎ | exemptions from the requirement of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval on golden parachute compensation not previously approved. |
We may choose to take advantage of some or all of these reduced burdens. For example, we have taken advantage of the reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this Information Statement. For as long as we take advantage of the reduced reporting obligations, the information we provide stockholders may be different from information provided by other public companies. In addition, it is possible that some investors will find our common stock less attractive as a result of these elections, which may result in a less active trading market for our common stock and higher volatility in our stock price.
In addition, we intend to take advantage of the extended transition period that allows an emerging growth company to delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. Our election to use the extended transition period permitted by this election may make it difficult to compare our financial statements to those of non-emerging growth companies and other emerging growth companies that have opted out of the extended transition period and who will comply with new or revised financial accounting standards.
Although we expect to pay dividends, we cannot provide assurance that we will pay dividends on our common stock, and our indebtedness may limit our ability to pay dividends on our common stock.
Following the Spin-Off, the timing, declaration, amount of and payment of future dividends, if any, to stockholders will fall within the discretion of our Board. Our Board’s decisions regarding the payment of future dividends, if any,
31
will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our business, covenants associated with certain of our debt service obligations, legal requirements or limitations, industry practice, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board. We have not adopted, and do not currently expect to adopt, a separate written dividend policy to reflect our Board’s policy. For more information, see the section entitled “Dividend Policy.” For a description of the covenants limiting our ability to pay dividends and distributions, see “—Our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is restricted by applicable laws and regulations and may be limited by requirements under our New Revolving Credit Facility.” There can be no assurance that we will pay a dividend in the future or continue to pay any dividend if we do commence paying dividends, and there can be no assurance that, in the future, the combined annual dividends paid on Jefferies common stock, if any, and our common stock, if any, after the Spin-Off will equal the annual dividends on Jefferies common stock prior to the Spin-Off.
Certain provisions in our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, Amended and Restated Bylaws and Delaware law may discourage takeovers.
Several provisions of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, Amended and Restated Bylaws and Delaware law may discourage, delay or prevent a merger or acquisition that is opposed by our Board. These include provisions that:
| ∎ | prevent our stockholders from calling a special meeting or acting by written consent; |
| ∎ | require advance notice of any stockholder nomination for the election of directors or any stockholder proposal; |
| ∎ | provide for a plurality voting standard in contested director elections; |
| ∎ | authorize only our Board to fill director vacancies and newly created directorships; |
| ∎ | authorize our Board to adopt, amend or repeal our Amended and Restated Bylaws without stockholder approval; and |
| ∎ | authorize our Board to issue one or more series of “blank check” preferred stock. |
In addition, Section 203 of the DGCL, prohibits a Delaware corporation from engaging in a business combination with any interested stockholder for a period of three years following the date the person became an interested stockholder, subject to certain exceptions. In general, Section 203 of the DGCL defines an “interested stockholder” as an entity or person who, together with the entity’s or person’s affiliates, beneficially owns, or is an affiliate of the corporation and within three years prior to the time of determination of interested stockholder status did own, 15% or more of the outstanding voting stock of the corporation. A Delaware corporation may “opt out” of these provisions with an express provision in its certificate of incorporation. We have not opted out of Section 203 of the DGCL in our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation.
These and other provisions of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, Amended and Restated Bylaws and Delaware law may discourage, delay or prevent certain types of transactions involving an actual or a threatened acquisition or change in control of us including unsolicited takeover attempts, even though the transaction may offer our stockholders the opportunity to sell their shares of our common stock at a price above the prevailing market price. For more information, see the section entitled “Description of Our Capital Stock—Certain Provisions of Delaware Law, Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws.”
Your percentage ownership in Vitesse may be diluted in the future.
Your percentage ownership in Vitesse may be diluted in the future because of the settlement or exercise of equity-based awards that we expect to grant to our directors, officers and other employees. Prior to completion of the Spin-Off, we expect to approve an equity incentive plan that will provide for the grant of equity-based awards to our directors, officers and other employees, including equity grants that are expected to be made upon completion of the Spin-Off. In addition, we may issue equity as all or part of the consideration paid for acquisitions and strategic investments that we may make in the future or as necessary to finance our ongoing operations.
In addition, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will authorize us to issue, without the approval of our stockholders, one or more classes or series of preferred stock having such designation, powers, preferences and relative, participating, optional and other special rights, including preferences over our common stock with respect to dividends and distributions, as our Board may generally determine. The terms of one or more classes or series of preferred stock could dilute the voting power or reduce the value of our common stock. For example, we could grant
32
the holders of preferred stock the right to elect some number of the members of our Board in all events or upon the happening of specified events, or the right to veto specified transactions. Similarly, the repurchase or redemption rights or liquidation preferences that we could assign to holders of preferred stock could affect the residual value of our common stock. For more information, see the section entitled “Description of Our Capital Stock.”
The rights associated with our common stock will differ from the rights associated with Jefferies common stock.
Upon completion of the Distribution, the rights of Jefferies shareholders who become our stockholders will be governed by our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws and by Delaware law. The rights associated with Jefferies shares are different from the rights associated with our shares. In addition, the rights of Jefferies shareholders are governed by New York law, while the rights of our stockholders will be governed by Delaware law. Material differences between the rights of Jefferies shareholders and the rights of our stockholders include differences with respect to, among other things, certain anti-takeover measures.
For more information, see the section entitled “Comparison of Rights of Jefferies Shareholders and Vitesse Stockholders.”
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will designate the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees.
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, in all cases to the fullest extent permitted by law, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for:
| ∎ | any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf; |
| ∎ | any action or proceeding asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any current or former director, officer or other employee or stockholder of our company to us or our stockholders; |
| ∎ | any action or proceeding asserting a claim arising pursuant to, or seeking to enforce any right, obligation or remedy under, any provision of Delaware law or our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation or our Amended and Restated Bylaws (with respect to each, as may be amended from time to time); or |
| ∎ | any action or proceeding asserting a claim governed by the internal affairs doctrine or any other action asserting an “internal corporate claim” as that term is defined in Section 115 of the DGCL. |
However, if the Court of Chancery of Delaware does not have jurisdiction, the action or proceeding may be brought in any other state or U.S. federal court located within the State of Delaware. Further, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, to the fullest extent permitted by law, the U.S. federal district courts will be the sole and exclusive forum for any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under U.S. federal securities laws.
Any person holding, purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of capital stock of us will be deemed to have notice of and have consented to this provision and deemed to have waived any argument relating to the inconvenience of the forum in connection with any action or proceeding described in this provision. This provision may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees, which may discourage such lawsuits. Alternatively, if a court of competent jurisdiction were to find this provision of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions.
Risks Relating to Our Business
The COVID-19 pandemic has had, and may continue to have, an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We face risks related to public health crises, including the COVID-19 pandemic. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, including travel bans, prohibitions on group events and gatherings, shutdowns of certain businesses, curfews, shelter-in-place orders and recommendations to practice social distancing in addition to other actions taken by both businesses and governments, resulted in a significant and swift reduction in international and U.S. economic activity. The collapse in the demand for oil caused by this unprecedented global health and economic crisis contributed to the significant decrease in oil prices in 2020 and had and could in the future continue to have an adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations.
33
Since the beginning of 2021, the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines progressed and many government-imposed restrictions were relaxed or rescinded. However, we continue to monitor the effects of the pandemic on our operations. As a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, our operations, and those of our operators, have and may continue to experience delays or disruptions and temporary suspensions of operations. In addition, our results of operations and financial condition have been and may continue to be adversely affected by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
The extent to which our operating and financial results are affected by COVID-19 will depend on various factors and consequences beyond our control, such as the emergence of more contagious and harmful variants of the COVID-19 virus, the duration and scope of the pandemic, additional actions by businesses and governments in response to the pandemic, and the speed and effectiveness of responses to combat the virus. COVID-19, and the volatile regional and global economic conditions stemming from the pandemic, could also aggravate the other risk factors that we identify herein. While the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic have lessened recently in the United States, we cannot predict the duration or future effects of the pandemic, or more contagious and harmful variants of the COVID-19 virus, and such effects may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition in a manner that is not currently known to us or that we do not currently consider to present significant risks to our operations.
Oil and natural gas prices are volatile. Extended declines in oil and natural gas prices have adversely affected, and could in the future adversely affect, our business, financial position, results of operations and cash flow.
The oil and natural gas markets are very volatile, and we cannot predict future oil and natural gas prices. Oil and natural gas prices have fluctuated significantly, including periods of rapid and material decline, in recent years. The prices we receive for our oil and natural gas production heavily influence our production, revenue, cash flows, profitability, reserve bookings and access to capital. Although we seek to mitigate volatility and potential declines in oil and natural gas prices through derivative arrangements that hedge a portion of our expected production, this merely seeks to mitigate (not eliminate) these risks, and such activities come with their own risks.
The prices we receive for our oil and natural gas production and the levels of our production depend on numerous factors beyond our control. These factors include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ∎ | changes in global supply and demand for oil and natural gas; |
| ∎ | changes in NYMEX WTI oil prices and NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas prices; |
| ∎ | the volatility and uncertainty of regional pricing Differentials; |
| ∎ | future repurchases (or additional possible releases) of oil from the strategic petroleum reserve by the United States Department of Energy; |
| ∎ | the actions of OPEC and other major oil producing countries; |
| ∎ | worldwide and regional economic, political and social conditions impacting the global supply and demand for oil and natural gas, which may be driven by various risks including war, terrorism, political unrest, or health epidemics (such as the global COVID-19 coronavirus outbreak); |
| ∎ | the price and quantity of imports of foreign oil and natural gas; |
| ∎ | political and economic conditions, including embargoes, in oil-producing countries or affecting other oil-producing activity; |
| ∎ | the outbreak or escalation of military hostilities, including between Russia and Ukraine, and the potential destabilizing effect such conflicts may pose for the European continent or the global oil and natural gas markets; |
| ∎ | inflation; |
| ∎ | the level of global oil and natural gas exploration, production activity and inventories; |
| ∎ | changes in U.S. energy policy; |
| ∎ | weather conditions; |
| ∎ | outbreak of disease; |
| ∎ | technological advances affecting energy consumption; |
| ∎ | domestic and foreign governmental taxes, tariffs and/or regulations; |
| ∎ | proximity and capacity of processing, gathering, and storage facilities, oil and natural gas pipelines and other transportation facilities; |
34
| ∎ | the price and availability of competitors’ supplies of oil and natural gas in captive market areas; and |
| ∎ | the price and availability of alternative fuels. |
These factors and the volatility of the energy markets make it extremely difficult to predict oil and natural gas prices. A substantial or extended decline in oil or natural gas prices, such as the significant and rapid decline that occurred in 2020, has resulted in and could result in future impairments of our proved oil and natural gas properties and may materially and adversely affect our future business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to finance planned capital expenditures. To the extent oil and natural gas prices received from production are insufficient to fund planned capital expenditures, we may be required to reduce spending or borrow or issue additional equity to cover any such shortfall. Lower oil and natural gas prices may limit our ability to comply with the covenants under our New Revolving Credit Facility and/or limit our ability to access borrowing availability thereunder, which is dependent on many factors including the value of our proved reserves.
Drilling for and producing oil and natural gas are high risk activities with many uncertainties that could adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations.
Our operators’ drilling activities are subject to many risks, including the risk that they will not discover commercially productive reservoirs. Drilling for oil or natural gas can be uneconomical, not only from dry holes, but also from productive wells that do not produce sufficient revenues to be commercially viable. In addition, drilling and producing operations on our acreage may be curtailed, delayed or canceled by our operators as a result of other factors, including:
| ∎ | declines in oil or natural gas prices; |
| ∎ | infrastructure limitations, such as the natural gas gathering and processing constraints experienced in the Williston Basin in 2019; |
| ∎ | the high cost, shortages or delays of equipment, materials and services; |
| ∎ | unexpected operational events, pipeline ruptures or spills, adverse weather conditions and natural disasters, facility or equipment malfunctions, and equipment failures or accidents; |
| ∎ | title problems; |
| ∎ | pipe or cement failures and casing collapses; |
| ∎ | lost or damaged oilfield development and services tools; |
| ∎ | laws, regulations, and other initiatives related to environmental matters, including those addressing alternative energy sources, the phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles and the risks of global climate change; |
| ∎ | compliance with environmental and other governmental requirements; |
| ∎ | increases in severance taxes; |
| ∎ | regulations, restrictions, moratoria and bans on hydraulic fracturing; |
| ∎ | unusual or unexpected geological formations, and pressure or irregularities in formations; |
| ∎ | loss of drilling fluid circulations; |
| ∎ | environmental hazards, such as oil, natural gas or well fluids spills or releases, pipeline or tank ruptures and discharges of toxic gas; |
| ∎ | fires, blowouts, craterings and explosions; |
| ∎ | uncontrollable flows of oil, natural gas or well fluids; |
| ∎ | pipeline capacity curtailments; and |
| ∎ | demand from investors to return capital to investors and/or conduct share repurchases. |
In addition to causing curtailments, delays and cancellations of drilling and producing operations, many of these events can cause substantial losses, including personal injury or loss of life, damage to or destruction of property, natural resources and equipment, pollution, environmental contamination, loss of wells and regulatory penalties. We ordinarily maintain insurance against various losses and liabilities arising from our operations; however, insurance against all operational risks is not available to us. Additionally, we may elect not to obtain insurance if we believe that the cost of available insurance is excessive relative to the perceived risks presented. Losses could therefore occur for uninsurable or uninsured risks or in amounts in excess of existing insurance coverage. The occurrence of an event that is not fully covered by insurance could have a material adverse impact on our business activities, financial condition and results of operations.
35
Due to previous declines in oil and natural gas prices, we have in the past taken writedowns of our oil and natural gas properties. We may be required to record further writedowns of our oil and natural gas properties in the future.
In 2020, we were required to write down the carrying value of certain of our oil and natural gas properties, and further writedowns could be required in the future. Under the successful efforts method of accounting, costs associated with the acquisition, drilling, and equipping of successful exploratory wells and costs of successful and unsuccessful development wells are capitalized and depleted, net of estimated salvage values, using the units-of-production method on the basis of a reasonable aggregation of properties within a common geological structural feature or stratigraphic condition, such as a reservoir or field. Exploration, geological and geophysical costs, delay rentals, and drilling costs of unsuccessful exploratory wells are charged to expense as incurred. The sale of a partial interest in a proved property is accounted for as a cost recovery, and no gain or loss is recognized as long as this treatment does not significantly affect the units-of-production amortization rate. A gain or loss is recognized for all other sales of proved properties.
We review our oil and natural gas properties for impairment whenever events and circumstances indicate a decline in the recoverability of their carrying value. We estimate the expected future cash flows of our oil and natural gas properties and compare such cash flows to the carrying amount of the proved oil and natural gas properties to determine if the amount is recoverable. If the carrying amount exceeds the estimated undiscounted future cash flows, we will adjust our proved oil and natural gas properties to estimated fair value. The factors used to estimate fair value include estimates of reserves, future oil and natural gas prices adjusted for basis Differentials, future production estimates, anticipated capital expenditures, and a discount rate commensurate with the risk associated with realizing the projected cash flows. The discount rate is a rate that management believes is representative of current market conditions and includes estimates for a risk premium and other operational risks.
A continued period of low prices may force us to incur further material write-downs of our oil and natural gas properties, which could have a material effect on the value of our properties and cause the value of our securities to decline in value. Additionally, impairments would occur if we were to experience sufficient downward adjustments to our estimated proved reserves or the present value of estimated future net revenues. An impairment recognized in one period may not be reversed in a subsequent period even if higher oil and natural gas prices increase the cost center ceiling applicable to the subsequent period. We have in the past and could in the future incur additional impairments of oil and natural gas properties which may be material.
We have incurred net losses in the past, in part due to fluctuations in oil and gas prices, and we may incur such losses again in the future.
We had net income of $18.1 million, net loss of $8.9 million and net income of $35.9 million during the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively. To the extent our production is not hedged, we are exposed to declines in oil and natural gas prices, and our derivative arrangements may be inadequate to protect us from continuing and prolonged declines in oil and natural gas prices. In prior periods, such declines have led to net losses. For example, our net loss for the year ended November 30, 2020 was largely caused by a decrease in oil and natural gas revenue, due primarily to a decrease in the average realized oil and natural gas prices. Unrealized hedging losses on commodity derivatives attributable to significant increases in oil prices may also cause a net loss for a given period.
In addition, fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices have impacted our unit-based compensation expense for prior periods and may impact our stock-based compensation expense in periods following the consummation of the Spin-Off. For example, in prior periods we have experienced increases to our unit-based compensation expense primarily due to increased oil and natural gas prices causing the estimated fair value of the liabilities associated with such unit-based compensation to increase, which contributed to net losses recorded during such periods. As a result of the foregoing and other factors, we may continue to incur net losses in the future.
Our estimated proved reserves are based on many assumptions that may prove to be inaccurate. Any material inaccuracies in these reserve estimates or underlying assumptions will materially affect the quantities and present value of our total reserves.
Determining the amount of oil and natural gas recoverable from various formations involves significant complexity and uncertainty. No one can measure underground accumulations of oil or natural gas in an exact way. Oil and natural gas reserve engineering requires subjective estimates of underground accumulations of oil and/or natural gas
36
and assumptions concerning future oil and natural gas prices, production levels, and operating, and development costs. Some of our reserve estimates are made without the benefit of a lengthy production history and are less reliable than estimates based on a lengthy production history. As a result, estimated quantities of proved reserves and projections of future production rates and the timing of development expenditures may prove to be inaccurate.
We routinely make estimates of oil and natural gas reserves in connection with managing our business and preparing reports to our lenders and investors, including in some cases estimates prepared by our internal reserve engineers and professionals that are not reviewed or audited by an independent reserve engineering firm. We make these reserve estimates using various assumptions, including assumptions as to oil and natural gas prices, development schedules, drilling and operating expenses, capital expenditures, taxes and availability of funds. Some of these assumptions are inherently subjective, and the accuracy of our reserve estimates relies in part on the ability of our management team, reserve engineers and other advisors to make accurate assumptions. Any significant variance from these assumptions by actual figures could greatly affect our estimates of total reserves, the economically recoverable quantities of oil and natural gas attributable to any particular group of properties, the classifications of reserves based on risk of recovery, and estimates of the future net cash flows. Numerous changes over time to the assumptions on which our reserve estimates are based result in the actual quantities of oil and natural gas our operators ultimately recover being different from our reserve estimates. Any significant variance could materially affect the estimated quantities and present value of reserves shown in this Information Statement, subsequent reports we file with the SEC or other company materials.
Our future success depends on our ability to replace reserves.
Because the rate of production from oil and natural gas properties generally declines as reserves are depleted, our future success depends upon our ability to economically find or acquire and produce additional oil and natural gas reserves. Except to the extent that we acquire additional properties containing proved reserves, conduct successful development activities or, through engineering studies, identify additional behind-pipe zones or secondary recovery reserves, our proved reserves will decline as our reserves are produced. We have added significant net wells and production from wellbore-only acquisitions, where we don’t hold the underlying leasehold interest that would entitle us to participate in future wells. Future oil and natural gas production, therefore, is highly dependent upon our level of success in acquiring or finding additional reserves that are economically recoverable. We cannot assure you that we will be able to find or acquire and develop additional reserves at an acceptable cost.
We may acquire significant amounts of unproved property to further our development efforts. Development and drilling and production activities are subject to many risks, including the risk that no commercially productive reservoirs will be discovered. We seek to acquire both proved and producing properties as well as undeveloped acreage that we believe will enhance growth potential and increase our earnings over time. However, we cannot assure you that all of these properties will contain economically viable reserves or that we will not abandon existing properties. Additionally, we cannot assure you that unproved reserves or undeveloped acreage that we acquire will be profitably developed, that new wells drilled on our properties will be productive or that we will recover all or any portion of our capital in our properties and reserves.
The present value of future net cash flows from our proved reserves is not necessarily the same as the current market value of our estimated proved reserves.
We base the estimated discounted future net cash flows from our proved reserves using Standardized Measure and PV-10, each of which uses specified pricing and cost assumptions. However, actual future net cash flows from our oil and natural gas properties will be affected by factors such as the volume, pricing and duration of our hedging contracts; actual prices we receive for oil and natural gas; our actual operating costs in producing oil and natural gas; the amount and timing of our capital expenditures; the amount and timing of actual production; and changes in governmental regulations or taxation. For example, our estimated proved reserves as of November 30, 2021 were calculated under SEC rules by applying year-end SEC prices based on the twelve-month unweighted arithmetic average of the first day of the month oil and natural gas prices for such year end of $64.81 per Bbl and $3.46 per MMBtu, which for certain periods during this time were substantially different from the available market prices. In addition, the 10% discount factor we use when calculating discounted future net cash flows may not be the most appropriate discount factor based on interest rates in effect from time to time and risks associated with us or the oil and natural gas industry in general. Any material inaccuracies in these reserve estimates or underlying assumptions will materially affect the quantities and present value of our reserves, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
37
Our business depends on transportation and processing facilities and other assets that are owned by third parties.
The marketability of our oil and natural gas depends in part on the availability, proximity and capacity of pipeline systems, processing facilities, oil trucking fleets and rail transportation assets owned by third parties. The lack of available capacity on these systems and facilities, whether as a result of proration, growth in demand outpacing growth in capacity, physical damage, scheduled maintenance, legal or other reasons such as suspension of service due to legal challenges (see below regarding the Dakota Access Pipeline), could result in a substantial increase in costs, declines in realized oil and natural gas prices, the shut-in of producing wells or the delay or discontinuance of development plans for our properties. In recent periods, we experienced significant delays and production curtailments, and declines in realized natural gas prices, that we believe were due in part to natural gas gathering and processing constraints in the Williston Basin. The negative effects arising from these and similar circumstances may last for an extended period of time. In many cases, operators are provided only with limited, if any, notice as to when these circumstances will arise and their duration. In addition, our wells may be drilled in locations that are serviced to a limited extent, if at all, by gathering and transportation pipelines, which may or may not have sufficient capacity to transport production from all of the wells in the area. As a result, we rely on third-party oil trucking to transport a significant portion of our production to third-party transportation pipelines, rail loading facilities and other market access points. In addition, the third parties on whom operators rely for transportation services are subject to complex federal, state, tribal, and local laws that could adversely affect the cost, manner, or feasibility of conducting business on our oil and natural gas properties. Further, concerns about the safety and security of oil and gas transportation by pipeline may result in public opposition to pipeline development and increased regulation of pipelines by PHMSA. In recent years, PHMSA has increased regulation of onshore gas transmission systems, hazardous liquids pipelines, and gas gathering systems. For example, in November 2021, PHMSA issued a final rule that extended pipeline safety requirements to onshore gas gathering pipelines, and therefore could result in less capacity to transport our products by pipeline. Further, although we do not expect to incur direct costs as a result of increased PHMSA regulation, additional regulation could impact rates charged by our operators and impact their ability to enter into gathering and transportation agreements, which costs could be passed through to us.
The Dakota Access Pipeline (the “DAPL”), a major pipeline transporting oil from the Williston Basin, is subject to ongoing litigation that could threaten its continued operation. In July 2020, a federal district court vacated the DAPL’s easement to cross the Missouri River at Lake Oahe and ordered the pipeline be shut down pending the completion of an environmental impact statement (“EIS”) to determine whether the DAPL poses a threat to the Missouri River and drinking water supply of the Standing Rock Sioux Reservation. The shut-down order was later reversed on appeal and the DAPL currently remains in operation while the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (the “Corps”) conducts the review, which is currently anticipated to be completed in the fall of 2022. Following completion of the EIS, the Corps will determine whether to grant the DAPL an easement to cross the Missouri River at Lake Oahe or to shut down the pipeline. Moreover, the EIS or the Corps’ decision with respect to an easement may subsequently be challenged in court. As a result, a shut-down remains possible, and there is no guarantee that the DAPL will be permitted to continue operations following the completion of the EIS. Any significant curtailment in gathering system or pipeline capacity, or the unavailability of sufficient third-party trucking or rail capacity, could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Seasonal weather conditions, which may be impacted by climate change, may adversely affect our operators’ ability to conduct drilling and completion activities and to sell oil and natural gas for periods of time, in some of the areas where our properties are located.
Seasonal weather conditions can limit drilling and completion activities, selling oil and natural gas, and other operations in some of our operating areas. In the Williston Basin, drilling and other oil and natural gas activities on our properties can be adversely affected during the winter months by severe winter weather and drilling on our properties is generally performed during the summer and fall months. These seasonal constraints can pose challenges for meeting well drilling objectives and increase competition for equipment, supplies and personnel during the summer and fall months, which could lead to shortages and increase costs or delay operations. Additionally, many municipalities impose weight restrictions on the paved roads that lead to jobsites due to the muddy conditions caused by spring thaws. This could limit access to jobsites and operators’ ability to service wells in these areas.
The frequency and severity of severe winter weather conditions which impact our business activities may also be impacted by the effects of climate change. Energy needs could increase or decrease as a result of extreme weather conditions depending on the duration and magnitude of any such climate changes. Increased energy use due to
38
weather changes may require us to invest in order to serve increased demand. A decrease in energy use due to weather changes may affect our financial condition through decreased revenues. To the extent the frequency of extreme weather events increases, this could increase our operators’ costs. If any of these results occur, it could have an adverse effect on our assets and cause us to incur costs in preparing for and responding to them. If any such effects were to occur, our financial condition and results of operations would be materially adversely affected.
As a non-operator, the successful development of our assets relies extensively on third parties, which could have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
We have only participated in wells operated by third parties. The success of our business operations depends on the timing of drilling activities and success of our third-party operators. If our operators are not successful in the development, exploitation, production and exploration activities relating to our leasehold interests, or are unable or unwilling to perform, our financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
These risks are heightened in a low oil and natural gas price environment, which may present significant challenges to our operators. The challenges and risks faced by our operators may be similar to or greater than our own, including with respect to their ability to service their debt, remain in compliance with their debt instruments and, if necessary, access additional capital. Oil and natural gas prices and/or other conditions have in the past and may in the future cause oil and natural gas operators to file for bankruptcy. The insolvency of an operator of any of our properties, the failure of an operator of any of our properties to adequately perform operations or an operator’s breach of applicable agreements could reduce our production and revenue and result in our liability to governmental authorities for compliance with environmental, safety and other regulatory requirements, to the operator’s suppliers and vendors and to royalty owners under oil and natural gas leases jointly owned with the operator or another insolvent owner.
Our operators will make decisions in connection with their operations (subject to their contractual and legal obligations to other owners of working interests), which may not be in our best interests. We may have no ability to exercise influence over the operational decisions of our operators, including the setting of capital expenditure budgets and drilling locations and schedules. Dependence on our operators could prevent us from realizing our target returns for those locations. The success and timing of development activities by our operators will depend on a number of factors that will largely be outside of our control, including oil and natural gas prices and other factors generally affecting the oil and natural gas industry’s operating environment; the timing and amount of capital expenditures; their expertise and financial resources; approval of other participants in drilling wells; selection of technology; and the rate of production of reserves, if any.
The inability of one or more of our operators to meet their obligations to us may adversely affect our financial results.
Our exposures to credit risk are, in part, through receivables resulting from the sale of our oil and natural gas production, which operators market on our behalf to energy marketing companies, refineries and their affiliates. We are subject to credit risk due to the relative concentration of our oil and natural gas receivables with a limited number of operators. This concentration may impact our overall credit risk since these entities may be similarly affected by changes in economic and other conditions. A low oil and natural gas price environment may strain our operators, which could heighten this risk. The inability or failure of our operators to meet their obligations to us or their insolvency or liquidation may adversely affect our financial results.
We could experience periods of higher costs as activity levels fluctuate or if oil and natural gas prices rise. These increases could reduce our profitability, cash flow, and ability to complete development activities as planned.
An increase in oil and natural gas prices or other factors could result in increased development activity and investment in our areas of operations, which may increase competition for and cost of equipment, labor and supplies. Shortages of, or increasing costs for, experienced drilling crews and equipment, labor or supplies could restrict our operators’ ability to conduct desired or expected operations. In addition, capital and operating costs in the oil and natural gas industry have generally risen during periods of increasing oil and natural gas prices as producers seek to increase production in order to capitalize on higher oil and natural gas prices. In situations where cost inflation exceeds oil and natural gas price inflation, our profitability and cash flow, and our operators’ ability to complete development activities as scheduled and on budget, may be negatively impacted. Any delay in the drilling of new wells or significant increase in drilling costs could reduce our revenues and profitability.
39
The development of our proved undeveloped reserves may take longer and may require higher levels of capital expenditures than we currently anticipate. Therefore, these undeveloped reserves may not be ultimately developed or produced.
Approximately 35.3% of our estimated net proved reserves volumes were classified as proved undeveloped as of November 30, 2021. Development of undeveloped reserves may take longer and require higher levels of capital expenditures than we currently anticipate. Delays in the development of our reserves or increases in costs to drill and develop such reserves will reduce the PV-10 value of our estimated proved undeveloped reserves and future net revenues estimated for such reserves and may result in some projects becoming uneconomic. In addition, delays in the development of reserves could cause us to have to reclassify our proved undeveloped reserves as unproved reserves.
Our acquisition strategy will subject us to certain risks associated with the inherent uncertainty in evaluating properties for which we have limited information.
We intend to continue to expand our operations in part through acquisitions. Our decision to acquire a property will depend in part on the evaluation of data obtained from production reports and engineering studies, geophysical and geological analyses and seismic and other information, the results of which are often inconclusive and subject to various interpretations. Also, our reviews of acquired properties are inherently incomplete because it generally is not economically feasible to perform an in-depth review of the individual properties involved in each acquisition. Even a detailed review of records and properties may not necessarily reveal existing or potential problems, nor will it permit us to become sufficiently familiar with the properties to assess fully their deficiencies and potential recoverable reserves. On-site inspections are often not performed on properties being acquired, and environmental matters, such as subsurface contamination, are not necessarily observable even when an on-site inspection is undertaken. Any acquisition involves other potential risks, including, among other things:
| ∎ | the validity of our assumptions about reserves, future production, revenues and costs; |
| ∎ | a decrease in our liquidity by using a significant portion of our cash from operations or borrowing capacity to finance acquisitions; |
| ∎ | a significant increase in our interest expense or financial leverage if we incur additional debt to finance acquisitions; |
| ∎ | the ultimate value of any contingent consideration agreed to be paid in an acquisition; |
| ∎ | dilution to stockholders if we use equity as consideration for, or to finance, acquisitions; |
| ∎ | the assumption of unknown liabilities, losses or costs for which we are not indemnified or for which our indemnity is inadequate; |
| ∎ | geological risk, which refers to the risk that hydrocarbons may not be present or, if present, may not be recoverable economically; |
| ∎ | an inability to hire, train or retain qualified personnel to manage and operate our growing business and assets; and |
| ∎ | an increase in our costs or a decrease in our revenues associated with any potential royalty owner or landowner claims or disputes, or other litigation encountered in connection with an acquisition. |
We may also acquire multiple assets in a single transaction. Portfolio acquisitions via joint-venture or other structures are more complex and expensive than single project acquisitions, and the risk that a multiple-project acquisition will not close may be greater than in a single-project acquisition. An acquisition of a portfolio of projects may result in our ownership of projects in geographically dispersed markets which place additional demands on our ability to manage such operations. A seller may require that a group of projects be purchased as a package, even though one or more of the projects in the portfolio does not meet our strategic objectives. In such cases, we may attempt to make a joint bid with another buyer, and such other buyer may default on its obligations.
Further, we may acquire properties subject to known or unknown liabilities and with limited or no recourse to the former owners or operators. As a result, if liability were asserted against us based upon such properties, we may have to pay substantial sums to dispute or remedy the matter, which could adversely affect our profitability. Unknown liabilities with respect to assets acquired could include, for example: liabilities for clean-up of undiscovered or undisclosed environmental contamination; claims by developers, site owners, vendors or other persons relating to the
40
asset or project site; liabilities incurred in the ordinary course of business; and claims for indemnification by general partners, directors, officers and others indemnified by the former owners of the asset or project sites.
We may be unable to successfully integrate any assets we may acquire in the future into our business or achieve the anticipated benefits of such acquisitions.
Our ability to achieve the anticipated benefits of any future acquisitions will depend in part upon whether we can integrate the acquired assets into our existing business in an efficient and effective manner. We may not be able to accomplish this integration process successfully. The successful acquisition of producing properties requires an assessment of several factors, including:
| ∎ | recoverable reserves; |
| ∎ | future oil and natural gas prices and their appropriate Differentials; |
| ∎ | availability and cost of transportation of production to markets; |
| ∎ | availability and cost of drilling equipment and of skilled personnel; |
| ∎ | development and operating costs including access to water and potential environmental and other liabilities; and |
| ∎ | regulatory, permitting and similar matters. |
The accuracy of these assessments is inherently uncertain. In connection with these assessments, we have performed reviews of the subject properties that we believe to be generally consistent with industry practices. The reviews are based on our analysis of historical production data, assumptions regarding capital expenditures and anticipated production declines without review by an independent petroleum engineering firm. Data used in such reviews are typically furnished by the seller or obtained from publicly available sources. Our review may not reveal all existing or potential problems or permit us to fully assess the deficiencies and potential recoverable reserves for all of the acquired properties, and the reserves and production related to the acquired properties may differ materially after such data is reviewed by an independent petroleum engineering firm or further by us. On-site inspections will not always be performed on every well, and environmental problems are not necessarily observable even when an on-site inspection is undertaken. Even when problems are identified, the seller may be unwilling or unable to provide effective contractual protection against all or a portion of the underlying deficiencies. We are often not entitled to contractual indemnification for environmental liabilities and acquire properties on an “as is” basis, and, as is the case with certain liabilities associated with the assets acquired in our recent acquisitions, we are entitled to indemnification for only certain operational liabilities. The integration process may be subject to delays or changed circumstances, and we can give no assurance that our recently acquired assets will perform in accordance with our expectations or that our expectations with respect to integration or cost savings as a result of such acquisitions will materialize.
The majority of our producing properties are located in the Williston Basin, making us vulnerable to risks associated with operating in one major geographic area.
Our oil and natural gas properties are focused on the Williston Basin, which means our current producing properties and new drilling opportunities are geographically concentrated in that area. Because our oil and natural gas properties are not as diversified geographically as some of our competitors, our profitability may be disproportionately exposed to the effect of any regional events, including fluctuations in prices of oil and natural gas produced from the wells in the region, natural disasters, restrictive governmental regulations, transportation capacity constraints, weather, curtailment of production or interruption of transportation and processing, and any resulting delays or interruptions of production from existing or planned new wells.
The loss of any member of our management team, upon whose knowledge, relationships with industry participants, leadership and technical expertise we rely could diminish our ability to conduct our operations and harm our ability to execute our business plan.
Our success depends heavily upon the continued contributions of those members of our management team whose knowledge, relationships with industry participants, leadership and technical expertise would be difficult to replace. In particular, our ability to successfully acquire additional properties, to increase our reserves, to participate in drilling opportunities and to identify and enter into commercial arrangements depends on developing and maintaining close working relationships with industry participants. In addition, our ability to select and evaluate suitable properties and to consummate transactions in a highly competitive environment is dependent on our
41
management team’s knowledge and expertise in the industry. To continue to develop our business, we rely on our management team’s knowledge and expertise in the industry and will use our management team’s relationships with industry participants to enter into strategic relationships. The members of our management team may terminate their employment with our company at any time. If we were to lose members of our management team, we may not be able to replace the knowledge or relationships that they possess and our ability to execute our business plan could be materially harmed.
Deficiencies of title to our leased interests could significantly affect our financial condition.
We typically do not incur the expense of a title examination prior to acquiring oil and natural gas leases or undivided interests in oil and natural gas leases or other developed rights. If an examination of the title history of a property reveals that an oil or natural gas lease or other developed rights have been purchased in error from a person who is not the owner of the mineral interest desired, our interest would substantially decline in value or be eliminated. In such cases, the amount paid for such oil or natural gas lease or leases or other developed rights may be lost. It is generally our practice not to incur the expense of retaining lawyers to examine the title to the mineral interest to be acquired. Rather, we typically rely upon the judgment of our own oil and natural gas landmen who conduct due diligence and perform the fieldwork in examining records in the appropriate governmental or county clerk’s office before attempting to acquire a lease or other developed rights in a specific mineral interest.
Prior to drilling an oil or natural gas well, however, it is the normal practice in the oil and natural gas industry for the company acting as the operator of the well to obtain a title examination of the spacing unit within which the proposed oil or natural gas well is to be drilled to ensure there are no obvious deficiencies in title to the well. Frequently, as a result of such examinations, certain curative work must be done to correct deficiencies in the marketability of the title, such as obtaining affidavits of heirship or causing an estate to be administered. Such curative work entails expense, and the operator may elect to proceed with a well despite defects to the title identified in the title opinion. Furthermore, title issues may arise at a later date that were not initially detected in any title review or examination. Any one or more of the foregoing could require us to reverse revenues previously recognized and potentially negatively affect our cash flows and results of operations. Our failure to obtain perfect title to our leaseholds may adversely affect our current production and reserves and our ability in the future to increase production and reserves.
We conduct business in a highly competitive industry.
The oil and natural gas industry is highly competitive. The key areas in respect of which we face competition include: acquisition of assets offered for sale by other companies; access to capital (debt and equity) for financing and operational purposes; purchasing, leasing, hiring, chartering or other procuring of equipment by our operators that may be scarce; and employment of qualified and experienced skilled management and oil and natural gas professionals.
Competition in our markets is intense and depends, among other things, on the number of competitors in the market, their financial resources, their degree of geological, geophysical, engineering and management expertise and capabilities, their pricing policies, their ability to develop properties on time and on budget, their ability to select, acquire and develop reserves and their ability to foster and maintain relationships with the relevant authorities.
Our competitors also include those entities with greater technical, physical and financial resources. Finally, companies and certain private equity firms not previously investing in oil and natural gas may choose to acquire reserves to establish a firm supply or simply as an investment. Any such companies will also increase market competition which may directly affect us. If we are unsuccessful in competing against other companies, our business, results of operations, financial condition or prospects could be materially adversely affected.
The ongoing military conflict between Ukraine and Russia has caused unstable market and economic conditions and is expected to have additional global consequences, such as heightened risks of cyberattacks. Our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be materially adversely affected by the negative global and economic impact resulting from the military conflict in Ukraine or any other geopolitical tensions.
U.S. and global markets are experiencing volatility and disruption following the escalation of geopolitical tensions and the start of the military conflict between Russia and Ukraine. On February 24, 2022, a full-scale military invasion of Ukraine by Russian troops began. Although the length and impact of the ongoing military conflict is highly unpredictable, the military conflict in Ukraine has led to market disruptions, including significant volatility in
42
oil and natural gas prices, credit and capital markets, as well as supply chain disruptions. Various of Russia’s actions have led to sanctions and other penalties being levied by the United States, the European Union, and other countries, as well as other public and private actors and companies, against Russia and certain other geographic areas, including restrictions on imports of Russian oil, LNG and coal. These disruptions in the oil and natural gas markets have caused, and could continue to cause, significant volatility in energy prices, which could have a material effect on our business. Additional potential sanctions and penalties have also been proposed and/or threatened.
In addition, the United States and other countries have imposed sanctions on Russia which increases the risk that Russia, as a retaliatory action, may launch cyberattacks against the United States, its government, infrastructure and businesses. On March 21, 2022, the Biden Administration issued warnings about the potential for Russia to engage in malicious cyber activity against the United States in response to the economic sanctions that have been imposed.
Prolonged unfavorable economic conditions or uncertainty as a result of the military conflict between Russia and Ukraine may adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Any of the foregoing may also magnify the impact of other risks described in this Information Statement.
Inflation could adversely impact our ability to control our costs, including the operating expenses and capital costs of our operators.
Although inflation in the United States has been relatively low in recent years, it rose significantly beginning in the second half of 2021 and has continued to rise through the first nine months of 2022. This is believed to be the result of the economic impact from the COVID-19 pandemic, including the effects of global supply chain disruptions and government stimulus packages, among other factors. Global, industry-wide supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have resulted in shortages in labor, materials and services. Such shortages have resulted in inflationary cost increases for labor, materials and services and could continue to cause costs to increase as well as scarcity of certain products and raw materials. We have experienced drilling and completion cost increases of approximately 10% between 2021 and 2022, and we cannot predict the extent of any future increases. To the extent elevated inflation remains, our operators may experience further cost increases for their operations, including oilfield services, labor costs, and equipment if drilling activity in our operators’ areas of operations increases. Higher oil and natural gas prices may cause the costs of materials and services to continue to rise. We cannot predict any future trends in the rate of inflation and a significant increase in inflation, to the extent we are unable to recover higher costs through higher oil and natural gas prices and revenues, would negatively impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our derivatives activities could adversely affect our profitability, cash flow, results of operations and financial condition.
To achieve more predictable cash flows and reduce our exposure to adverse fluctuations in the price of oil and natural gas, we enter into derivative instrument contracts for a portion of our expected production, which may include swaps, collars, puts and other structures. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk—Commodity Price Risk.” By using derivative instrument contracts to reduce our exposure to adverse fluctuations in the price of oil and natural gas, we could limit the benefit we would receive from increases in the prices for oil and natural gas, which could have an adverse effect on our profitability, cash flow, results of operations and financial condition. Likewise, to the extent our production is not hedged, we are exposed to declines in oil and natural gas prices, and our derivative arrangements may be inadequate to protect us from continuing and prolonged declines in oil and natural gas prices. In accordance with applicable accounting principles, we are required to record our derivatives at fair market value, and they are included on our balance sheet as assets or liabilities and in our statements of operations as gain (loss) on commodity derivatives, net. Accordingly, our earnings may fluctuate significantly as a result of changes in the fair market value of our derivative instruments. In addition, while intended to mitigate the effects of volatile oil and natural gas prices, our derivatives transactions may limit our potential gains and increase our potential losses if oil and natural gas prices were to rise substantially over the price established by the hedge.
Our actual future production may be significantly higher or lower than we estimate at the time we enter into derivative contracts for such period. If the actual amount of production is higher than we estimate, we will have greater oil and natural gas price exposure than we intended. If the actual amount of production is lower than the
43
notional amount that is subject to our derivative financial instruments, we might be forced to satisfy all or a portion of our derivative transactions without the benefit of the cash flow from our sale of the underlying physical commodity, resulting in a substantial diminution of our liquidity. As a result of these factors, our hedging activities may not be as effective as we intend in reducing the volatility of our cash flows, and in certain circumstances may actually increase the volatility of our cash flows. In addition, such transactions may expose us to the risk of loss in certain circumstances, including instances in which a counterparty to our derivative contracts is unable to satisfy its obligations under the contracts; our production is less than expected; or there is a widening of price Differentials between delivery points for our production and the delivery point assumed in the derivative arrangement. Disruptions in the financial markets could lead to sudden decreases in a counterparty’s liquidity, which could make it unable to perform under the terms of the contracts, and we may not be able to realize the benefit of the contracts. We are unable to predict sudden changes in a counterparty’s creditworthiness or ability to perform. Even if we do accurately predict sudden changes, our ability to negate the risk may be limited depending upon market conditions.
Asset retirement costs may be difficult to predict and may be substantial. Unplanned costs could divert resources from other projects.
We are responsible for costs associated with plugging, abandoning and reclaiming wells, pipelines and other facilities that we use for production of oil and natural gas reserves. Abandonment and reclamation of these facilities and the costs associated therewith is often referred to as “asset retirement.” We accrue a liability for asset retirement costs associated with our wells, but have not established any cash reserve account for these potential costs in respect of any of our properties. It may be difficult for us to predict such asset retirement costs. If asset retirement is required before economic depletion of our properties or if our estimates of the costs of asset retirement exceed the value of the reserves remaining at any particular time to cover such asset retirement costs, we may have to draw on funds from other sources to satisfy such costs, which may be substantial. The use of other funds to satisfy such asset retirement costs could impair our ability to dedicate our capital to other areas of our business.
We depend on computer and telecommunications systems, and failures in our systems or cyber security threats, attacks or other disruptions could significantly disrupt our business operations.
We have entered into agreements with third parties for hardware, software, telecommunications and other information technology services in connection with our business. In addition, we have developed or may develop proprietary software systems, management techniques and other information technologies incorporating software licensed from third parties. It is possible that we, or these third parties, could incur interruptions from cyber security attacks, computer viruses or malware, or that third-party service providers could cause a breach of our data. We believe that we have positive relations with our related vendors and maintain adequate anti-virus and malware software and controls; however, any interruptions to our arrangements with third parties for our computing and communications infrastructure or any other interruptions to, or breaches of, our information systems could lead to data corruption, communication interruption, loss of sensitive or confidential information or otherwise significantly disrupt our business operations. Although we utilize various procedures and controls to monitor these threats and mitigate our exposure to such threats, there can be no assurance that these procedures and controls will be sufficient in preventing security threats from materializing. Furthermore, various third-party resources that we rely on, directly or indirectly, in the operation of our business (such as pipelines and other infrastructure) could suffer interruptions or breaches from cyber-attacks or similar events that are entirely outside our control, and any such events could significantly disrupt our business operations and/or have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. To our knowledge we have not experienced any material losses relating to cyber-attacks; however, there can be no assurance that we will not suffer material losses in the future.
In addition, our operators face various security threats, including cyber security threats to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or to render data or systems unusable, threats to the security of their facilities and infrastructure or third-party facilities and infrastructure, such as processing plants and pipelines, and threats from terrorist acts. If any of these security breaches were to occur, they could lead to losses of sensitive information, critical infrastructure or capabilities essential to operations and could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows. The U.S. government has issued warnings that U.S. energy assets may be the future targets of terrorist organizations. These developments subject operations on our oil and natural gas properties to increased risks. Any future terrorist attack at our operators’ facilities, or those of their purchasers or vendors, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and operations.
44
Fuel conservation measures and related governmental initiatives, technological advances and negative shift in market perception towards the oil and natural gas industry could reduce demand for oil and natural gas.
Fuel conservation measures, alternative fuel requirements, increasing consumer demand for alternatives to oil and natural gas, technological advances in fuel economy and energy generation devices, and the increased competitiveness of alternative energy sources could reduce demand for oil and natural gas. Additionally, the increased competitiveness of alternative energy sources (such as wind, solar, geothermal, tidal, fuel cells and biofuels) could reduce demand for oil and natural gas and, therefore, our revenues.
Our business could also be impacted by governmental initiatives to encourage the conservation of energy or the use of alternative energy sources. For example, in November 2021, the Biden Administration released “The Long-Term Strategy of the United States: Pathways to Net-Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2050,” which establishes a roadmap to net zero emissions in the United States by 2050 through, among other things, improving energy efficiency; decarbonizing energy sources via electricity, hydrogen, and sustainable biofuels; and reducing non-CO2 GHG emissions, such as methane and nitrous oxide. In addition, in August 2022, Congress passed, and President Biden signed, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 includes a variety of clean-energy tax credits and establishes a program designed to reduce methane emissions from oil and gas operations. These initiatives or similar state or federal initiatives to reduce energy consumption or encourage a shift away from fossil fuels could reduce demand for hydrocarbons and have a material adverse effect on our earnings, cash flows and financial condition.
Additionally, certain segments of the investor community have recently expressed negative sentiment towards investing in the oil and natural gas industry. Recent equity returns in the sector versus other industry sectors have led to lower oil and natural gas representation in certain key equity market indices. Some investors, including certain pension funds, university endowments and family foundations, have stated policies to reduce or eliminate their investments in the oil and natural gas sector based on social and environmental considerations. Furthermore, certain other stakeholders have pressured commercial and investment banks to stop funding oil and natural gas projects. With the continued volatility in oil and natural gas prices, and the possibility that interest rates will continue to rise in the near term, increasing the cost of borrowing, certain investors have emphasized capital efficiency and free cash flow from earnings as key drivers for energy companies, especially shale producers. This may also result in a reduction of available capital funding for potential development projects, further impacting our future financial results.
The impact of the changing demand for oil and natural gas services and products, together with a change in investor sentiment, may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Furthermore, if we are unable to achieve the desired level of capital efficiency or free cash flow within the timeframe expected by the market, our stock price may be adversely affected.
Increased attention to ESG matters may impact our business.
Increasing attention to climate change, increasing societal expectations on companies to address climate change, increasing investor and societal expectations regarding voluntary ESG disclosures, and increasing consumer demand for alternatives to oil and natural gas may result in increased costs, reduced demand for our products, reduced profits, increased investigations and litigation, and negative impacts on our access to capital markets. Increasing attention to climate change and any related negative public perception regarding our industry, for example, may result in demand shifts for natural gas and oil products, increased litigation risk, and increased regulatory, legislative and judicial scrutiny, which may, in turn, lead to new state and federal safety and environmental laws, regulations, guidelines and enforcement interpretations.
In addition, organizations that provide information to investors on corporate governance and related matters have developed ratings processes for evaluating companies on their approach to ESG matters. Such ratings are used by some investors to inform their investment and voting decisions. Unfavorable ESG ratings and recent activism directed at shifting funding away from companies with energy-related assets could lead to increased negative investor sentiment toward us and our industry and to the diversion of investment to other industries, which could have a negative impact on our stock price and our access to and costs of capital. Also, institutional lenders may, of their own accord, elect not to provide funding for fossil fuel energy companies based on climate change related concerns, which could affect our access to capital for potential growth projects.
45
Risks Relating to Our Indebtedness
Any significant reduction in the borrowing base under our New Revolving Credit Facility may negatively impact our liquidity and could adversely affect our business and financial results.
Availability under our New Revolving Credit Facility is expected to be subject to a borrowing base, with scheduled semiannual and other elective borrowing base redeterminations based upon, among other things, projected revenues from, and asset values of, the oil and natural gas properties securing the New Revolving Credit Facility. As a result of these borrowing base redeterminations, the lenders under the New Revolving Credit Facility are expected to be able to unilaterally determine and adjust the borrowing base and the borrowings permitted to be outstanding under our New Revolving Credit Facility. Reductions in estimates of our producing oil and natural gas reserves could result in a reduction of our borrowing base thereunder. The same could also arise from other factors, including but not limited to lower commodity prices or production; operating difficulties; changes in oil and natural gas reserve engineering; increased operating and/or capital costs; lending requirements or regulations; or other factors affecting our lenders’ ability or willingness to lend (including factors that may be unrelated to our company). Any significant reduction in our borrowing base could result in a default under current and/or future debt instruments, negatively impact our liquidity and our ability to fund our operations and, as a result, could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations and cash flow. Further, if the outstanding borrowings under our New Revolving Credit Facility were to exceed the borrowing base as a result of any such redetermination, we could be required to repay the excess. If we do not have sufficient funds and we are otherwise unable to arrange new financing, we may have to sell significant assets or take other actions. Any such sale or other actions could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial results.
Our New Revolving Credit Facility and other agreements governing indebtedness may contain operating and financial restrictions that may restrict our business and financing activities.
Our New Revolving Credit Facility and any future indebtedness we incur may contain a number of restrictive covenants that will impose operating and financial restrictions on us, including restrictions on our ability to, among other things: declare or pay any dividend or make any other distributions on, purchase or redeem our equity interests; make loans or certain investments; make certain acquisitions; incur or guarantee additional indebtedness or issue certain types of equity securities; incur liens; transfer or sell assets; create subsidiaries; consolidate, merge or transfer all or substantially all of our assets; and engage in transactions with our affiliates. For a description of the covenants limiting our ability to pay dividends and distributions, see “—Our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is restricted by applicable laws and regulations and may be limited by requirements under our New Revolving Credit Facility.” In addition, we expect the New Revolving Credit Facility to require us to maintain compliance with certain financial covenants and other covenants. As a result of these anticipated covenants, we could be limited in the manner in which we conduct our business, and we may be unable to engage in favorable business activities or finance future operations or capital needs.
Our ability to comply with some of the anticipated covenants and restrictions may be affected by events beyond our control. If market or other economic conditions deteriorate, our ability to comply with these covenants may be impaired. A failure to comply with the covenants, ratios or tests in our New Revolving Credit Facility or any other indebtedness could result in an event of default under our New Revolving Credit Facility, which, if not cured or waived, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. If an event of default under our New Revolving Credit Facility occurs and remains uncured, the lenders thereunder would not be required to lend any additional amounts to us and could elect to declare all borrowings outstanding, together with accrued and unpaid interest and fees, to be immediately due and payable. If the payment of debt were accelerated, cash flows from our operations may be insufficient to repay such debt in full and our stockholders could experience a partial or total loss of their investment. We anticipate that our New Revolving Credit Facility will contain customary events of default, including the occurrence of a change in control.
An event of default or an acceleration under our New Revolving Credit Facility could result in an event of default and an acceleration under other existing or future indebtedness. Conversely, an event of default or an acceleration under any other existing or future indebtedness could result in an event of default and an acceleration under our New Revolving Credit Facility. In addition, we expect that our obligations under the New Revolving Credit Facility will be collateralized by perfected liens and security interests on substantially all of our assets and if we default thereunder the lenders could seek to foreclose on our assets.
46
We may not be able to generate enough cash flow to meet our debt obligations or to pay dividends to our stockholders.
Our earnings and cash flow may vary significantly from year to year due to the cyclical nature of our industry. As a result, the amount of debt that we can service in some periods may not be appropriate for us in other periods. Additionally, our future cash flow may be insufficient to meet our debt obligations and commitments, or to permit us to pay dividends to our stockholders. Any insufficiency could negatively impact our business. A range of economic, competitive, business and industry factors will affect our future financial performance, and, as a result, our ability to generate cash flow from operations and to pay our debt or dividends. Many of these factors, such as oil and natural gas prices, economic and financial conditions in our industry and the global economy or competitive initiatives of our competitors, are beyond our control.
If we do not generate enough cash flow from operations to satisfy our debt obligations, we may have to undertake alternative financing plans, such as refinancing or restructuring our debt; selling assets; reducing or delaying capital investments; or seeking to raise additional capital. However, we cannot assure you that undertaking alternative financing plans, if necessary, would allow us to meet our debt obligations or pay dividends. Our inability to generate sufficient cash flow to satisfy our debt obligations or pay dividends, or to obtain alternative financing, could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is restricted by applicable laws and regulations and may be limited by requirements under our New Revolving Credit Facility.
Holders of our common stock are only entitled to receive such cash dividends as our Board, in its sole discretion, may declare out of funds legally available for such payments. We made cash distributions to our members totaling $25.0 million during 2019, $0.0 during 2020, $12.0 million during 2021, and $42.0 million during the nine months ended August 31, 2022. We do not currently intend to pay additional cash distributions pending completion of the Spin-Off. We cannot assure you that we will pay dividends following the Spin-Off. Our Board may change the timing and amount of any future dividend payments or eliminate the payment of future dividends to our stockholders at its discretion, without notice to our stockholders. Any future determination relating to our dividend policy will be dependent on a variety of factors, including our financial condition, earnings, legal requirements, our general liquidity needs, and other factors that our Board deems relevant. Our ability to declare and pay dividends to our stockholders is subject to certain laws, regulations, and policies, including minimum capital requirements and, as a Delaware corporation, we are subject to certain restrictions on dividends under the DGCL. Under the DGCL, our Board may not authorize payment of a dividend unless it is either paid out of our surplus, as calculated in accordance with the DGCL, or if we do not have a surplus, it is paid out of our net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend is declared and/or the preceding fiscal year. Finally, our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is limited by covenants in the Existing Revolving Credit Facility and may be limited by covenants in any debt agreements that we may enter into in the future, including our New Revolving Credit Facility. Under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility, we are permitted to make cash distributions without limit to our equity holders if (i) no event of default or borrowing base deficiency (i.e., outstanding debt (including loans and letters of credit) exceeds the borrowing base) then exists or would result from such distribution, and (ii) after giving effect to such distribution, (a) our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 70% of the least of (the following collectively referred to as “Commitments”): (1) $500 million, (2) our then-effective borrowing base, and (3) the then-effective aggregate amount of our lenders’ commitments and (b) as of the date of such distribution, the ratio of our total funded debt to EBITDAX (as defined in our Existing Revolving Credit Facility) for the four fiscal quarters ending on the last day of the fiscal quarter most recently ended for which financial statements are available (the “EBITDAX Ratio”) does not exceed 1.50 to 1.00. If our total outstanding credit usage is between 70% and 80% of the Commitments, we may make distributions if, in addition to the foregoing conditions, (i) our EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 2.25 to 1.00, (ii) we have free cash flow, as defined under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, greater than $0 and (iii) we have delivered a certificate to our lenders attesting to the foregoing. Under the New Revolving Credit Facility, we anticipate we will be permitted to make cash distributions without limit to our equity holders if (i) no event of default or borrowing base deficiency (i.e., outstanding debt (including loans and letters of credit) exceeds the borrowing base) then exists or would result from such distribution and (ii) after giving effect to such distribution, (a) our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 80% of the least of (the following collectively referred to as “Commitments”): (1) $500 million, (2) our then-effective borrowing base, and (3) the then-effective aggregate amount of our lenders’ commitments and (b) as of the date of such distribution, the EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 1.50 to 1.00. If our EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 2.25 to 1.00, and if our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 80% of the Commitments, we may also make distributions if our free cash flow (as defined under the New
47
Revolving Credit Facility) is greater than $0 and we have delivered a certificate to our lenders attesting to the foregoing. We expect that the dividend restrictions under our New Revolving Credit Facility will be no less favorable than those in our Existing Revolving Credit Facility. The summaries above do not purport to be complete and you are encouraged to read the Existing Revolving Credit Facility and the form of the New Revolving Credit Facility, which are filed as exhibits to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is part, for greater detail with respect to these provisions. As a consequence of these various limitations and restrictions, we may not be able to make, or may have to reduce or eliminate at any time, the payment of dividends on our common stock. If as a result, we are unable to pay dividends, investors may be forced to rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize a return on their investment. Any change in the level of our dividends or the suspension of the payment thereof could have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common stock.
Variable rate indebtedness could subject us to interest rate risk, which could cause our debt service obligations to increase significantly.
Our New Revolving Credit Facility may use SOFR as a reference rate for borrowings. Borrowings under our New Revolving Credit Facility may bear interest at variable rates and expose us to interest rate risk. If interest rates increase and we are unable to effectively hedge our interest rate risk, our debt service obligations on the variable rate indebtedness would increase even if the amount borrowed remained the same, and our net income and cash available for servicing our indebtedness would decrease.
We may be adversely affected by developments in the SOFR market, changes in the methods by which SOFR is determined or the use of alternative reference rates.
In 2017, the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority announced that it intended to phase out LIBOR, and in 2021, it announced that all LIBOR settings will either cease to be provided by any administrator or no longer be representative immediately after December 31, 2021, in the case of one-week and two-month U.S. Dollar settings, and immediately after June 30, 2023, in the case of the remaining U.S. Dollar settings. The Federal Reserve also has advised banks to cease entering into new contracts that use U.S. Dollar LIBOR as a reference rate. The Alternative Refinance Rate Committee, a committee convened by the Federal Reserve that includes major market participants, has identified SOFR, a new index calculated by short-term repurchase agreements, backed by U.S. Treasury securities, as its preferred alternative rate for LIBOR in the U.S. Although SOFR appears to be the preferred replacement rate for U.S. Dollar LIBOR, it is unclear if other benchmarks may emerge. The consequences of these developments cannot be entirely predicted, and there can be no assurance that they will not result in financial market disruptions, significant increases in benchmark interest rates, substantially higher financing costs or a shortage of available debt financing, any of which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial position and results of operations, and our ability to pay dividends on our common stock.
Our business plan requires the expenditure of significant capital, which we may be unable to obtain on favorable terms or at all.
Our acquisition and development activities require substantial capital expenditures. Historically, we have funded our capital expenditures through a combination of cash flow from operations, borrowings under our credit facilities and equity issuances. Cash reserves, cash from operations and borrowings under our New Revolving Credit Facility may not be sufficient to fund our continuing operations and business plan and goals. We may require additional capital and we may be unable to obtain such capital if and when required. If our access to capital were limited due to numerous factors, which could include a decrease in operating cash flow due to lower oil and natural gas prices or decreased production or deterioration of the credit and capital markets, we would have a reduced ability to develop our properties, replace our reserves and pursue our business plan and goals. We may not be able to incur additional debt under our New Revolving Credit Facility, issue debt or equity, engage in asset sales or access other methods of financing on acceptable terms or at all. If the amount of capital we are able to raise from financing activities, together with our cash from operations, is not sufficient to satisfy our capital requirements, we may not be able to implement our business plan and may be required to scale back our operations, sell assets at unattractive prices or obtain financing on unattractive terms, any of which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
48
Risks Relating to Legal and Regulatory Matters
The current presidential administration, acting through the executive branch and/or in coordination with Congress, already has ordered or proposed, and could enact additional rules and regulations that restrict our ability to acquire federal leases in the future and/or impose more onerous permitting and other costly environmental, health and safety requirements.
We are affected by the adoption of laws, regulations and policy directives that, for economic, environmental protection or other policy reasons, could curtail exploration and development drilling for oil and natural gas. For example, in January 2021, President Biden signed an Executive Order directing the DOI to temporarily pause new oil and natural gas leases on federal lands and waters pending completion of a comprehensive review of the federal government’s existing oil and natural gas leasing and permitting program. In June 2021, a federal district court enjoined the DOI from implementing the pause and leasing resumed, although litigation over the leasing pause remains ongoing. As a result, it is difficult to predict if and when such areas may be made available for future exploration activities. In addition, in November 2021, the EPA proposed a new rule that would impose more stringent methane emissions standards for new and modified sources in the oil and natural gas industry, and to regulate existing sources in the oil and natural gas industry for the first time. A supplemental proposed rule, which may expand or modify the current proposed rule, and final rule are expected by the end of 2022. For existing sources, the current proposed rule would require each state to incorporate the emission guidelines proposed by the EPA or to adopt their own standards that achieve the same degree of emissions limitations. Further, in September 2021, President Biden publicly announced the Global Methane Pledge, an international pact that aims to reduce global methane emissions to at least 30% below 2020 levels by 2030. These efforts, among others, are intended to support the current administration’s stated goal of addressing climate change. Potential actions of a Democratic-controlled Congress include imposing more restrictive laws and regulations pertaining to permitting, limitations on GHG emissions, increased requirements for financial assurance and bonding for decommissioning liabilities, and carbon taxes. For example, in August 2022, Congress passed, and President Biden signed, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 includes a variety of clean-energy tax credits and establishes a program designed to reduce methane emissions from certain oil and natural gas facilities. Any of these administrative or Congressional actions could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations by restricting the lands available for development and/or access to permits required for such development, or by imposing additional and costly environmental, health and safety requirements.
Certain U.S. federal income tax deductions currently available with respect to oil and natural gas development may be eliminated as a result of future legislation.
From time to time, legislation has been proposed that would, if enacted into law, make significant changes to U.S. tax laws, including certain key U.S. federal income tax provisions currently available to oil and natural gas companies. Such legislative changes have included, but not been limited to, (1) the repeal of the percentage depletion allowance for natural gas and oil properties, (2) the elimination of current deductions for intangible drilling and development costs, and (3) an extension of the amortization period for certain geological and geophysical expenditures. Although these provisions were largely unchanged in the most recent federal tax legislation, certain of these changes were considered for inclusion in the proposed “Build Back Better Act” and Congress could consider, and could include, some or all of these proposals as part of future tax reform legislation. Moreover, other more general features of any additional tax reform legislation, including changes to cost recovery rules, may be developed that also would change the taxation of oil and natural gas companies. It is unclear whether these or similar changes will be enacted in future legislation and, if enacted, how soon any such changes could take effect. The passage of any legislation as a result of these proposals or any similar changes in U.S. federal income tax laws could eliminate or postpone certain tax deductions that currently are available with respect to oil and natural gas development or increase costs, and any such changes could have an adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
Our business involves the selling and shipping by rail of oil, which involves risks of derailment, accidents and liabilities associated with cleanup and damages, as well as potential regulatory changes that may adversely impact our business, financial condition or results of operations.
A portion of our oil production is transported to market centers by rail. Derailments in North America of trains transporting oil have caused various regulatory agencies and industry organizations, as well as federal, state and municipal governments, to focus attention on transportation by rail of flammable liquids. Any changes to existing
49
laws and regulations, or promulgation of new laws and regulations, including any voluntary measures by the rail industry, that result in new requirements for the design, construction or operation of tank cars used to transport oil could increase our costs of doing business and limit our ability to transport and sell our oil at favorable prices at market centers throughout the United States, the consequences of which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. In addition, any derailment of oil involving oil that we have sold or are shipping may result in claims being brought against us that may involve significant liabilities.
Our derivative activities expose us to potential regulatory risks.
The FTC, FERC and the CFTC have statutory authority to monitor certain segments of the physical and futures energy commodities markets. These agencies have imposed broad regulations prohibiting fraud and manipulation of such markets. With regard to derivative activities that we undertake with respect to oil, natural gas or other energy commodities, we are required to observe the market-related regulations enforced by these agencies. Failure to comply with such regulations, as interpreted and enforced, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Legislative and regulatory developments could have an adverse effect on our ability to use derivative instruments to reduce the effect of volatile oil and natural gas price, interest rate and other risks associated with our business.
The Dodd-Frank Act contains measures aimed at increasing the transparency and stability of the OTC derivatives market and preventing excessive speculation. On January 14, 2021, the CFTC published a final rule imposing position limits for certain futures and options contracts in various commodities (including oil and gas) and for swaps that are their economic equivalents, though certain types of derivative transactions are exempt from these limits, provided that such derivative transactions satisfy the CFTC’s requirements for certain enumerated “bona fide” derivative transactions. The CFTC also has adopted final rules regarding aggregation of positions, under which a party that controls the trading of, or owns ten percent or more of the equity interests in, another party will have to aggregate the positions of the controlled or owned party with its own positions for purposes of determining compliance with position limits unless an exemption applies. The CFTC’s aggregation rules are now in effect, although CFTC staff has granted relief until August 12, 2022 from various conditions and requirements in the final aggregation rules. These rules may affect both the size of the positions that we may hold and the ability or willingness of counterparties to trade with us, potentially increasing the costs of transactions. Moreover, such changes could materially reduce our access to derivative opportunities, which could adversely affect revenues or cash flow during periods of low oil and natural gas prices.
The CFTC also has designated certain interest rate swaps and credit default swaps for mandatory clearing and the associated rules also will require us, in connection with covered derivative activities, to comply with clearing and trade-execution requirements or to take steps to qualify for an exemption to such requirements. Although we believe we qualify for the end-user exception from the mandatory clearing requirements for swaps entered to mitigate its commercial risks, the application of the mandatory clearing and trade execution requirements to other market participants, such as swap dealers, may change the cost and availability of the swaps that we use. If our swaps do not qualify for the commercial end-user exception, or if the cost of entering into uncleared swaps becomes prohibitive, we may be required to clear such transactions. The ultimate effect of these rules and any additional regulations on our business is uncertain.
The full impact of the Dodd-Frank Act and related regulatory requirements on our business will not be known until the regulations are fully implemented and the market for derivatives contracts has adjusted. In addition, it is possible that the current administration could expand regulation of the OTC derivatives market and the entities that participate in that market through either the Dodd-Frank Act or the enactment of new legislation. Regulations issued under the Dodd-Frank Act (including any further regulations implemented thereunder) and any new legislation also may require certain counterparties to our derivative instruments to spin off some of their derivative activities to a separate entity, which may not be as creditworthy as the current counterparty. Such legislation and regulations could significantly increase the cost of derivative contracts (including from swap recordkeeping and reporting requirements and through requirements to post collateral which could adversely affect our available liquidity), materially alter the terms of derivative contracts, reduce the availability of derivatives to protect against risks we encounter, reduce our ability to monetize or restructure our existing derivative contracts, and increase our exposure to less creditworthy counterparties. We maintain an active hedging program related to oil and natural gas price risks. Such legislation and regulations could reduce trading positions and the market-making activities of our counterparties. If we reduce
50
our use of derivatives as a result of legislation and regulations or any resulting changes in the derivatives markets, our results of operations may become more volatile and our cash flows may be less predictable, which could adversely affect our ability to plan for and fund capital expenditures or to make payments on our debt obligations. Finally, the Dodd-Frank Act was intended, in part, to reduce the volatility of oil and natural gas prices, which some legislators attributed to speculative trading in derivatives and commodity instruments related to oil and natural gas. Our revenues could therefore be adversely affected if a consequence of the legislation and regulations is to lower oil and natural gas prices. Any of these consequences could have a material adverse effect on our business, our financial condition, and our results of operations.
Our business is subject to complex federal, state, and local laws, as well as other laws and regulations that could adversely affect the cost, manner or feasibility of doing business.
Our operational interests, as operated by our third-party operators, are regulated extensively at the federal, state, tribal and local levels. Environmental and other governmental laws and regulations have increased the costs to plan, design, drill, install, operate and abandon oil and natural gas wells. Under these laws and regulations, our company (either directly or indirectly through our operators) could also be liable for personal injuries, property and natural resource damage and other damages. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in the suspension or termination of our business and subject us to administrative, civil and criminal penalties. Moreover, public interest in environmental protection has increased in recent years, and environmental organizations have opposed, with some success, certain drilling projects.
Part of the regulatory environment in which we do business includes, in some cases, legal requirements for obtaining environmental assessments, environmental impact studies and/or plans of development before commencing drilling and production activities. In addition, our activities are subject to the regulations regarding conservation practices and protection of correlative rights. These regulations affect our business and limit the quantity of natural gas we may produce and sell. A major risk inherent in the drilling plans in which we participate is the need for our operators to obtain drilling permits from state and local authorities. Delays in obtaining regulatory approvals or drilling permits, the failure to obtain a drilling permit for a well or the receipt of a permit with unreasonable conditions or costs could have a material adverse effect on the development of our properties. Additionally, the oil and natural gas regulatory environment could change in ways that might substantially increase the financial and managerial costs of compliance with these laws and regulations and, consequently, adversely affect our profitability. At this time, we cannot predict the effect of this increase on our results of operations. Furthermore, we may be put at a competitive disadvantage to larger companies in our industry that can spread these additional costs over a greater number of wells and larger operating staff.
Failure to comply with federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations could result in substantial penalties and adversely affect our business.
All phases of the oil and natural gas business can present environmental risks and hazards and are subject to a variety of federal, state and municipal laws and regulations. Environmental laws and regulations, among other things, restrict and prohibit spills, releases or emissions of various substances produced in association with oil and natural gas operations, and require that wells and facility sites be operated, maintained, abandoned and reclaimed to the satisfaction of applicable regulatory authorities. There is risk of incurring significant environmental costs and liabilities as a result of the handling of petroleum hydrocarbons and wastes, air emissions and wastewater discharges related to our business, and historical operations and waste disposal practices. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in the assessment of administrative, civil and criminal penalties, loss of our leases, incurrence of investigatory or remedial obligations and the imposition of injunctive relief.
Environmental legislation and regulations are evolving in a manner we expect may result in stricter standards and enforcement, larger fines and liability and potentially increased capital expenditures and operating costs. The discharge of oil, natural gas or other pollutants into the air, soil or water may give rise to liabilities to governments and third parties and may require us to incur costs to remedy such discharge, regardless of whether we were responsible for the release or contamination and regardless of whether our operators met previous standards in the industry at the time they were conducted. In addition, claims for damages to persons, property or natural resources may result from environmental and other impacts of operations on our properties. The application of new or more stringent environmental laws and regulations to our business may cause us to curtail production or increase the costs of our production or development activities.
51
Federal and state legislative and regulatory initiatives relating to hydraulic fracturing could result in increased costs and additional operating restrictions or delays.
Hydraulic fracturing involves the injection of water, sand and chemicals under pressure into formations to fracture the surrounding rock and stimulate production. Hydraulic fracturing is used extensively by our third-party operators. The hydraulic fracturing process is typically regulated by state oil and natural gas commissions. However, in April 2012, the EPA issued regulations specifically applicable to the oil and natural gas industry that require operators to significantly reduce VOC emissions from gas wells that are hydraulically fractured through the use of “green completions” to capture natural gas that would otherwise escape into the air. The EPA issued additional regulations in 2016 targeting methane and VOC emissions from new, modified and reconstructed oil and natural gas wells that have been hydraulically fractured. Then in November 2021, the EPA proposed rules to further reduce methane and VOC emissions from new and existing sources in the oil and natural gas sector. From time to time, there have also been various other proposals to regulate hydraulic fracturing at the federal level. Any federal or state legislative or regulatory changes with respect to hydraulic fracturing could cause us to incur substantial compliance costs or result in operational delays, and the consequences of any failure to comply by us or our third-party operators could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, in response to concerns relating to recent seismic events near underground disposal wells used for the disposal by injection of flowback and produced water or certain other oilfield fluids resulting from oil and natural gas activities (so-called “induced seismicity”), regulators in some states have imposed, or are considering imposing, additional requirements in the permitting of produced water disposal wells or otherwise to assess any relationship between seismicity and the use of such wells. States may, from time to time, develop and implement plans directing certain wells where seismic incidents have occurred to restrict or suspend disposal well operations. These developments could result in additional regulation and restrictions on the use of injection wells by our operators to dispose of flowback and produced water and certain other oilfield fluids. Increased regulation and attention given to induced seismicity also could lead to greater opposition to, and litigation concerning, oil and natural gas activities utilizing injection wells for waste disposal. Until such pending or threatened legislation or regulations are finalized and implemented, it is not possible to estimate their impact on our business.
Any of the above risks could impair our ability to manage our business and have a material adverse effect on our operations, cash flows and financial position.
The adoption of climate change legislation or regulations restricting emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases could result in increased operating costs and reduced demand for the oil and natural gas we produce.
The oil and natural gas industry is affected from time to time in varying degrees by political developments and a wide range of federal, tribal, state and local statutes, rules, orders and regulations that may, in turn, affect the operations and costs of the companies engaged in the oil and natural gas industry. In response to findings that emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other GHGs present an endangerment to public health and the environment, the EPA has adopted regulations under existing provisions of the CAA that, among other things, require preconstruction and operating permits for GHG emissions from certain large stationary sources that already emit conventional pollutants above a certain threshold. In addition, the EPA has adopted rules requiring the monitoring and reporting of GHG emissions from specified onshore and offshore oil and natural gas production sources in the United States on an annual basis, which may include operations on the Properties. Additional GHG regulation could also result from the agreement crafted during the United Nations climate change conference in Paris, France in December 2015 (the “Paris Agreement”). Under the Paris Agreement, the United States committed to reducing its GHG emissions by 26-28% by the year 2025 as compared with 2005 levels. Moreover, in November 2021, at the U.N. Framework Convention on Climate Change 26th Conference of the Parties, the United States and the European Union advanced a Global Methane Pledge to reduce global methane emissions at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030, which over 100 countries have signed. Congress has from time to time considered legislation to reduce emissions of GHGs. Most recently, in August 2022, Congress passed, and President Biden signed, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. The Inflation Reduction Act establishes a program designed to reduce methane emissions from certain oil and natural gas facilities, which includes a charge on methane emissions above certain thresholds.
In addition, a number of state and regional efforts have emerged that are aimed at tracking or reducing GHG emissions by means of cap and trade programs. These programs typically require major sources of GHG emissions to acquire and surrender emission allowances in return for emitting those GHGs.
52
Although it is not possible at this time to predict how legislation or new regulations that may be adopted to address GHG emissions would impact us or our operators, any future laws and regulations imposing reporting obligations on, or limiting emissions of GHGs from, operators’ equipment and operations could require them to incur costs to reduce emissions of GHGs associated with their operations. For example, although EPA regulations implementing the methane charge requirements associated with the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 have not yet been developed, the future implementation of these requirements could result in direct costs for our operators based on methane emissions above set thresholds or require capital expenditure by our operators to reduce their emissions. In addition, substantial limitations on GHG emissions could adversely affect demand for the oil and natural gas produced from our oil and natural gas properties. Restrictions on emissions of methane or carbon dioxide, such as restrictions on venting and flaring of natural gas that may be imposed at the federal or state level, as well as federal, state and local climate change initiatives, such as increased energy efficiency standards or mandates for renewable energy sources, could adversely affect the oil and natural gas industry, and, at this time, it is not possible to accurately estimate how potential future laws or regulations addressing GHG emissions would impact oil and natural gas assets. Finally, it should be noted that climate changes may have significant physical effects, such as increased frequency and severity of storms, freezes, floods, drought, hurricanes and other climatic events; if any of these effects were to occur, they could have an adverse effect on us or our operators.
In addition, spurred by increasing concerns regarding climate change, the oil and natural gas industry faces growing demand for corporate transparency and a demonstrated commitment to sustainability goals. ESG goals and programs, which may include extralegal targets related to environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and corporate governance, have become an increasing focus of investors and stakeholders across the industry, and companies without robust ESG programs may find access to capital and investors more challenging in the future. Further, in March 2022, the SEC issued a proposed rule that would require public companies to disclose certain climate-related information, including climate-related risks, impacts, oversight and management, financial statement metrics and emissions, targets, goals and plans. While the proposed rule is not yet effective and is expected to be subject to a lengthy comment process, compliance with the proposed rule as drafted could result in increased legal, accounting and financial compliance costs, make some activities more difficult, time-consuming and costly, and place strain on our personnel, systems and resources.
Regulatory requirements to reduce gas flaring and to further restrict emissions could have an adverse effect on our operations.
Wells in the Williston Basin of North Dakota, where we own significant oil and natural gas properties, produce natural gas as well as oil. Constraints in third party natural gas gathering and processing systems in certain areas have resulted in some of that natural gas being flared instead of gathered, processed and sold. In 2014, the NDI Commission, North Dakota’s chief energy regulator, adopted a policy to reduce the volume of natural gas flared from oil wells in the Williston Basin. The NDI Commission requires operators to develop gas capture plans that describe how much natural gas is expected to be produced, how it will be delivered to a processor and where it will be processed. Production caps or penalties may be imposed on certain wells that cannot meet the capture goals. It is possible that other states in which we operate, including Montana, will require gas capture plans or otherwise institute new regulatory requirements in the future to reduce flaring.
Gas capture requirements and other regulatory requirements, in North Dakota or our other locations, could increase our operators’ operational costs and restrict production on our oil and natural gas properties, which could materially and adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. If our interpretation of the applicable regulations is incorrect, or if we receive a non-appealable order to pay royalty on past and future flared volumes in North Dakota, such royalty payments could materially and adversely affect our financial condition and cash flows.
53
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT CONCERNING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Information Statement and other materials we have filed or will file with the SEC contain or incorporate by reference statements which, to the extent they are not statements of historical or present fact, constitute “forward-looking statements” under the securities laws. From time to time, oral or written forward-looking statements may also be included in other information released to the public. These forward-looking statements are intended to provide management’s current expectations or plans for our future operating and financial performance, based on assumptions currently believed to be valid. Forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of words such as “believe,” “expect,” “expectations,” “plans,” “strategy,” “prospects,” “estimate,” “project,” “target,” “anticipate,” “will,” “should,” “see,” “guidance,” “outlook,” “confident” and other words of similar meaning in connection with a discussion of future operating or financial performance or the Spin-Off. Forward-looking statements may include, among other things, statements relating to future earnings, cash flow, results of operations, uses of cash, tax rates and other measures of financial performance or potential future plans, strategies or transactions of Vitesse, the Spin-Off, including the expected timing of completion of the Spin-Off and estimated costs associated with the Spin-Off, and other statements that are not historical facts. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future results and conditions, but rather are subject to numerous assumptions, risks, and uncertainties that may cause actual future results to be materially different from those contemplated, projected, estimated, or budgeted. Such assumptions, risks, uncertainties and other factors include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ∎ | the timing and extent of changes in oil and natural gas prices; |
| ∎ | our ability to successfully implement our business plan; |
| ∎ | the pace of our operators’ drilling and completion activity on our properties, including in connection with refrac campaigns and extended length three-mile lateral infills; |
| ∎ | our operators’ ability to complete projects on time and on budget; |
| ∎ | uncertainties about estimates of reserves, identification of drilling locations and the ability to add reserves in the future; |
| ∎ | our ability to complete acquisitions; |
| ∎ | actions taken by third-party operators, processors, transporters and gatherers; |
| ∎ | natural disasters, adverse weather conditions, war (such as the ongoing military conflict in Ukraine), financial or political instability, casualty losses and other matters beyond our control; |
| ∎ | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the measures implemented to contain it; |
| ∎ | changes in general economic conditions; |
| ∎ | our ability to achieve the benefits that we expect to achieve as an independent publicly traded company; |
| ∎ | the qualification of the Distribution and certain related transactions as tax-free under the Code; |
| ∎ | inflation; |
| ∎ | infrastructure constraints and related factors affecting our properties; |
| ∎ | competitive conditions in our industry; |
| ∎ | the effects of existing and future laws and governmental regulations; |
| ∎ | the availability and price of oil and natural gas to the consumer compared to the price of alternative and competing fuels; |
| ∎ | operating hazards and other risks incidental to gathering, storing and transporting oil and natural gas; |
| ∎ | restrictions in our New Revolving Credit Facility; |
| ∎ | interest rates; |
| ∎ | the effects of ongoing or future litigation; |
| ∎ | cyber-related risks; |
| ∎ | changes in insurance markets impacting costs and the level and types of coverage available; |
| ∎ | climate change and the physical and financial risks associated with fluctuating regional and global weather conditions or patterns; |
| ∎ | energy efficiency and technology trends; |
54
| ∎ | competition from the same and alternative energy sources; |
| ∎ | changes in the availability and cost of capital; |
| ∎ | large customer defaults; |
| ∎ | labor relations; and |
| ∎ | changes in tax status. |
There can be no assurance that the Spin-Off or any other transactions described above will in fact be consummated in the manner described or at all. The above list of factors is not exhaustive. For additional information on identifying factors that may cause actual results to vary materially from those stated in forward-looking statements, see the discussion under the section entitled “Risk Factors.” Any forward-looking statements made by us in this Information Statement speak only as of the date on which they are made. We are under no obligation to, and expressly disclaim any obligation to, update or alter our forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, subsequent events or otherwise.
55
On July 19, 2022, Jefferies announced plans for the complete legal and structural separation of Vitesse from Jefferies.
At the time of the Spin-Off, Vitesse will hold substantially all of those businesses or investments of Jefferies that acquire, develop, manage and monetize non-operated oil and natural gas working, royalty and mineral interests in the United States, primarily in the Bakken and Three Forks formations in the Williston Basin in North Dakota and Montana.
To effect the separation, first, Jefferies and Jefferies Capital Partners, among others, will undertake the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions described below under the section entitled “—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions.” Jefferies will subsequently distribute all of Vitesse’s outstanding common stock held by Jefferies, representing 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock immediately prior to the Distribution, to Jefferies shareholders, and Vitesse will become an independent, publicly traded company. After the Distribution, Jefferies will not own any shares of our common stock.
Prior to completion of the Spin-Off, we intend to enter into a Separation and Distribution Agreement and a Tax Matters Agreement with Jefferies related to the Spin-Off. These agreements will govern the relationship between Jefferies and us up to and after completion of the Spin-Off. See the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions” for more detail. No approval of Jefferies shareholders is required in connection with the Spin-Off, and Jefferies shareholders will not have any appraisal rights in connection with the Spin-Off.
Completion of the Spin-Off is subject to the satisfaction, or the waiver by the Jefferies Board, of a number of conditions. If the Jefferies Board waives any condition prior to the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, and the result of such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will file an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement accordingly. In the event that the Jefferies Board waives a condition after this Registration Statement becomes effective and such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will communicate such change to Jefferies shareholders by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change.
In addition, Jefferies has the right not to complete the Spin-Off if, at any time, the Jefferies Board determines, in its sole and absolute discretion, that the Spin-Off is not in the best interests of Jefferies or its shareholders, or is otherwise not advisable. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, Jefferies and Vitesse will have incurred significant costs related to the Spin-Off, including fees for consultants, financial and legal advisors, accountants and auditors, that will not be recouped. Total one-time transaction costs associated with the Spin-Off are preliminarily estimated to range from $14 million to $16 million if the Spin-Off is completed. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, the one-time transaction costs will generally be limited to the transaction costs incurred for services rendered as of the date the Spin-Off is abandoned, which will be less than the ranges noted above. Our management has devoted significant time to manage the Spin-Off process, which has decreased the time they have had to manage the business of Vitesse. See the section entitled “—Conditions to the Spin-Off” for more detail.
In 2017, Jefferies announced that its primary business initiative would be to become a focused financial services company with clear drive and direction, concentrating on investment banking and capital markets and alternative asset management. Since that time, Jefferies has strategically and opportunistically monetized a significant portion of its merchant banking portfolio and realigned its internal structure to achieve those goals. Jefferies has continued to make clear that it would continue to liquidate its merchant banking portfolio, with the intention of selling the businesses and investments comprising the portfolio to third parties, distributing the businesses and investments comprising the portfolio to shareholders or transferring the balance of the businesses and investments comprising the portfolio to its asset management reportable segment. As they contemplated the Spin-Off, the Jefferies Board and management determined that positioning Vitesse as an independent publicly traded company would further
56
Jefferies’ long-term goals and enhance stockholder value. In reaching the decision to pursue the Spin-Off, Jefferies considered a range of potential structural alternatives for Vitesse Energy, including a sale or merger of Vitesse and/or its assets to or with third parties, and management recommended the Spin-Off as the most attractive alternative for enhancing shareholder value.
As a result of this evaluation, the Jefferies Board determined that proceeding with the Spin-Off would be in the best interests of Jefferies and its shareholders. The Jefferies Board considered several potential benefits of this approach, including:
| ∎ | Strategic goals. Following the Spin-Off, Jefferies will be one step closer to its previously announced goal of liquidating its merchant banking portfolio and focusing solely on financial services. |
| ∎ | Maximizing shareholder value and choice. Jefferies shareholders should benefit from both the benefits to be reaped as Jefferies further reduces its merchant banking portfolio and further dedicates its management’s focus on financial services and from the potential for value enhancement that might be achieved in a stand-alone, publicly traded Vitesse. Jefferies believes the Spin-Off will help unlock the value in Vitesse that may not be clear to investors while it remains part of Jefferies. Those investors looking for a pure play company that is focused on creating long-term stockholder value through the profitable acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas assets will be able to invest directly in Vitesse, which should result in greater alignment between the interests of each company’s stockholder base and the characteristics of its respective business, capital structure and financial results. |
| ∎ | Separate capital structures and allocation flexibility. The Spin-Off will enable each of Jefferies and Vitesse to leverage its distinct profile and cash flow characteristics to optimize its capital structure and capital allocation strategy. The Spin-Off will permit each company to allocate its financial resources to meet the unique needs of its own businesses, which will allow each company to intensify its focus on its distinct strategic priorities and individual business risk and return profiles. |
The Jefferies Board also considered several potentially negative factors in evaluating the Spin-Off, including:
| ∎ | Risk of failure to achieve the anticipated benefits of the Spin-Off. Jefferies and Vitesse may not achieve the anticipated benefits of the Spin-Off for a variety of reasons, including, among others: the Spin-Off will require significant amounts of management’s time and effort, which may divert our management’s attention from operating each company’s business; there may be dis-synergy costs related to the Spin-Off; and following the Spin-Off, Vitesse may be more susceptible to certain economic and market fluctuations and other adverse events than if Vitesse were still a part of Jefferies. For more information on the specific risks to Vitesse of the failure to achieve the anticipated benefits of the Spin-Off, see the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to the Spin-Off—We may be unable to achieve some or all of the benefits that we expect to achieve from the Spin-Off, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.” |
| ∎ | Disruptions and costs related to the Spin-Off. The actions required to separate Vitesse from Jefferies could disrupt both Jefferies’ and Vitesse’s operations. |
| ∎ | Uncertainty regarding share prices. The effect of the Distribution on the trading prices of Jefferies’ and Vitesse’s common stock cannot be predicted, and there is no guarantee that the combined market value of the shares of Vitesse common stock to be distributed per share of Jefferies common stock in the Distribution and Jefferies common stock following the Distribution will be less than, equal to or greater than the market value of the shares of Jefferies common stock prior to the Distribution. Furthermore, there is the risk of volatility in each company’s stock price following the Distribution due to sales by certain shareholders whose investment objectives may not be met by each company’s common stock, and it may take time for each company to attract its optimal stockholder base. |
Notwithstanding these potentially negative factors, the anticipated effects of which are not reasonably determinable, and considering the factors discussed above, the Jefferies Board determined that the Spin-Off provided the best opportunity to achieve the above benefits and enhance stockholder value. Neither Jefferies nor Vitesse can assure you that, following the Spin-Off, any of the benefits described above or otherwise will be realized to the extent anticipated or at all. For additional information, see the section entitled “Risk Factors.”
57
To effect the Spin-Off, we expect the following transactions, among others, to be consummated prior to the completion of the Spin-Off:
| ∎ | Vitesse was incorporated on August 5, 2022; |
| ∎ | 3B Energy will transfer all of its Vitesse Energy equity interests to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for prior loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to 3B Energy; |
| ∎ | Each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will transfer all of their vested Vitesse Energy MIUs to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for prior loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree; |
| ∎ | Vitesse Energy Finance and the remaining holders of vested Vitesse Energy MIUs will transfer all of their Vitesse Energy equity interests to Vitesse in exchange for newly issued shares of Vitesse common stock; |
| ∎ | Jefferies Capital Partners and Gerrity Bakken will transfer all of their Vitesse Oil equity interests to Vitesse in exchange for newly issued shares of Vitesse common stock; |
| ∎ | Through a series of distributions, all of the Vitesse common stock held by Vitesse Energy Finance will ultimately become held directly by Jefferies; |
| ∎ | Through a series of distributions, a portion of the Vitesse common stock held by Jefferies Capital Partners will ultimately become held directly by Jefferies; and |
| ∎ | Vitesse will enter into the New Revolving Credit Facility, which will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, and will use a portion of the proceeds from borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility to repay in full and terminate the Vitesse Oil Revolving Credit Facility. Borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility will remain outstanding as borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility. |
Pursuant to the above described transactions, Jefferies will directly hold approximately 94.37% of the total issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately prior to the Distribution. For more information, see “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons.”
When and How You Will Receive Vitesse Shares
Jefferies will distribute to its shareholders, as a pro rata dividend, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding as of the close of business on December 27, 2022, one share of our common stock.
Prior to the Distribution, Jefferies will deliver all of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock held by Jefferies to the distribution agent. AST will serve as distribution agent in connection with the Distribution and as transfer agent and registrar for our common stock.
If you own Jefferies common stock as of the close of business on December 27, 2022, the shares of our common stock that you are entitled to receive in the Distribution will be issued to your account as follows:
| ∎ | Registered shareholders. If you own your shares of Jefferies common stock directly through Jefferies’ transfer agent, AST, you are a registered shareholder. In this case, the distribution agent will credit the whole shares of our common stock you receive in the Distribution by way of direct registration in book-entry form to a new account with our transfer agent. Registration in book-entry form refers to a method of recording share ownership where no physical stock certificates are issued to shareholders, as is the case in the Distribution. You will be able to access information regarding your book-entry account holding the Vitesse shares at www.astfinancial.com or by calling (800) 937-5449. |
| ∎ | Commencing on or shortly after the Distribution Date, the distribution agent will mail to you an account statement that indicates the number of whole shares of our common stock that have been registered in book-entry form in your name. We expect it will take the distribution agent up to five business days after the Distribution Date to complete the distribution of the shares of our common stock and mail statements of holding to all registered shareholders. |
| ∎ | “Street name” or beneficial shareholders. If you own your shares of Jefferies common stock beneficially through a bank, broker or other nominee, such bank, broker or other nominee holds the shares in “street name” and records your ownership on its books. If you own your shares of Jefferies common stock through a bank, broker or other nominee, your bank, broker or other nominee will credit your account with the whole shares of our common stock that you receive in the Distribution on or shortly after the Distribution Date. We |
58
| encourage you to contact your bank, broker or other nominee if you have any questions concerning the mechanics of having shares held in “street name.” |
If you sell any of your shares of Jefferies common stock on or before the Distribution Date, the buyer of those shares may in some circumstances be entitled to receive the shares of our common stock to be distributed in respect of the Jefferies shares you sold. For more information, see the section entitled “—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date.”
We are not asking Jefferies shareholders to take any action in connection with the Spin-Off. No shareholder approval of the Spin-Off is required. We are not asking you for a proxy and request that you not send us a proxy. We are also not asking you to make any payment or surrender or exchange any of your shares of Jefferies common stock for shares of our common stock. The number of outstanding shares of Jefferies common stock will not change as a result of the Spin-Off.
Number of Shares You Will Receive
On the Distribution Date, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock you owned as of the Record Date, you will receive one share of our common stock.
Treatment of Fractional Shares
The distribution agent will not distribute any fractional shares of our common stock in connection with the Spin-Off. Instead, the distribution agent will aggregate all fractional shares into whole shares and sell the whole shares in the open market at prevailing market prices on behalf of Jefferies shareholders entitled to receive a fractional share. The distribution agent will then distribute the aggregate cash proceeds of the sales, net of brokerage fees, transfer taxes and other costs, pro rata to these holders (net of any required withholding for taxes applicable to each holder). The distribution agent will, in its sole discretion, without any influence by Jefferies or us, determine when, how, through which broker-dealer and at what price to sell the whole shares. The distribution agent is not, and any broker-dealer used by the distribution agent will not be, an affiliate of either Jefferies or us.
The distribution agent will send to each registered holder of Jefferies common stock entitled to a fractional share a check in the cash amount deliverable in lieu of that holder’s fractional share as soon as practicable following the Distribution Date. We expect the distribution agent to take up to five business days after the Distribution Date to complete the distribution of cash in lieu of fractional shares to Jefferies shareholders. If you hold your shares through a bank, broker or other nominee, your bank, broker or nominee will receive, on your behalf, your pro rata share of the aggregate net cash proceeds of the sales. No interest will be paid on any cash you receive in lieu of a fractional share. The cash you receive in lieu of a fractional share will generally be taxable to you for U.S. federal income tax purposes. For more information, see the section below entitled “—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.”
Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off
Consequences to Holders of Jefferies Common Stock
The following is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to holders of Jefferies common stock in connection with the Distribution. This summary is based on the Code, the Treasury Regulations promulgated under the Code and judicial and administrative interpretations of those laws, in each case as in effect and available as of the date of this Information Statement and all of which are subject to change at any time, possibly with retroactive effect. Any such change could affect the tax consequences described below.
This summary is limited to U.S. Holders of Jefferies common stock that hold their Jefferies common stock as a capital asset. For purposes of this summary, a “U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of Jefferies common stock that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| ∎ | an individual who is a citizen or a resident of the U.S.; |
| ∎ | a corporation, or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, created or organized under the laws of the U.S. or any state thereof or the District of Columbia; |
| ∎ | an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| ∎ | a trust if (1) a court within the U.S. is able to exercise primary jurisdiction over its administration and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all of its substantial decisions or (2) in the case of a trust |
59
| that was treated as a domestic trust under law in effect before 1997, a valid election is in place under applicable Treasury Regulations. |
This summary does not discuss all tax considerations that may be relevant to shareholders in light of their particular circumstances, nor does it address the consequences to shareholders subject to special treatment under the U.S. federal income tax laws, such as:
| ∎ | dealers or traders in securities or currencies; |
| ∎ | tax-exempt entities; |
| ∎ | banks, financial institutions or insurance companies; |
| ∎ | real estate investment trusts, regulated investment companies or grantor trusts; |
| ∎ | persons who acquired Jefferies common stock pursuant to the exercise of employee stock options or otherwise as compensation; |
| ∎ | shareholders who own, or are deemed to own, 10% or more, by voting power or value, of Jefferies common stock; |
| ∎ | shareholders owning Jefferies common stock as part of a position in a straddle or as part of a hedging, conversion or other risk reduction transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes; |
| ∎ | certain former citizens or long-term residents of the United States; |
| ∎ | shareholders who are subject to the alternative minimum tax; |
| ∎ | persons who own Jefferies common stock through partnerships or other pass-through entities; or |
| ∎ | persons who hold Jefferies common stock through a tax-qualified retirement plan. |
This summary does not address any U.S. state or local or foreign tax consequences or any estate, gift or other non-income tax consequences.
If a partnership, or any other entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, holds Jefferies common stock, the tax treatment of a partner in that partnership will generally depend on the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. Such a partner or partnership is urged to consult its own tax advisor as to its tax consequences.
YOU ARE URGED TO CONSULT YOUR OWN TAX ADVISOR WITH RESPECT TO THE U.S. FEDERAL, STATE AND LOCAL AND FOREIGN TAX CONSEQUENCES OF THE DISTRIBUTION.
The consummation of the Distribution and certain related transactions is conditioned on Jefferies’ receipt of the IRS Ruling to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code. Jefferies has received the IRS Ruling. The IRS Ruling relies on certain assumptions and representations made, and information submitted, in connection with the ruling request. If any of the assumptions, representations or information are incorrect or not otherwise satisfied, Jefferies may not be able to rely on the IRS Ruling
In addition, the consummation of the Distribution and certain related transactions is also conditioned upon Jefferies’ receipt of a written opinion from Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP substantially to the effect that, based on the IRS Ruling and their analysis of the issues not addressed in the IRS Ruling, the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code. The opinion will rely on (a) customary representations and covenants made by Jefferies and Vitesse and (b) specified assumptions, including an assumption regarding the completion of the Distribution and certain related transactions in the manner contemplated by the transaction agreements. In addition, the ability to provide the tax opinion will depend on the absence of changes in existing facts or law between the date of this Information Statement and the date of the Distribution. If any of those representations, covenants or assumptions is inaccurate, Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP may not be able to provide the tax opinion or the tax consequences of the Distribution could differ from those described below. An opinion of tax counsel neither binds the IRS nor precludes the IRS or the courts from adopting a contrary position.
60
Accordingly, notwithstanding the IRS Ruling and the tax opinion, there can be no assurance that the IRS will not assert a position contrary to one or more of the conclusions set forth herein and if the IRS prevails in such challenge, the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, to Jefferies, Vitesse and the holders of Jefferies common stock could be materially different from, and worse than, the U.S. federal income tax consequences described below.
On the basis that the Distribution and related transactions will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code, subject to the qualifications and limitations set forth herein (including the discussion below relating to the receipt of cash in lieu of fractional shares), for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| ∎ | no gain or loss should be recognized by, or be includible in the income of, a U.S. Holder as a result of the Distribution, except with respect to any cash received in lieu of fractional shares; |
| ∎ | the aggregate tax basis of the Jefferies common stock and our common stock held by each U.S. Holder immediately after the Distribution should be the same as the aggregate tax basis of the Jefferies common stock held by the U.S. Holder immediately before the Distribution, allocated between the Jefferies common stock and our common stock in proportion to their relative fair market values on the date of the Distribution (subject to reduction upon the deemed sale of any fractional shares, as described below); and |
| ∎ | the holding period of our common stock received by each U.S. Holder should include the holding period of its Jefferies common stock, provided that such Jefferies common stock is held as a capital asset on the date of the Distribution. |
U.S. Holders that have acquired different blocks of Jefferies common stock at different times or at different prices are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding the allocation of their aggregate adjusted tax basis among, and the holding period of, shares of our common stock distributed with respect to such blocks of Jefferies common stock.
If a U.S. Holder receives cash in lieu of a fractional share of common stock as part of the Distribution, the U.S. Holder will be treated as though it first received a distribution of the fractional share in the Distribution and then sold it for the amount of cash actually received. Provided the fractional share is considered to be held as a capital asset on the date of the Distribution, the U.S. Holder will generally recognize capital gain or loss measured by the difference between the cash received for such fractional share and the U.S. Holder’s tax basis in that fractional share, as determined above. Such capital gain or loss will be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the Jefferies common stock is more than one year on the date of the Distribution.
If it were determined that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, did not qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution did not qualify as a distribution to which Section 355 applies, the above consequences would not apply, and U.S. Holders could be subject to tax. In this case, each U.S. Holder who receives our common stock in the Distribution would generally be treated as receiving a distribution in an amount equal to the fair market value of our common stock received, which would generally result in:
| ∎ | a taxable dividend to the U.S. Holder to the extent of that U.S. Holder’s pro rata share of Jefferies’ current and accumulated earnings and profits; |
| ∎ | a reduction in the U.S. Holder’s basis (but not below zero) in Jefferies common stock to the extent the amount received exceeds the shareholder’s share of Jefferies’ earnings and profits; and |
| ∎ | a taxable gain from the exchange of Jefferies common stock to the extent the amount received exceeds the sum of the U.S. Holder’s share of Jefferies’ earnings and profits and the U.S. Holder’s basis in its Jefferies common stock. |
Treasury Regulations generally require any Jefferies shareholder that owns at least five percent of the total outstanding stock of Jefferies (by vote or value) to attach to its U.S. federal income tax return for the year in which the Distribution occurs a detailed statement setting forth certain information relating to the tax-free nature of the Distribution. Jefferies and/or Vitesse will provide the appropriate information to each holder upon request, and each such holder is required to retain permanent records of this information.
61
Backup Withholding and Information Statement
Payments of cash in lieu of a fractional share of our common stock may, under certain circumstances, be subject to “backup withholding,” unless a U.S. Holder provides proof of an applicable exemption or a correct taxpayer identification number, and otherwise complies with the requirements of the backup withholding rules. Corporations will generally be exempt from backup withholding, but may be required to provide a certification to establish their entitlement to the exemption. Backup withholding is not an additional tax, and it may be refunded or credited against a holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability if the required information is timely supplied to the IRS.
Treasury Regulations require each Jefferies shareholder that, immediately before the Distribution, owned 5% or more (by vote or value) of the total outstanding stock of Jefferies to attach to such shareholder’s U.S. federal income tax return for the year in which the Distribution occurs a statement setting forth certain information related to the Distribution.
Consequences to Jefferies
If the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, were not to qualify as a tax-free transaction under Sections 368(a)(1)(D) and 355 of the Code, Jefferies would recognize a material amount of taxable gain for U.S. federal income tax purposes on the Distribution and/or certain related transactions, which could result in a material additional U.S. federal and state income tax liability to Jefferies.
Even if the Distribution were otherwise to qualify as a tax-free transaction under Sections 368(a)(1)(D) and 355 of the Code, the Distribution would be taxable to Jefferies (but not to Jefferies stockholders) pursuant to Section 355(e) of the Code if there were a 50% or greater change in ownership of either Jefferies or Vitesse, directly or indirectly, as part of a plan or series of related transactions that included the Distribution. For this purpose, any acquisitions of Jefferies or Vitesse common stock within the period beginning two years before the Distribution and ending two years after the Distribution are presumed to be part of such a plan, although Jefferies or Vitesse may be able to rebut that presumption. If the IRS were to determine that other acquisitions of Jefferies common stock or Vitesse common stock, either before or after the Distribution, were part of a plan or series of related transactions that included the Distribution, such determination could result in the recognition of a material amount of taxable gain for U.S. federal income tax purposes by Jefferies under Section 355(e) of the Code. In connection with the IRS Ruling and the tax opinion, Jefferies and Vitesse (to their knowledge) have represented (or will represent at or prior to the closing of the Distribution) that the Distribution is not part of any such plan or series of related transactions.
In general, under the Tax Matters Agreement, we will be required to indemnify Jefferies against any tax consequences arising as a result of certain prohibited actions by us or our respective subsidiaries. See “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.” If the Distribution were to be a taxable transaction to Jefferies, the liability for payment of such tax by Jefferies, or by us under the Tax Matters Agreement, could have a material adverse effect on Jefferies or us, as the case may be.
After the Spin-Off, we will be an independent, publicly traded company. Immediately following the Spin-Off, we expect to have approximately 1,200 holders of record of shares of our common stock and approximately 28,202,019 shares of our common stock outstanding, based on (1) the number of Jefferies shareholders and shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on December 16, 2022 and (2) the expected number of Vitesse stockholders (other than Jefferies) and the expected number shares of Vitesse common stock outstanding (other than shares held by Jefferies) immediately prior to the Distribution as a result of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. The actual number of shares of our common stock Jefferies will distribute in the Spin-Off will depend on the actual number of shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on the Record Date, which will reflect any issuance of new shares in respect of settlements or exercises of outstanding equity-based awards pursuant to Jefferies’ equity plans, on or prior to the Record Date. The Spin-Off will not affect the number of outstanding shares of Jefferies common stock or any rights of Jefferies shareholders, although we expect the trading price of shares of Jefferies common stock immediately following the Distribution to be lower than immediately prior to the Distribution because the trading price of Jefferies common stock will no longer reflect the value of Vitesse Energy. Furthermore, until the market has fully analyzed the value of Jefferies without Vitesse Energy, the trading price of shares of Jefferies common stock may fluctuate and result in a higher volatility in stock price.
62
Before our separation from Jefferies, we intend to enter into a Separation and Distribution Agreement and a Tax Matters Agreement with Jefferies related to the Spin-Off. These agreements will govern the relationship between Jefferies and us up to and after completion of the Spin-Off. We describe these arrangements in greater detail under the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.”
Listing and Trading of our Common Stock
We are an indirect majority owned subsidiary of Jefferies. Immediately prior to the Distribution, Jefferies will hold approximately 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock. Accordingly, no public market for our common stock currently exists, although a “when-issued” market in our common stock may develop prior to the Distribution. For an explanation of a “when-issued” market, see the section below entitled “—Trading Prior to the Distribution Date.” We intend to list our shares of common stock on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “VTS.” Following the Spin-Off, Jefferies common stock will continue to trade on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “JEF.”
Neither we nor Jefferies can assure you as to the trading price of Jefferies common stock or our common stock after the Spin-Off, or as to whether the combined trading prices of our common stock and the Jefferies common stock after the Spin-Off will be less than, equal to or greater than the trading prices of Jefferies common stock prior to the Spin-Off. The trading price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly following the Spin- Off and result in a higher volatility in stock price. For more detail, see the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Common Stock.”
The shares of our common stock distributed to Jefferies shareholders will be freely transferable, except for shares received by individuals who are our affiliates. Individuals who may be considered our affiliates after the Spin-Off include individuals who control, are controlled by or are under common control with us, as those terms generally are interpreted for U.S. federal securities law purposes. These individuals may include some or all of our directors and executives. Individuals who are our affiliates will be permitted to sell their shares of our common stock only pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act or an exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act, such as those afforded by Section 4(a)(1) of the Securities Act or Rule 144 thereunder.
Trading Prior to the Distribution Date
We expect a “when-issued” market in our common stock to develop on the third trading day before the Distribution Date and continue up to and including the Distribution Date. “When-issued” trading refers to a sale or purchase made conditionally on or before the Distribution Date because the securities of the spun-off entity have not yet been distributed. If you own shares of Jefferies common stock at the close of business on the Record Date, you will be entitled to receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. You may trade this entitlement to receive shares of our common stock, without the shares of Jefferies common stock you own, on the “when-issued” market. We expect “when-issued” trades of our common stock to settle within two trading days after the Distribution Date. On the first trading day following the Distribution Date, we expect that “when-issued” trading of our common stock will end and “regular-way” trading will begin.
We also anticipate that, on the third trading day before the Distribution Date and continuing up to and including the Distribution Date, there will be two markets in Jefferies common stock: a “regular-way” market and an “ex-distribution” market. Shares of Jefferies common stock that trade on the “regular-way” market will trade with an entitlement to receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. Shares that trade on the “ex-distribution” market will trade without an entitlement to receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. Therefore, if you sell shares of Jefferies common stock in the “regular-way” market up to and including the Distribution Date, you will be selling your right to receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. However, if you own shares of Jefferies common stock at the close of business on the Record Date and sell those shares on the “ex-distribution” market up to and including the Distribution Date, you will still receive the shares of our common stock that you would otherwise be entitled to receive in the Distribution.
Following the Distribution Date, we expect shares of our common stock to be listed on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “VTS.” If “when-issued” trading occurs, the listing for our common stock is expected to be under a ticker symbol different from our “regular-way” ticker symbol. We will announce our “when-issued” ticker symbol when and if it becomes available. If the Spin-Off does not occur, all “when-issued” trading will be null and void.
63
Holders of Jefferies convertible preferred stock will not be entitled to participate in the Distribution unless they convert such securities into Jefferies common stock prior to the Record Date. Jefferies expects that, as a result of the Distribution, the conversion price of its convertible preferred stock will be adjusted in accordance with Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation.
We expect that the Separation will be effective on the Distribution Date, provided that the following conditions shall have been satisfied or waived by Jefferies:
| ∎ | the Jefferies Board shall have authorized and approved the applicable Pre-Spin-Off Transactions (as described in the section entitled “—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions”) and Distribution and not withdrawn such authorization and approval, and shall have declared the dividend of our common stock to Jefferies shareholders; |
| ∎ | the ancillary agreements contemplated by the Separation and Distribution Agreement, including the Tax Matters Agreement, shall have been executed by each party to those agreements; |
| ∎ | our common stock shall have been accepted for listing on the NYSE or another national securities exchange approved by Jefferies, subject to official notice of issuance; |
| ∎ | the SEC shall have declared effective our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, under the Exchange Act, and no stop order suspending the effectiveness of the Registration Statement shall be in effect and no proceedings for that purpose shall be pending before or threatened by the SEC; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have received the IRS Ruling, substantially to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have received the written opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, which shall remain in full force and effect, subject to the limitations specified therein and the accuracy of and compliance with certain representations, warranties and covenants, to the effect that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, will qualify as a tax-free “reorganization” for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and the Distribution will qualify as a tax-free distribution within the meaning of Section 355 of the Code; |
| ∎ | the Jefferies Board shall have received one or more opinions (which have not been withdrawn or adversely modified) in customary form from one or more nationally recognized valuation, appraisal or accounting firms or investment banks as to the solvency and financial viability of Jefferies prior to the Spin-Off and each of Jefferies and Vitesse after the consummation of the Spin-Off; |
| ∎ | the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions shall have been completed; |
| ∎ | no order, injunction or decree issued by any governmental authority of competent jurisdiction or other legal restraint or prohibition preventing consummation of the Distribution shall be in effect, and no other event outside the control of Jefferies shall have occurred or failed to occur that prevents the consummation of the Distribution; |
| ∎ | no other events or developments shall have occurred prior to the Distribution Date that, in the judgment of the Jefferies Board, would result in the Distribution having a material adverse effect on Jefferies or its shareholders; |
| ∎ | prior to the Distribution Date, notice of Internet availability of this Information Statement or this Information Statement shall have been mailed to the holders of Jefferies common stock as of the Record Date; |
| ∎ | Jefferies shall have duly elected the individuals listed as members of our post-Distribution Board in this Information Statement, and such individuals shall be the members of our Board, immediately after the Distribution; provided, however, that to the extent required by any law or requirement of the NYSE or any other national securities exchange, as applicable, the existing directors shall appoint one independent director prior to the date on which “when-issued” trading of our common stock begins and this independent |
64
| director shall begin his or her term prior to the Distribution and shall serve on our Audit Committee, Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee and Compensation Committee; and |
| ∎ | immediately prior to the Distribution Date, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws, each in substantially the form filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, shall be in effect. |
The fulfillment of the above conditions will not create any obligation on Jefferies’ part to complete the Spin-Off. We are not aware of any material U.S. federal, foreign or state regulatory requirements with which we must comply, other than SEC rules and regulations, or any material approvals that we must obtain, other than the approval for listing of our common stock and the SEC’s declaration of the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, in connection with the Distribution.
The IRS Ruling and the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP are intended to provide support that the intended tax-free treatment of the Distribution will be respected. Were Jefferies to waive the requirement of receipt of either or both of the IRS Ruling or the opinion of Morgan, Lewis & Bockius LLP, there would be less comfort that the intended tax-free treatment of the Distribution will be respected. Such waiver would be deemed to be material to Jefferies shareholders, and therefore Jefferies would communicate such change to shareholders by, depending on the timing of the waiver, either filing an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement or filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change. Were the Distribution treated as a taxable transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (1) Jefferies generally would be subject to tax as if it sold the Vitesse common stock in a transaction taxable to Jefferies, which could result in a material tax liability, and (2) Jefferies shareholders who are U.S. Holders generally would be, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, treated as receiving a distribution in an amount equal to the fair market value of our common stock received, which could result in a material tax liability for those U.S. Holders. For more information, see the section entitled “—Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Spin-Off.”
If the Jefferies Board waives any condition prior to the effectiveness of the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, and the result of such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will file an amendment to the Registration Statement to revise the disclosure in this Information Statement accordingly. In the event that the Jefferies Board waives a condition after this Registration Statement becomes effective and such waiver is material to Jefferies shareholders, Jefferies will communicate such change to Jefferies shareholders by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K describing the change.
In addition, Jefferies has the right not to complete the Spin-Off if, at any time, the Jefferies Board determines, in its sole and absolute discretion, that the Spin-Off is not in the best interests of Jefferies or its shareholders, or is otherwise not advisable. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, Jefferies and Vitesse will have incurred significant costs related to the Spin-Off, including fees for consultants, financial and legal advisors, accountants and auditors, that will not be recouped. Total one-time transaction costs associated with the Spin-Off are preliminarily estimated to range from $14 million to $16 million if the Spin-Off is completed. If the Spin-Off is not completed for any reason, the one-time transaction costs will generally be limited to the transaction costs incurred for services rendered as of the date the Spin-Off is abandoned, which will be less than the ranges noted above. Our management has devoted significant time to manage the Spin-Off process, which has decreased the time they have had to manage the business of Vitesse.
Reasons for Furnishing This Information Statement
We are furnishing this Information Statement solely to provide information to Jefferies shareholders who will receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution. You should not construe this Information Statement as an inducement or encouragement to buy, hold or sell any of our securities or any securities of Jefferies. We believe that the information contained in this Information Statement is accurate as of the date set forth on the cover. Changes to the information contained in this Information Statement may occur after that date, and neither we nor Jefferies undertakes any obligation to update the information except in the normal course of our and Jefferies’ public disclosure obligations and practices.
65
We expect that, following the Distribution, Vitesse will initially pay quarterly cash dividends and dividend equivalents totaling approximately $66.0 million per fiscal year. Notwithstanding this current expectation regarding our dividend policy, the timing, declaration, amount of and payment of any dividends will be within the discretion of our Board and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our operating subsidiaries, covenants associated with certain of our debt service obligations, legal requirements or limitations, industry practice, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board. Moreover, if as expected we determine to initially pay a dividend following the Distribution, there can be no assurance that we will continue to pay dividends in the same amounts or at all thereafter. We pay dividends out of distributable cash flow, which we define as Adjusted EBITDA less interest expense and cash taxes. During the year ended November 30, 2021, we generated Adjusted EBITDA of $102.3 million, and during the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, we generated Adjusted EBITDA of $158.0 million. Historically, we have used our distributable cash flow for multiple purposes, including capital expenditures (which includes acquisitions), repayment of debt and payment of distributions. Due to our strategy to grow oil and natural gas production levels during 2021 and 2022, we incurred levels of capital expenditures above a maintenance level. Given the amount of these capital expenditures and the discretionary amount of debt repaid, we would not have been able to pay a $66.0 million distribution during the year ended November 30, 2021. However, going forward, we expect to prioritize the dividend while sustaining production through maintenance capital expenditures. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil paid cash distributions totaling $59.0 million. We have not adopted, and do not currently expect to adopt, a separate written dividend policy to reflect our Board’s policy. For a description of the covenants limiting our ability to pay dividends, see the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Common Stock—Our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is restricted by applicable laws and regulations and may be limited by requirements under our New Revolving Credit Facility.” The covenants under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility have not limited our ability to pay distributions in the amounts declared by our Board.
66
The following table sets forth the cash and capitalization of Vitesse Energy as of August 31, 2022 (1) on a historical basis and (2) on a pro forma basis to give effect to the Spin-Off, as if it occurred on August 31, 2022. The information below is not necessarily indicative of what our capitalization would have been had the Spin-Off been completed as of August 31, 2022. In addition, it is not indicative of our future capitalization and may not reflect the capitalization or financial condition that would have resulted had we operated as an independent, publicly traded company as of August 31, 2022. You should review the following table in conjunction with the sections entitled “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Statements” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
| AUGUST 31, 2022 | ||||||||
| HISTORICAL | PRO FORMA (1) | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 8,085 | $ | 3,513 | ||||
| Long-term debt: |
||||||||
| Existing Revolving Credit Facility |
66,000 | — | ||||||
| New Revolving Credit Facility (2) |
— | 67,800 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total debt |
66,000 | 67,800 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Equity: |
||||||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value; 95,000,000 shares authorized pro forma; 28,202,019 shares issued and outstanding pro forma (3) |
— | 282 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
— | 546,878 | ||||||
| Members’ equity |
505,345 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total equity |
505,345 | 547,160 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total capitalization |
$ | 571,345 | $ | 614,960 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Reflects combined totals of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil. |
| (2) | Reflects the use the proceeds from the New Revolving Credit Facility to repay in full and terminate the outstanding indebtedness under the Vitesse Oil Revolving Credit Facility. |
| (3) | Represents (i) the expected distribution of approximately 26,614,467 shares of our common stock to holders of Jefferies common stock, based on the number of shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on December 16, 2022, and (ii) the expected number of shares of our common stock outstanding (other than shares held by Jefferies) immediately prior to the Distribution as a result of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. |
67
SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL DATA
The following tables present selected historical financial data as of and for the periods indicated. We derived the summary historical statements of operations data for the years ended November 30, 2021, November 30, 2020 and November 30, 2019, and summary historical balance sheet data as of November 30, 2021 and November 30, 2020, as set forth below, from Vitesse Energy’s Audited Consolidated Financial Statements. We derived the summary historical statements of operations data for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and August 31, 2021, and summary historical balance sheet data as of August 31, 2022, as set forth below, from Vitesse Energy’s Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. The summary historical balance sheet data as of August 31, 2021 and November 30, 2019, as set forth below, are derived from Vitesse Energy’s unaudited condensed consolidated balance sheet as of August 31, 2021 and audited consolidated balance sheet as of November 30, 2019, respectively, which are not included in this Information Statement.
The selected historical financial data presented below should be read in conjunction with the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements and the accompanying notes thereto, the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and the section entitled “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Statements.” The selected historical financial data does not necessarily reflect what our results of operations and financial position would have been if we had operated as an independent, publicly traded company during the periods presented. In addition, our historical financial data does not reflect changes that we expect to experience in the future as a result of our separation from Jefferies or changes related to the Spin-Off. Accordingly, the historical results should not be relied upon as an indicator of our future performance.
| NINE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31, |
YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2022 | 2021 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 179,177 | $ | 106,986 | $ | 151,838 | $ | 91,542 | $ | 157,112 | ||||||||||
| Natural gas |
45,510 | 17,496 | 33,340 | 5,688 | 14,189 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total revenue |
224,687 | 124,482 | 185,178 | 97,230 | 171,301 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Production |
35,179 | 32,591 | 43,910 | 41,731 | 42,875 | |||||||||||||||
| Production taxes |
17,828 | 10,082 | 14,535 | 9,173 | 15,572 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
11,496 | 7,704 | 10,581 | 9,196 | 7,957 | |||||||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
46,310 | 45,476 | 60,846 | 58,307 | 64,721 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties |
— | — | — | 13,200 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
7,539 | 814 | 1,409 | (544 | ) | 3,295 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
118,352 | 96,667 | 131,281 | 131,063 | 134,420 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) |
106,335 | 27,815 | 53,897 | (33,833 | ) | 36,881 | ||||||||||||||
| Other (Expense) Income |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodity derivative (loss) gain, net (1) |
(47,990 | ) | (32,934 | ) | (32,590 | ) | 29,633 | 3,778 | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(2,847 | ) | (2,517 | ) | (3,207 | ) | (4,679 | ) | (4,825 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other income |
10 | 11 | 14 | 22 | 54 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total other (expense) income |
(50,827 | ) | (35,440 | ) | (35,783 | ) | 24,976 | (993 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 55,508 | $ | (7,625 | ) | $ | 18,114 | $ | (8,857 | ) | $ | 35,888 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
68
| NINE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31, |
YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2022 | 2021 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Selected Cash Flow and Other Financial Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 55,508 | $ | (7,625 | ) | $ | 18,114 | $ | (8,857 | ) | $ | 35,888 | ||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
46,310 | 45,476 | 60,846 | 58,307 | 64,721 | |||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss (gain) on derivative instruments |
7,852 | 26,263 | 18,687 | (2,472 | ) | 280 | ||||||||||||||
| Other non-cash items |
7,863 | 1,017 | 1,685 | 13,018 | 2,985 | |||||||||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities |
(9,116 | ) | (7,329 | ) | (12,361 | ) | 16,313 | (2,680 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 108,417 | $ | 57,802 | $ | 86,971 | $ | 76,309 | $ | 101,194 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
$ | 57,317 | $ | 31,504 | $ | 43,317 | $ | 70,808 | $ | 104,367 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| AS OF AUGUST 31, | AS OF NOVEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2022 | 2021 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 8,085 | $ | 4,505 | $ | 2,801 | $ | 1,734 | $ | 1,761 | ||||||||||
| Revenue receivable |
44,737 | 25,889 | 31,959 | 15,999 | 34,662 | |||||||||||||||
| Oil and gas properties, net of accumulated depreciation, depletion, amortization and impairment |
593,400 | 575,632 | 576,496 | 593,958 | 619,029 | |||||||||||||||
| Commodities derivative assets |
— | — | 1,513 | 11,528 | 9,055 | |||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
2,522 | 1,989 | 1,359 | 3,911 | 2,882 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 648,744 | $ | 608,015 | $ | 614,128 | $ | 627,130 | $ | 667,389 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Current liabilities |
47,322 | 31,539 | 32,200 | 22,373 | 48,856 | |||||||||||||||
| Revolving credit facility |
66,000 | 75,000 | 68,000 | 98,500 | 104,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities (2) |
22,691 | 16,628 | 14,705 | 13,784 | 13,857 | |||||||||||||||
| Redeemable management incentive units |
7,386 | 4,266 | 4,831 | 2,665 | 3,044 | |||||||||||||||
| Members’ equity |
505,345 | 480,582 | 494,392 | 489,808 | 497,632 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable units and members’ equity |
$ | 648,744 | $ | 608,015 | $ | 614,128 | $ | 627,130 | $ | 667,389 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Composed of (i) actual cash gains and losses recognized on settled commodity derivative instruments during the period and (ii) unsettled gains and losses based on mark-to-market accounting incurred on commodity derivative instruments outstanding at period end. |
| (2) | Composed of unit-based compensation liability, commodity derivatives liability and asset retirement obligations. |
Non-GAAP Financial Information
We include financial information prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, which we refer to as “GAAP,” as well as the non-GAAP financial measures Net Debt, which we use as a measure of liquidity, and Adjusted EBITDA and PV-10, which we use as measures of our operational performance. Non-GAAP measures, such as Net Debt, Adjusted EBITDA and PV-10, should not be viewed as a supplement to nor a substitute for net income (loss) or any other performance measure calculated in accordance with GAAP or as a measure of our profitability or liquidity. As a result of the adjustments made in calculating Net Debt, Adjusted EBITDA and PV-10, there are significant limitations to using such measures as measures of performance or liquidity, as applicable, including the inability to analyze the effect of certain recurring and non-recurring items that materially affect our net income (loss). Such non-GAAP measures are not necessarily comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies.
69
Reconciliations of Net Debt and Adjusted EBITDA to Most Directly Comparable GAAP Measures
Net Debt is calculated by deducting cash on hand from the amount outstanding on our Existing Revolving Credit Facility as of the balance sheet or measurement date. We believe Net Debt is meaningful to investors because it is frequently used by analysts, investors and other interested parties in our industry to evaluate a company’s debt position in relation to cash relative to its peers and competitors as a point in time measurement relative to other liquidity-based metrics.
Adjusted EBITDA is defined as net income before expenses for interest, income taxes, depletion, depreciation, amortization and accretion, and excludes non-cash gains and losses on unsettled derivative instruments and non-cash unit-based compensation in addition to certain items we consider non-routine in nature, including non-cash oil and natural gas property impairments and material non-recurring general and administrative costs related to the Spin-Off. We believe Adjusted EBITDA is useful to us and external users of our financial statements in understanding our operating results and the ongoing performance of our underlying business because it allows our management and investors to compare our operating performance on a consistent basis across periods and against our peers, since it removes or adjusts for the impact of, among other things, the impact of our capital structure, non-cash gains and losses on unsettled derivative instruments, non-cash unit-based compensation and the non-routine charges noted in the table below. We also use Adjusted EBITDA as a basis for strategic planning and forecasting.
| TWELVE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31, |
YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands except for ratio) | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Revolving Credit Facility |
$ | 66,000 | $ | 68,000 | $ | 98,500 | $ | 104,000 | ||||||||
| Cash |
8,085 | 2,801 | 1,734 | 1,761 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Debt |
$ | 57,915 | $ | 65,199 | $ | 96,766 | $ | 102,239 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 81,248 | $ | 18,114 | $ | (8,857 | ) | $ | 35,888 | |||||||
| Interest expense |
3,537 | 3,207 | 4,679 | 4,825 | ||||||||||||
| Income taxes |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
61,680 | 60,846 | 58,307 | 64,721 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| EBITDA |
146,465 | 82,167 | 54,129 | 105,434 | ||||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
8,135 | 1,409 | (544 | ) | 3,295 | |||||||||||
| Unrealized loss (gain) on derivatives |
277 | 18,687 | (2,473 | ) | 280 | |||||||||||
| Adjustments for non-routine items (1) |
3,130 | — | 13,200 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 158,007 | $ | 102,263 | $ | 64,312 | $ | 109,009 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio |
0.37 | 0.64 | 1.50 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Our Adjusted EBITDA calculation excludes certain items we consider non-routine and non-recurring. In 2020, adjustments for non-routine items were comprised of a $13.2 million impairment charge to our Colorado and Wyoming properties because of the significant decline in oil and natural gas prices as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. During the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, adjustments for non-routine items were composed of a $3.1 million of costs related to the Spin-Off. |
Reconciliation of PV-10 to Standardized Measure
PV-10 is derived from the Standardized Measure, which is the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure for proved reserves calculated using SEC pricing. PV-10 is a computation of the Standardized Measure on a pre-tax basis. PV-10 is equal to the Standardized Measure at the applicable date, before deducting future income taxes, discounted at ten percent. We believe that the presentation of PV-10 is relevant and useful to investors because it presents the discounted future net cash flows attributable to our estimated proved reserves prior to taking into account future income taxes, and it is a useful measure for evaluating the relative monetary significance of our oil and natural gas properties. We use this measure when assessing the potential return on investment related to our oil and natural gas properties. PV-10, however, is not a substitute for the Standardized Measure. PV-10 and the Standardized Measure do not purport to represent the fair value of our oil and natural gas reserves.
70
The table below reconciles the pre-tax PV-10 value of our proved reserves at SEC prices as of November 30, 2021 to the Standardized Measure.
| (in thousands) | YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, 2021 (1) |
|||
| Standardized Measure |
$ | 601,613 | ||
| Future Income Taxes, Discounted at 10% (2) |
— | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Pre-Tax Present Value of Estimated Future Net Revenues (Pre-Tax PV-10) (3) |
$ | 601,613 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| (1) | Discounted future net cash flows are valued as of November 30, 2021 based on average prices of $64.81 per barrel of oil and $3.46 per MMBtu of natural gas. Under SEC guidelines, these prices represent the unweighted average prices per barrel of oil and per MMBtu of natural gas at the beginning of each month in the twelve-month period prior to the end of the reporting period. |
| (2) | Future income taxes for Vitesse as of November 30, 2021 were zero due to our tax status as a pass-through entity. |
| (3) | Vitesse’s PV-10 has historically been computed on the same basis as our Standardized Measure because it does not include a provision for future income taxes. Following the Spin-Off, we will be a corporation subject to entity-level income taxes. As a result, our calculation of PV-10 for annual periods following the Spin-Off will be adjusted upward for estimated future income tax expense, computed by applying the then applicable year end statutory tax rates to future pretax net cash flows, less the tax basis of the properties involved and utilization of available tax carryforwards related to oil and gas operations. |
Uncertainties are inherent in estimating quantities of proved reserves, including many risk factors beyond our control. Reserve engineering is a subjective process of estimating subsurface accumulations of oil and natural gas that cannot be measured in an exact manner. As a result, estimates of proved reserves may vary depending upon the engineer estimating the reserves. Further, our actual realized price for our oil and natural gas is not likely to equal the pricing parameters used to calculate our proved reserves. As such, the oil and natural gas quantities and the value of those commodities ultimately recovered from our properties will vary from reserve estimates.
Additional discussion of our proved reserves is set forth under “Supplemental Oil and Gas Information (Unaudited)” in the notes to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
71
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On July 19, 2022, Jefferies announced plans for the complete legal and structural separation of Vitesse from Jefferies. To effect the separation, first, Vitesse will undertake the transactions described under the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions” in this Information Statement. Jefferies will subsequently distribute all of Vitesse’s common stock held by Jefferies, representing 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock immediately prior to the Distribution, to Jefferies shareholders, and Vitesse will become an independent, publicly traded company. After the Distribution, Jefferies will not own any shares of our common stock.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements of Vitesse have been derived from the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements of Vitesse Energy (“VE”), included in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.” Vitesse is currently a shell company created to effectuate the Spin-Off. The predecessor of Vitesse is Vitesse Energy.
The unaudited pro forma financial information of Vitesse Oil (“VO”) has been derived from the historical financial statements of Vitesse Oil, which are not included in this Information Statement as Vitesse Oil is not a significant acquisition with respect to Vitesse Energy.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and the year ended November 30, 2021 have been prepared as though the Spin-Off occurred on December 1, 2020. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of August 31, 2022 has been prepared as though the Spin-Off occurred on August 31, 2022. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements were prepared in accordance with Article 11 of the Regulation S-X, updated for Release No. 33-10786, which was effective January 1, 2021. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements have been adjusted to give effect to certain pro forma adjustments referred to as “Spin Transaction Accounting Adjustments,” including:
| ∎ | the distribution of our common stock by Jefferies to its shareholders in connection with the Spin-Off; and |
| ∎ | the recognition of additional estimated transaction costs related to the Spin-Off that are expected to be incurred after August 31, 2022. |
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements are presented for illustrative purposes only and are not necessarily indicative of the operating results or financial position that would have been achieved had the Spin-Off occurred on December 1, 2020 or August 31, 2022, respectively, nor are they indicative of our future operating results or financial position. The pro forma adjustments are based upon information and assumptions available at the time of the filing of this Information Statement as set forth in the notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements. Because these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements have been prepared based upon preliminary estimates, the impact of the Spin-Off and the timing thereof could cause material differences from the information presented herein.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements should be read in conjunction with our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes included under the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements” and the sections entitled “Capitalization” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information constitutes forward-looking information and is subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated. For more information, see the sections entitled “Cautionary Statement Concerning Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors.”
72
Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations
For the Nine Months Ended August 31, 2022
| (in thousands except share and per share data) |
VE HISTORICAL |
VO HISTORICAL |
VO TRANSACTION ACCOUNTING ADJUSTMENTS |
SUB TOTAL | SPIN TRANSACTION ACCOUNTING ADJUSTMENTS |
VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 179,177 | $ | 14,455 | $ | — | $ | 193,632 | $ | — | $ | 193,632 | ||||||||||||
| Natural gas |
45,510 | 2,500 | — | 48,010 | — | 48,010 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
224,687 | 16,955 | — | 241,642 | — | 241,642 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Production |
35,179 | 2,518 | — | 37,697 | — | 37,697 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Production taxes |
17,828 | 1,439 | — | 19,267 | — | 19,267 | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and Administrative |
11,496 | 951 | — | 12,447 | — | 12,447 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
46,310 | 4,653 | 628 | b | 51,591 | — | 51,591 | |||||||||||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
7,539 | — | — | 7,539 | 6,105 | g | 13,644 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
118,352 | 9,561 | 628 | 128,541 | 6,105 | 134,646 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) |
106,335 | 7,394 | (628 | ) | 113,101 | (6,105 | ) | 106,996 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other (Expense) Income |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodity derivative (loss) gain, net |
(47,990 | ) | (1,465 | ) | — | (49,455 | ) | — | (49,455 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(2,847 | ) | (157 | ) | — | (3,004 | ) | — | (3,004 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other income |
10 | — | — | 10 | — | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total other (expense) income |
(50,827 | ) | (1,622 | ) | — | (52,449 | ) | — | (52,449 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Net Income (loss) before income tax |
55,508 | 5,772 | (628 | ) | 60,652 | (6,105 | ) | 54,547 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
— | — | — | — | (13,410 | ) i | (13,410 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 55,508 | $ | 5,772 | $ | (628 | ) | $ | 60,652 | $ | (19,515 | ) | $ | 41,137 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Pro forma earnings per common share—basic |
$ | 0.12 | $ | 1.36 | c,d | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma earnings per common share—diluted |
$ | 0.12 | $ | 1.25 | c,d | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted average common shares outstanding—basic |
450,000,000 | 30,151,354 | c,d | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted average common shares outstanding—diluted |
450,000,000 | 33,000,000 | c,d | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
73
Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Balance Sheet
As of August 31, 2022
| (in thousands) | VE HISTORICAL |
VO HISTORICAL |
VO TRANSACTION ACCOUNTING ADJUSTMENTS |
SUB TOTAL | SPIN TRANSACTION ACCOUNTING ADJUSTMENTS |
VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 8,085 | $ | 363 | $ | — | $ | 8,448 | $ | (4,935 | ) h | $ | 3,513 | |||||||||||
| Revenue receivable |
44,737 | 4,190 | — | 48,927 | — | 48,927 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Oil and gas properties, net of accumulated depreciation, depletion, amortization, and impairment |
593,400 | 60,534 | 11,038 | a | 664,972 | 4,935 | h | |
— 669,907 |
| ||||||||||||||
| Commodities derivative assets |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
2,522 | 194 | — | 2,716 | — | 2,716 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total assets |
648,744 | 65,281 | 11,038 | 725,063 | — | 725,063 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Current liabilities |
47,321 | 2,070 | — | 49,391 | 8,500 | e | 57,891 | |||||||||||||||||
| Revolving credit facility |
66,000 | 1,800 | — | 67,800 | — | 67,800 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities (1) |
22,691 | 549 | — | 23,240 | (15,892 | ) f | 7,348 | |||||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
— | — | — | 44,864 | j | 44,864 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Redeemable management incentive units |
7,386 | — | — | 7,386 | (7,386 | ) f | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock |
— | — | — | — | 282 | c,d,f | 282 | |||||||||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
— | — | — | — | 546,878 | c,d,f | 546,878 | |||||||||||||||||
| Members’ equity |
505,346 | 60,862 | 11,038 | a | 577,246 | (577,246 | ) c,d | — | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable units and equity |
$ | 648,744 | $ | 65,281 | $ | 11,038 | $ | 725,063 | $ | — | $ | 725,063 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (1) | Composed of unit-based compensation liability, commodity derivatives liability and asset retirement obligations. |
74
Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations
For the Year Ended November 30, 2021
| (in thousands except share and per share data) |
VE HISTORICAL | VO HISTORICAL |
VO TRANSACTION ACCOUNTING ADJUSTMENTS |
SUB TOTAL | SPIN TRANSACTION ACCOUNTING ADJUSTMENTS |
VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oil |
151,838 | 10,800 | — | 162,638 | — | 162,638 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Natural gas |
33,340 | 2,061 | — | 35,401 | — | 35,401 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
185,178 | 12,861 | — | 198,039 | — | 198,039 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Production |
43,910 | 2,695 | — | 46,605 | — | 46,605 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Production taxes |
14,535 | 1,041 | — | 15,576 | — | 15,576 | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and Administrative |
10,581 | 1,190 | — | 11,771 | 8,500 | e | 20,271 | |||||||||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
60,846 | 5,249 | 833 | b | 66,928 | — | 66,928 | |||||||||||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
1,409 | — | — | 1,409 | 45,100 | g | 46,509 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
131,281 | 10,175 | 833 | 142,289 | 53,600 | 195,889 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) |
53,897 | 2,686 | (833 | ) | 55,750 | (53,600 | ) | 2,150 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other (Expense) Income |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodity derivative (loss) gain, net |
(32,590 | ) | (824 | ) | — | (33,414 | ) | — | (33,414 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(3,207 | ) | (122 | ) | — | (3,329 | ) | — | (3,329 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other income |
14 | — | — | 14 | — | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total other (expense) income |
(35,783 | ) | (946 | ) | — | (36,729 | ) | — | (36,729 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Net Income (loss) before income tax |
18,114 | 1,740 | (833 | ) | 19,021 | (53,600 | ) | (34,579 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
— | — | — | — | (1,489 | ) i | (1,489 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) |
18,114 | 1,740 | (833 | ) | 19,021 | (55,089 | ) | (36,068 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Pro forma earnings per common share—basic |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (1.23 | ) c,d | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma earnings per common share—diluted |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (1.23 | ) c,d | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted average common shares outstanding—basic |
450,000,000 | 29,335,635 | c,d | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted average common shares outstanding—diluted |
450,000,000 | 29,335,635 | c,d | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
75
The historical financial information of Vitesse Energy included in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements of Vitesse is derived from the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements of Vitesse Energy. The pro forma adjustments in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements of Vitesse have been prepared (a) in the case of the pro forma condensed combined balance sheet, as if the Spin-Off had taken place on August 31, 2022, and (b) in the case of the pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and the year ended November 30, 2021, as if the Spin-Off had taken place on December 1, 2020.
The pro forma adjustments are based on currently available information and certain estimates and assumptions; therefore, the actual effects of these transactions will differ from the pro forma adjustments. A general description of these transactions and adjustments is provided as follows.
1. VO Transaction
a) The VO Transaction will be accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification 805. The allocation of the preliminary estimated purchase price with respect to the business combination is based upon management’s estimates of and assumptions related to the fair values of the assets to be acquired and liabilities to be assumed using currently available information. The purchase price allocation resulted only in the step-up of oil and natural gas properties to its estimated fair value as all other assets acquired and liabilities assumed book values approximated their fair values. Due to the fact the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements have been prepared using these preliminary estimates, the final purchase price allocation and the resulting effect may differ significantly from the pro forma amounts included herein.
The following table presents the preliminary purchase price allocation of the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed in the VO Transaction:
| (in thousands) | PRELIMINARY PURCHASE PRICE ALLOCATION |
|||
| Assets acquired |
||||
| Cash |
$ | 363 | ||
| Revenue receivable |
4,190 | |||
| Oil and gas properties |
71,572 | |||
| Other assets |
194 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total assets to be acquired |
$ | 76,319 | ||
| Liabilities assumed |
||||
| Current liabilities |
$ | 2,070 | ||
| Credit facility |
1,800 | |||
| Other long-term liabilities |
549 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total liabilities to be assumed |
4,419 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Net assets to be acquired |
$ | 71,900 | ||
b) Reflects depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion expense of approximately $5.3 million and $6.1 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and the year ended November 30, 2021, respectively, associated with the stepped-up basis of the acquired assets and the elimination of historical depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion expense of approximately $4.7 million and $5.3 million attributable to oil and natural gas properties, respectively, for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and the year ended November 30, 2021.
2. Pre-Spin-Off Transactions
We intend to enter into a New Revolving Credit Facility in connection with the Spin-Off. The New Revolving Credit Facility will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility of Vitesse Energy and borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility will remain outstanding as borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility. We anticipate the New Revolving Credit Facility will include the same bank group and be similar in aggregate size and with similar
76
terms to our Existing Revolving Credit Facility and the Vitesse Oil Revolving Credit Facility. We will use the proceeds from the New Revolving Credit Facility to repay in full and terminate the outstanding indebtedness under the Vitesse Oil Revolving Credit Facility with little or no impact to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements, as borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility are expected to be at similar levels and terms (including the fees, the interest rate margin and the market-based indices that such interest rate is tied to under such facility) as the Existing Revolving Credit Facility.
c) We intend to issue approximately 2.1 million shares of common stock to the owners of Vitesse Oil in connection with the acquisition of Vitesse Oil, which for purposes of these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements is assumed to be $71.9 million. This transaction eliminates members’ equity of Vitesse Oil and reflects the issuance of shares of Vitesse common stock to the owners of Vitesse Oil.
d) To implement the Spin-Off, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock held by each Jefferies shareholder on the Record Date, such shareholder will receive a distribution of one share of Vitesse common stock, with such shareholder receiving cash in lieu of fractional shares of Vitesse common stock. We estimate that Jefferies will distribute approximately 26,614,467 shares of our common stock, based on 226,134,603 shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding as of December 16, 2022. For more information, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Treatment of Fractional Shares.” Vitesse will have a new long-term incentive plan and the historical incentive compensation structure of Vitesse Energy will be eliminated. Basic common shares outstanding includes 28,202,019 shares expected to be issued as described in note c) and this note d), as well as vested restricted stock units to be issued under the VTS LTIP and vested restricted stock units and options to be issued under the Transitional Plan. Diluted common shares outstanding for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 also includes unvested restricted stock units to be issued under the VTS LTIP and unvested restricted stock units and options to be issued under the Transitional Plan. Diluted and basic common shares outstanding for the year ended November 30, 2021 were the same because there was a net loss during such period and adding unvested restricted stock units and options to be issued under the VTS LTIP and Transitional Plan would be anti-dilutive.
e) Reflects additional estimated one-time transaction costs related to the Spin-Off that are expected to be incurred after August 31, 2022 and are therefore not reflected in the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements of Vitesse Energy. Approximately $3.0 million of transaction costs related to the Spin-Off are included in the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements of Vitesse Energy. These transaction costs are not expected to recur beyond twelve months after the Spin-Off.
f) Reflects the elimination of unit-based compensation liabilities and redeemable management incentive units pursuant to certain of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. For more information, see the section entitled “Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons.”
g) Reflects anticipated awards of time-vested restricted stock units of Vitesse in connection with the Spin-Off. For more information, see the sections entitled “Executive Compensation” and “Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons.”
h) Reflects the termination of the Employee Participation Plan of Vitesse Energy and repurchase of working interests from participants on November 30, 2022. While this transaction would be expected to increase production, revenues and expenses subsequent to the repurchase, the impact is immaterial to the Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statements of Operations.
3. Income Taxes
i) Reflects the income tax effect of the pro forma adjustments related to the acquisition of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil, each a limited liability company, by Vitesse. The tax rate applied to the pro forma adjustments was the estimated combined statutory rate of 23.3%.
j) Reflects pro forma adjustments resulting in a $44.9 million increase to the net deferred tax liability of Vitesse at the estimated statutory tax rate. The deferred tax liability results from taxable temporary differences related to the financial accounting versus tax basis of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil. The Vitesse Energy acquisition is expected to
77
qualify for tax deferred treatment under Sections 368(a)(1)(D) and 351 of the Code, with the carryover tax basis being lower than the historical financial accounting basis. The VO Transaction was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting and is expected to qualify as a tax deferred transaction for income tax purposes under Section 351 of the Code. Accordingly, the VO Transaction reflects the assumption of a deferred tax liability in connection with the acquisition, as the carryover tax basis is lower than the financial accounting basis. The lower tax bases for both Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil result primarily from the ability to deduct intangible drilling costs and depreciation on an accelerated basis for income tax purposes. Additional adjustments to the carryover tax basis are expected, which will impact the amount of the deferred tax liability. Expected increases in the carryover tax basis relate primarily to partner elections to capitalize a portion of the intangible drilling costs and the anticipated step-up in tax basis resulting from the exchange of Vitesse Energy MIUs and equity interests of Vitesse Energy in satisfaction of loans from Vitesse Energy Finance.
4. Supplemental Pro Forma Oil and Natural Gas Reserves Information
The following tables present the combined net proved developed and undeveloped oil and natural gas reserves as of November 30, 2021, along with a summary of changes in quantities of net remaining proved reserves during the year ended November 30, 2021. The combined reserve information set forth below gives effect to the Spin-Off as if it had occurred on December 1, 2020.
The following combined reserve information is presented for illustrative purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of the operating results or financial position that would have been achieved had the Spin-Off occurred on December 1, 2020 nor is it indicative of our future operating results or financial position. Because the following combined reserve information has been prepared based upon preliminary estimates, the impact of the Spin-Off and the timing thereof could cause material differences from the information presented herein.
| OIL (MBbls) | ||||||||||||
| VE HISTORICAL | VO HISTORICAL | VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2020 |
33,106 | 3,518 | 36,624 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Revisions of previous estimates |
(2,998 | ) | (349 | ) | (3,347 | ) | ||||||
| Extensions, discoveries and other additions |
899 | 20 | 919 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of reserves |
959 | 82 | 1,041 | |||||||||
| Production |
(2,436 | ) | (167 | ) | (2,603 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2021 |
29,530 | 3,104 | 32,634 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
17,841 | 1,324 | 19,165 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
17,764 | 1,320 | 19,084 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Undeveloped Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
15,265 | 2,194 | 17,459 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
11,766 | 1,784 | 13,550 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
78
| GAS (MMcf) | ||||||||||||
| VE HISTORICAL | VO HISTORICAL | VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2020 |
84,829 | 6,296 | 91,125 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Revisions of previous estimates |
(4,181 | ) | (84 | ) | (4,265 | ) | ||||||
| Extensions, discoveries and other additions |
2,648 | 36 | 2,684 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of reserves |
1,793 | 173 | 1,966 | |||||||||
| Production |
(7,065 | ) | (399 | ) | (7,464 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2021 |
78,024 | 6,022 | 84,046 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
47,418 | 2,960 | 50,378 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
58,437 | 3,224 | 61,661 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Undeveloped Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
37,411 | 3,336 | 40,747 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
19,587 | 2,798 | 22,385 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| COMBINED (MBoe) | ||||||||||||
| VE HISTORICAL | VO HISTORICAL | VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2020 |
47,244 | 4,567 | 51,811 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Revisions of previous estimates |
(3,694 | ) | (363 | ) | (4,057 | ) | ||||||
| Extensions, discoveries and other additions |
1,340 | 26 | 1,366 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of reserves |
1,258 | 111 | 1,369 | |||||||||
| Production |
(3,614 | ) | (234 | ) | (3,848 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2021 |
42,534 | 4,107 | 46,641 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
25,744 | 1,817 | 27,561 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
27,504 | 1,857 | 29,361 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Undeveloped Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
21,500 | 2,750 | 24,250 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
15,030 | 2,250 | 17,280 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Notable changes in Vitesse Energy proved reserves for the year ended November 30, 2021 included the following:
| ∎ | Revisions to previous estimates. In 2021, revisions to previous estimates increased proved developed and decreased proved undeveloped reserves by a net amount of 3,694 MBoe. Included in these revisions were 4,331 MBoe of upward adjustments caused by higher oil and natural gas prices and 6,875 MBoe of downward adjustments related to the removal of undeveloped drilling locations due to a slower than expected recovery of rig activity in the Williston Basin, 524 MBoe of downward adjustments related to the removal of drilled uncompleted wells in the Central Rockies related to the SEC five year development rule and 626 MBoe of downward adjustments attributable to well performance when comparing our reserve estimates at November 30, 2021 to November 30, 2020. |
79
| ∎ | Extensions and discoveries. In 2021, total extensions and discoveries of 1,340 MBoe were attributable to additions of proved undeveloped locations in the Williston Basin. |
Notable changes in Vitesse Oil proved reserves for the year ended November 30, 2021 included the following:
| ∎ | Revisions to previous estimates. In 2021, revisions to previous estimates increased proved developed and decreased proved undeveloped reserves by a net amount of 363 MBoe. Included in these revisions were 452 MBoe of upward adjustments caused by higher oil and natural gas prices, 667 MBoe of downward adjustments related to the removal of undeveloped drilling locations due to a slower than expected recovery of rig activity in the Williston Basin and 148 MBoe of downward adjustments attributable to well performance when comparing our reserve estimates at November 30, 2021 to November 30, 2020. |
The combined Standardized Measure related to proved oil and natural gas reserves as of November 30, 2021 is as follows:
| (in thousands) | VE HISTORICAL | VO HISTORICAL | SPIN TRANSACTION ADJUSTMENT |
VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||||
| Future cash inflows |
$ | 2,151,098 | $ | 223,762 | $ | — | $ | 2,374,860 | ||||||||
| Future production costs |
(816,329 | ) | (71,164 | ) | — | (887,493 | ) | |||||||||
| Future development costs |
(230,101 | ) | (22,339 | ) | — | (252,440 | ) | |||||||||
| Future income tax expense |
— | — | (202,177 | ) | (202,177 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Future net cash inflows |
$ | 1,104,668 | $ | 130,259 | $ | (202,177 | ) | $ | 1,032,750 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 10% annual discount |
(503,055 | ) | (71,274 | ) | 90,153 | (484,176 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| SMOG Future Net Cashflows |
$ | 601,613 | $ | 58,985 | $ | (112,024 | ) | $ | 548,574 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Changes in the combined Standardized Measure for the year ended November 30, 2021 are as follows:
| (in thousands) | VE HISTORICAL | VO HISTORICAL | SPIN TRANSACTION ADJUSTMENT |
VITESSE PRO FORMA |
||||||||||||
| Beginning of Period |
$ | 191,178 | $ | 19,394 | $ | — | $ | 210,572 | ||||||||
| Sales of oil and natural gas produced, net of production costs |
(126,733 | ) | (9,125 | ) | — | (135,858 | ) | |||||||||
| Extensions and discoveries |
17,911 | 464 | — | 18,375 | ||||||||||||
| Previously estimated development cost incurred during the period |
16,924 | 1,417 | — | 18,341 | ||||||||||||
| Net change of prices and production costs |
415,685 | 45,562 | — | 461,247 | ||||||||||||
| Change in future development costs |
22,606 | 3,229 | — | 25,835 | ||||||||||||
| Revisions of quantity and timing estimates |
(17,833 | ) | (1,733 | ) | — | (19,566 | ) | |||||||||
| Accretion of discount |
19,118 | 1,939 | — | 21,057 | ||||||||||||
| Change in income taxes |
— | — | (112,024 | ) | (112,024 | ) | ||||||||||
| Purchases of minerals in place |
23,272 | 2,223 | — | 25,495 | ||||||||||||
| Other |
39,485 | (4,385 | ) | — | 35,100 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| End of Period |
$ | 601,613 | $ | 58,985 | $ | (112,024 | ) | $ | 548,574 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
80
Vitesse is an independent energy company engaged in the acquisition, development and production of non-operated oil and natural gas properties in the United States that are generally operated by leading oil companies and are primarily in the Bakken and Three Forks formations in the Williston Basin of North Dakota and Montana. We also have properties in the Central Rockies, including the Denver-Julesburg Basin and the Powder River Basin. Since our inception in 2014, we have built a strong and diversified asset base through a combination of property acquisitions, development activities and the implementation of proprietary platforms and processes utilizing our extensive data resources. We believe the location and concentration of our assets in some of North America’s leading unconventional oil and natural gas resource plays, along with our technical and data capabilities, will continue to provide us with acquisition and development opportunities that will result in significant incremental long-term value.
Vitesse has historically created value by acquiring non-operated minority working and mineral interests in oil and natural gas properties, comprising producing wells, near-term development opportunities and undeveloped acreage, and partnering with premier operators with significant experience in developing and producing oil and natural gas in our core areas. Over the past eight years, we have executed on our technical, data driven, and financially disciplined acquisition and development strategy to build our core position in the Williston Basin and Central Rockies and grow our oil and natural gas production. During that time, we have focused on limiting our downside by maintaining conservative acquisition guidelines, limiting our debt leverage and opportunistically locking in future prices for a portion of our oil production. As a result, we have been able to preserve value when many independent energy companies were forced into financial recapitalizations and restructurings when commodity prices declined significantly in 2014, 2018 and 2020.
With the current higher oil and natural gas price environment, we are focused on using free cash flow to maintain a strong balance sheet, provide growing returns of capital to our stockholders, and grow our oil and natural gas production by developing our extensive inventory of drilling locations, as well as acquiring both producing wells and new development opportunities.
We owned an average working interest of 2.6% in 5,203 gross (133.9 net) productive wells and royalty interests in an additional 998 productive wells as of August 31, 2022. We engage in oil and natural gas well development by participating on a proportionate basis alongside third-party interests in wells drilled and completed in spacing units that include our acreage. As of August 31, 2022, we owned a working interest in a further 253 gross (6.5 net) wells that were being drilled or completed, and an additional 413 gross (8.5 net) wells that had been permitted for development by our operating partners. We rely on our operators to propose, permit and initiate the drilling and completion of wells. We assess each drilling and completion opportunity on a case-by-case basis and participate in wells that are expected to meet a desired return based upon estimates of recoverable oil and natural gas reserves, anticipated oil and natural gas prices, the expertise of the operator, and the anticipated completed well cost, as well as other factors.
Our non-operated business model provides us with inherent flexibility regarding the cadence of capital deployment and the agility to allocate a portion of our cash flow to the drilling and completion opportunities that we believe will achieve the highest rate of return. We work with more than 35 experienced operators that provide technical insights and opportunities for additional acquisitions and continued development. In addition, our business model allows us to not be burdened with various contractual arrangements with respect to minimum drilling obligations, and we can minimize exploratory, upfront leasing and infrastructure costs customarily incurred by operators.
Our operators generally market and sell the oil and natural gas extracted from our wells on their behalf and on our behalf. In addition, these operators coordinate the transportation of oil and natural gas production from wells in which we participate to appropriate pipelines or rail transport facilities pursuant to arrangements that such operators negotiate and maintain with various parties purchasing such production. The price at which our production is sold generally ties to a market spot price, and the Differential between the market spot price and our realized sales price represents the imbedded transportation and marketing costs of moving the oil and natural gas from the wellhead to
81
the refinery or processing plant. The Differential will fluctuate based on availability of pipeline, rail and other transportation methods.
Vitesse is led by a dedicated management team with extensive experience in the energy industry. Our management team includes Bob Gerrity, our Chief Executive Officer, a successful industry leader who was the founder and chief executive officer of Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation, which pioneered low-cost “reserve manufacturing” in the Wattenberg field of Colorado during the 1990s. Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation was one of the most active operators in the United States following its IPO in 1990, at times running more than 15 active drilling rigs and completing as many as 500 wells per year. Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation merged with Snyder Oil Corporation to form Patina Oil & Gas Corporation in 1996, which was merged with Noble Energy, Inc. in 2005. Today, these former assets comprise a material portion of Chevron Corporation’s position in the Denver-Julesburg Basin.
Leveraging his prior experience and acknowledging the trend in advances in shale drilling and completion technologies, Mr. Gerrity believed the shale industry would transition to a reserve manufacturing phase marked by well-capitalized and efficient low-cost operators. In 2013, Mr. Gerrity and Brian Cree, our President and Chief Operating Officer, began to seek out non-operated lease and mineral interests with development opportunities in areas of the Williston Basin that were in the core of the field and operated by premier industry leaders, at which time an affiliate of Jefferies made an initial investment in Vitesse Oil to partially fund the acquisition of non-operated working and mineral interests primarily in undeveloped oil and natural gas assets. In 2014, Messrs. Gerrity and Cree began to see a growing number of acquisition and development opportunities in the Williston Basin, and Jefferies made a direct investment in Vitesse to support larger scale acquisition and development efforts. Since that time, Vitesse has completed over 120 acquisitions totaling approximately $520 million and deployed over a further $400 million in the development of oil and natural gas properties.
Vitesse Oil, which will be acquired by Vitesse as part of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, is an independent energy company also engaged in the acquisition, development and production of non-operated oil and natural gas properties in the Williston Basin of North Dakota. As of August 31, 2022, Vitesse Oil had 2,515 net acres in the Williston Basin and owned working interests in approximately 871 gross (7.8 net) productive wells and royalty interests in an additional 120 productive wells, with average production of 816 Boe per day during the month ended August 31, 2022. In addition, Vitesse Oil had 73 gross (0.3 net) wells that were being drilled or completed, and an additional 83 gross (0.3 net) wells that had been permitted for future development by its operators as of August 31, 2022. Based on year-end SEC prices, as of December 31, 2021, Vitesse Oil had approximately 4,107 MBoe of estimated proved reserves located primarily in the core of the Williston Basin, and average production of 641 Boe per day for the year ended December 31, 2021.
The following table provides a summary of certain information regarding our assets as of November 30, 2021, including proved reserves as prepared by our third-party independent reserve engineers, Cawley.
| AS OF NOVEMBER 30, 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NET ACRES |
PRODUCTIVE WELLS (1) |
AVERAGE DAILY PRODUCTION (2) (Boe/d) |
PROVED RESERVES (3) (MBoe) |
PV-10 (3) (in thousands) |
% OIL | % PROVED DEVELOPED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GROSS | NET | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
46,013 | 4,821 | 112 | 9,394 | 39,609 | $ | 547,294 | 70 | % | 63 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Rockies (4) |
179 | 66 | 13 | 770 | 2,925 | 54,319 | 61 | % | 95 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total |
46,192 | 4,887 | 125 | 10,164 | 42,534 | $ | 601,631 | 69 | % | 65 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| (1) | In addition, we have royalty interests in 992 productive wells. |
| (2) | Represents the average daily production over the month ended November 30, 2021. |
| (3) | Proved reserve quantities and related PV-10 values have been derived from a WTI oil price of $64.81 per Bbl and Henry Hub natural gas price of $3.46 per MMBtu, which were calculated using an average of the first-day-of-the-month price for each month within the 12 months ended November 30, 2021 as required by SEC and FASB guidelines. PV-10 is a non-GAAP financial measure that does not include the effects of income taxes on future net revenues, and is not intended to represent fair market value of our oil and natural gas properties. For a definition of and reconciliation of PV-10 to Standardized Measure, the nearest GAAP financial measure, see “Selected Historical Financial Data—Non-GAAP Financial Information.” Vitesse’s PV-10 has historically been computed on the same basis as our Standardized Measure because it does not include a provision for future income taxes. Following the Spin-Off, we will be a corporation |
82
| subject to entity-level income taxes. As a result, our calculation of PV-10 for annual periods following the Spin-Off will be adjusted upward for estimated future income tax expense, computed by applying the then applicable year end statutory tax rates to future pretax net cash flows, less the tax basis of the properties involved and utilization of available tax carryforwards related to oil and gas operations. |
| (4) | Includes Denver-Julesburg and Powder River Basin assets, consisting primarily of wellbore only ownership. |
In addition to the proved reserves shown in the table above, we believe our acreage includes over 200 net undeveloped drilling locations not currently classified as proved as of November 30, 2021, using the same pricing as above. We identify drilling locations based on our assessment of current geologic, engineering and land data. This includes current well spacing information per drilling and spacing unit derived from state agencies and our operators. We generally do not have evidence of our operators’ long-term development plans, but we use a deterministic approach to define and allocate locations to proved, probable and possible reserves. While many of our undeveloped drilling locations qualify as geologic and engineering proved reserves, we limit our proved undeveloped reserves to those locations that are reasonably certain to be developed over the next five years.
Our business strategy going forward is focused on creating long-term stockholder value through the acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas assets at attractive rates of return, while maintaining a strong and conservative balance sheet and distributing a portion of our free cash flow to our stockholders, in the form of a regular cash dividend on a quarterly basis. The key elements of our business strategy include the following:
| ∎ | Dividends to Stockholders. Our business plan focuses on building a diversified, low-leverage, free cash flow generating business that can deliver regular cash dividends to our stockholders. We made cash distributions to our members totaling $25.0 million during 2019, $0.0 during 2020, $12.0 million during 2021, and $42.0 million during the nine months ended August 31, 2022. In addition, to the aforementioned cash distribution payments, Jefferies retained close to $25.0 million in hedging gain proceeds that were attributable to derivatives associated with our oil production during 2019 and 2020, further demonstrating our commitment to generating value for our investors. Following the Distribution, we expect that Vitesse will initially pay quarterly cash dividends and dividend equivalents totaling approximately $66.0 million per fiscal year. |
| ∎ | Growth through Value-Enhancing Acquisitions. We have been a consolidator and clearing house of non-operated working interests in various leading oil and natural gas shale plays in the United States, and we will continue that strategy and potentially pursue operated asset packages and other acquisition strategies going forward. Our near-term drilling acquisition strategy is centered around building a strong presence in our core basins by acquiring smaller non-operated lease and wellbore positions with direct exposure to near-term drilling activity. By virtue of their smaller footprint, these targeted acquisitions have been completed at a significant discount to the prices paid for contiguous acreage positions typically sought by larger producers and operators of oil and natural gas wells. Acquisitions such as these have been a significant driver of increasing our production. Over the last eight years, we have closed approximately 120 discrete acquisitions totaling more than $520 million, and we intend to continue these activities, while at the same time evaluating and pursuing larger asset packages in both our current area of operations and other areas. We believe our disciplined acquisition strategy can responsibly add production, cash flow and scale to existing operations. |
| ∎ | Built to Last. From our inception, we have focused on creating a durable organization that generates strong financial returns and sustainable free cash flow through commodity cycles. Rather than primarily acquiring producing reserves, we have focused our efforts on acquiring an attractive inventory of undeveloped drilling locations that afford us flexibility in the face of oil and natural gas price fluctuations and taking advantage of technical improvements and cost reductions over time, supporting the sustainable generation of free cash flow. Our management team fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement, constantly looking for ways to improve our operations and technical and data analysis, and strengthen our organizational agility and adaptability. |
| ∎ | Risk Diversification. We seek to diversify our capital and operational risk through participation in a large number of oil and natural gas wells with multiple operators across multiple basins. We seek to diversify our risk by operator, formation, value concentration and commodity (oil and natural gas). As of August 31, 2022, we owned an average working interest of 2.6% in 5,203 gross (133.9 net) productive wells and |
83
| royalty interests in an additional 998 productive wells, with more than 35 experienced operators that provide development and production activities on our oil and natural gas properties. We believe we can further diversify our risk over time with acquisitions in additional basins, focusing on accretive acquisitions of high-quality assets with experienced operators in the most prolific basins in the United States. During the nine months ended August 31, 2022, our average production was 10,048 Boe per day, consisting of approximately 8,910 Boe per day in the Williston Basin and 1,138 Boe per day in the Central Rockies. During the month ended August 31, 2022, our average production was 10,898 Boe per day, consisting of approximately 9,462 Boe per day in the Williston Basin and 1,436 Boe per day in the Central Rockies. |
| ∎ | Strong Balance Sheet and Financial Flexibility. We maintain financial strength and flexibility through the prudent management of our balance sheet and free cash flow. During 2020, 2021 and the first nine months of 2022, we were free cash flow positive and reduced our outstanding debt from $104.0 million at November 30, 2019 to $68.0 million at November 30, 2021 and to $66.0 million at August 31, 2022. Following the Spin-Off, we intend to maintain conservative indebtedness and a simple capital structure consisting only of our New Revolving Credit Facility and common stock. We intend to maintain the flexibility to manage our free cash flow by continuing to adhere to a target Net Debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (last twelve months) of less than 1.0. As of August 31, 2022, our Net Debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (last twelve months) was 0.4. For the twelve months ended August 31, 2022, we generated net income and Adjusted EBITDA of $81.2 million and $158.0 million, respectively. From our inception in 2014 through August 31, 2022, we generated approximately $144.0 million of net income during a volatile commodity price environment. For definitions and reconciliations of Net Debt and Adjusted EBITDA to their most directly comparable financial measures in accordance with GAAP, see “Selected Historical Financial Data—Non-GAAP Financial Information.” |
| ∎ | Hedging Strategy. To reduce our exposure to the volatility of oil prices and protect our ability to pay distributions, we have entered into hedging derivative instruments for a portion of our expected oil production, which have included swaps, collars, puts and other structures. We historically have bought oil futures both on an opportunistic basis when WTI prices have allowed us to lock in attractive rates of return on our asset base and upon acquisitions of larger producing assets to protect returns. We currently do not hedge natural gas production due to the mismatch between our operators’ pricing formulas and settlement mechanics on natural gas hedges. Our current hedged position mitigates our exposure to volatile oil prices, with approximately 30% of our expected oil production hedged through November 30, 2024 at attractive prices. However, in the past, based on then-existing market conditions, we have hedged significantly higher percentages of our actual oil production. For further information see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk—Commodity Price Risk.” |
| ∎ | Responsible Stewards. We are committed to ESG initiatives and seek a culture of improvement in ESG practices. We work to provide safe, reliable and affordable energy in a responsible manner by partnering with responsible operators in our core areas, while being cognizant of the broader energy transition. The key tenets of our ESG philosophy are to identify opportunities to reduce our environmental impact, improve safety, invest in our employees, and support the communities in which we live and work while improving transparency and accountability. At the time of the Distribution, our Board will be majority independent and composed of experienced professionals with a strong background in the energy industry and more broadly in business. |
We believe that we will be able to successfully execute our business strategies because of the following competitive strengths:
| ∎ | Every Decision is a Financial Decision. Our business culture encourages employees to think like owners and to make decisions with a long-term perspective. We have developed a systematic approach of responsibly reviewing acquisition and development opportunities. As part of our efforts to maximize returns, we have established a capital allocation framework with the objective of allocating capital to acquisitions and development of oil and natural gas properties to drive sustainability and growth in free cash flow, the repayment of debt and stockholder dividends. This framework entails disciplined investment in capital expenditures and acquisitions, allowing us to distribute a significant portion of our cash flow to our |
84
| stockholders. We also retain flexibility with respect to share repurchases, subject to approval from our Board and as conditions warrant. We will continue to evaluate and pursue profitable and accretive acquisition and consolidation opportunities that enhance stockholder value and build scale. As opportunities arise, we intend to identify and acquire additional acreage and producing assets to supplement our existing operations. |
| ∎ | Data and Technology Driven. Our proprietary data-driven approach allows for rapid multi-disciplinary evaluation to determine the most attractive acquisition and development opportunities. We created customized data systems (vLuminis) that are integrated, centralized and utilized by our employees so that decisions are based on a common base of information. We maintain real-time business intelligence dashboards to monitor operators, rigs, well performance, drilling and completion costs and production results. This data informs model forecasts, type curves and decisions about acquisition and development opportunities. We maintain responsive, basin-wide models that are updated in real time and incorporate historical data by operator and region. These models, along with our proprietary systems and platforms, provide necessary inputs and evaluation metrics, which allow us to make informed investment decisions based on forecasted production, operating expenses, type curves, drilling inventory, cash flow and other operational and financial outputs. As a result, we have the capability to process multiple opportunities quickly with the current team in place. |
| ∎ | Experienced Management and Industry Relationships. Vitesse’s management team has developed deep and longstanding relationships with many of our operators, other working interest and mineral owners, investment banks, acquisition and divestiture companies and investors. A majority of our evaluated and executed acquisitions and transactions are self-sourced. We have become a preferred non-operator to some of the largest companies operating in the Williston Basin and Central Rockies given our track record of evaluating and acquiring non-operated oil and natural gas working interests, and being a responsible financial partner. As a result, we see broad deal flow from single wellbore near-term development acquisition opportunities to packages consisting of both producing and undeveloped assets worth hundreds of millions of dollars. Our management team has an over 30-year track record of creating value together at both private and public oil and natural gas companies. |
| ∎ | Proactive Asset Management Philosophy. Our experienced team of landmen and accountants review acquired assets to unlock incremental value. Many assets we acquire have title defects or other land related issues where deep analysis and consistent, quality diligence adds value in many areas, including increased working interest ownership and working capital management. Our long-term view provides the time to solve issues and find additional well interests to increase the velocity of overall returns. This is enabled by strong departmental relationships with operators and accurate data management. |
Williston Basin (North Dakota and Montana)
The Williston Basin stretches from western North Dakota into eastern Montana, with the majority of drilling activity conducted by our operators, all of which is horizontal, located in Dunn, McKenzie, Mountrail, and Williams Counties, North Dakota. Approximately 75% of our 46,222 net acres as of August 31, 2022 are in the above counties of the Bakken and Three Forks formations and approximately 99% of our acreage in the Williston Basin is held by production. As of August 31, 2022, we had a working interest in 5,120 gross (118.3 net) productive wells and royalty interests in an additional 998 productive wells. In addition to these productive wells, we had 223 gross (4.4 net) working interest wells that are being drilled or completed, and 409 gross (8.4 net) wells that have been permitted for future development by our operating partners. Our estimated proved reserves in North Dakota and Montana as of November 30, 2021 were 39,609 MBoe (70% oil), which represented 93% of our total estimated proved reserves and contributed average production of 9,394 Boe per day during the month ended November 30, 2021.
We have been active in the Williston Basin since 2014 and have seen our thesis for continued growth and expansion of the field come to fruition. The Williston Basin is a world class oil field and we expect to see continued growth in recoverable reserves for many years. We have a significant inventory of remaining undeveloped drilling locations that we expect to see developed over the next 10 to 15 years. In addition, we are seeing the early signs of incremental growth and development throughout the field from successful refrac programs, extended length three-mile lateral infills and consolidation of assets to more active and basin focused operators.
85
The map below illustrates our acreage position in the Williston Basin as of August 31, 2022.

86
Denver-Julesburg Basin (Colorado and Wyoming)
The Denver-Julesburg Basin is located in Northeast Colorado and Southeast Wyoming, with the majority of operator horizontal drilling activity located in Weld and Broomfield Counties, Colorado, and Laramie County, Wyoming. Our assets in this area primarily consist of wellbore only ownership and target the Codell formation and several productive zones within the Niobrara formation. We owned a working interest in 77 gross (14.6 net) productive wells as of August 31, 2022 operated primarily by Civitas Resources, Inc., PDC Energy, Inc., EOG Resources Inc. and Chevron Corporation. In addition to the productive wells, we have 30 gross (2.1 net) wells that were being completed by our operating partners as of August 31, 2022.
Powder River Basin (Wyoming)
Our Powder River Basin assets primarily target the Parkman, Sussex, Turner and Niobrara formations. We owned a working interest in six gross (1.02 net) productive wells as of August 31, 2021. In addition to these productive wells, we have three gross (0.6 net) wells that have been permitted for future drilling by our operators as of August 31, 2022.
The diagrams below illustrate our net production and working interest net acres by operator for the month ended August 31, 2022.
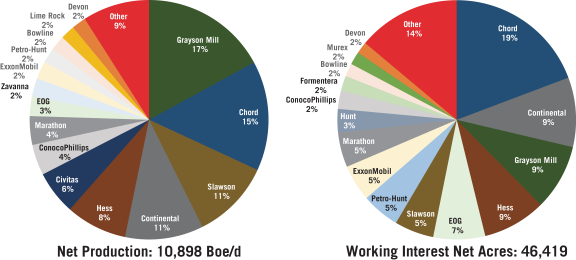
Estimated Net Proved Reserves
The table below summarizes our estimated net proved reserves for the periods indicated based on reports prepared by Cawley, our third-party independent reserve engineer, except that a portion of our proved undeveloped reserves for the years ended November 30, 2020 and 2019 are based on internal reserve estimates. In preparing its reports, Cawley evaluated properties representing our total proved reserves for the year ended November 30, 2021 and our proved developed reserves and a portion of our proved undeveloped reserves for the years ended November 30, 2020
87
and 2019 in accordance with the rules and regulations of the SEC applicable to companies involved in oil and natural gas producing activities. Our estimated net proved reserves in the table below do not include probable or possible reserves and do not in any way include or reflect our commodity derivatives.
| AS OF NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Estimated proved developed: |
||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
17,764 | 17,841 | 18,928 | |||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
58,437 | 47,418 | 39,059 | |||||||||
| Total (MBoe) |
27,504 | 25,744 | 25,438 | |||||||||
| Estimated proved undeveloped: |
||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
11,765 | 15,265 | 22,342 | |||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
19,586 | 37,410 | 48,264 | |||||||||
| Total (MBoe) |
15,030 | 21,500 | 30,386 | |||||||||
| Estimated total proved reserves: |
||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
29,530 | 33,106 | 41,271 | |||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
78,023 | 84,829 | 87,324 | |||||||||
| Total (MBoe) |
42,534 | 47,244 | 55,825 | |||||||||
| Percent proved developed |
64.7 | % | 54.5 | % | 45.6 | % | ||||||
Estimated net proved reserves as of November 30, 2021 were 42,534 MBoe, and we held working interests in 32.5 net proved undeveloped drilling locations included in such reserves as of November 30, 2021.
The table below sets forth summary information by reserve category with respect to estimated proved reserves volumes and related PV-10 values as of November 30, 2021.
| SEC PRICING PROVED RESERVES (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RESERVE VOLUMES | PV-10 (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| RESERVE CATEGORY |
OIL (MBbls) |
NATURAL GAS (MMcf) |
TOTAL (MBoe) (2) |
% | AMOUNT (in thousands) |
% | ||||||||||||||||||
| PDP Properties |
15,926 | 52,150 | 24,618 | 58 | % | $ | 409,515 | 68 | % | |||||||||||||||
| PDNP Properties |
1,838 | 6,287 | 2,886 | 7 | % | 50,631 | 8 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| PUD Properties |
11,766 | 19,586 | 15,030 | 35 | % | 141,467 | 24 | % | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
29,530 | 78,023 | 42,534 | 100 | % | $ | 601,613 | 100 | % | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (1) | Oil and natural gas reserve quantities and related discounted future net cash flows are valued as of November 30, 2021 based on average prices of $64.81 per barrel of oil and $3.46per MMBtu of natural gas. Under SEC guidelines, these prices represent the average prices per barrel of oil and per MMBtu of natural gas at the beginning of each month in the twelve-month period prior to the end of the reporting period. |
| (2) | Boe are computed based on a conversion ratio of one Boe for each barrel of oil and one Boe for every 6 Mcf of natural gas. |
| (3) | PV-10 is a non-GAAP financial measure that does not include the effects of income taxes on future net revenues, and is not intended to represent fair market value of our oil and natural gas properties. For a definition of and reconciliation of PV-10 to Standardized Measure, the nearest GAAP financial measure, see “Selected Historical Financial Data—Non-GAAP Financial Information.” Vitesse’s PV-10 has historically been computed on the same basis as our Standardized Measure because it does not include a provision for future income taxes. Following the Spin-Off, we will be a corporation subject to entity-level income taxes. As a result, our calculation of PV-10 for annual periods following the Spin-Off will be adjusted upward for estimated future income tax expense, computed by applying the then applicable year end statutory tax rates to future pretax net cash flows, less the tax basis of the properties involved and utilization of available tax carryforwards related to oil and gas operations. |
88
Proved Undeveloped Reserves
As of November 30, 2021, we had approximately 15,030 MBoe of proved undeveloped reserves. Changes in proved undeveloped reserves that occurred from November 30, 2020 to November 30, 2021 were due to:
| MBoe | ||||
| Balance at November 30, 2020 |
21,500 | |||
| Acquisitions |
1,258 | |||
| Extensions, discoveries and other additions |
1,340 | |||
| Transfers to estimated proved developed reserves |
(2,193 | ) | ||
| Revisions |
(6,875 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance at November 30, 2021 |
15,030 | |||
|
|
|
|||
Notable changes in proved undeveloped reserves for the year ended November 31, 2021 included the following:
| ∎ | Acquisitions: We acquired 1,258 MBoe of proved undeveloped reserves related to 63 gross (2.2 net) uncompleted wells in the Williston Basin and Central Rockies during 2021. |
| ∎ | Extensions, discoveries and other additions: Total extensions and discoveries of 1,340 MBoe were attributable to additions of proved undeveloped locations in the Williston Basin. |
| ∎ | Transfers to estimated proved developed reserves. Development costs of $17.6 million were incurred in connection with the development of locations that were classified as proved undeveloped reserves as of November 30, 2021, and 2,193 MBoe of proved undeveloped reserves were converted to proved developed reserves during the period. |
| ∎ | Revisions: Approximately 6,875 MBoe of downward adjustments related to reducing the number of undeveloped drilling locations due to a slower recovery of drilling rig activity than previously expected in the Williston Basin at year end 2021. |
We expect that our proved undeveloped reserves will continue to be converted to proved developed producing reserves as additional wells are drilled on our acreage. All locations comprising our remaining proved undeveloped reserves are forecast to be drilled within five years from initially being recorded in accordance with our development plan.
As of November 30, 2021, the PV-10 value of our proved undeveloped reserves amounted to approximately 24% of the PV-10 value of our total proved reserves. There are numerous uncertainties regarding undeveloped reserves. The development of these reserves is dependent upon a number of factors which include but are not limited to: financial targets such as drilling within cash flow or reducing debt, satisfactory rates of return on proposed drilling projects, and the level of drilling activity by operators in areas where we hold leasehold interests. With 68% of the PV-10 value of our total proved reserves supported by producing wells, we believe we will have sufficient cash flows and adequate liquidity to execute our development plan. PV-10 is a non-GAAP financial measure that does not include the effects of income taxes on future net revenues and is not intended to represent the fair market value of our oil and natural gas properties. For a definition of and reconciliation of PV-10 to Standardized Measure, the nearest GAAP financial measure, see “Selected Historical Financial Data—Non-GAAP Financial Information.”
Independent Petroleum Engineers
We have engaged Cawley to independently prepare our estimated proved reserves. Cawley is an independent reservoir-evaluation consulting firm who evaluates oil and natural gas properties and independently certifies petroleum reserves quantities for various clients throughout the United States. Cawley has substantial experience calculating the reserves of various other companies with operations targeting the Bakken and Three Forks formations and, as such, we believe Cawley has sufficient experience to appropriately determine our reserves. Cawley utilizes proprietary technology, systems and data to calculate our reserves commensurate with this experience. The reports of our estimated proved reserves in their entirety are based on the information we provide to them. Cawley is a Texas Registered Engineering Firm (F-693). The technical person at Cawley who is primarily responsible for preparing our reserves estimates is Todd Brooker, President. Mr. Brooker is a state of Texas Licensed Professional Engineer
89
(License # 83462). He is also a member of the Society of Petroleum Engineers and has over 25 years of experience in oil and natural gas reservoir studies and evaluations.
In accordance with applicable requirements of the SEC, estimates of our net proved reserves and future net revenues are made using average prices at the beginning of each month in the 12-month period prior to the date of such reserve estimates and are held constant throughout the life of the properties.
The reserves set forth in the Cawley report for our properties are estimated by performance methods or analogy. In general, reserves attributable to producing wells and/or reservoirs are estimated by performance methods such as decline curve analysis which utilizes extrapolations of historical production data. Reserves attributable to non-producing and undeveloped reserves included in our report are estimated by analogy.
To estimate economically recoverable oil and natural gas reserves and related future net cash flows, Cawley considers many factors and assumptions including, but not limited to, the use of reservoir parameters derived from geological, geophysical and engineering data which cannot be measured directly, economic criteria based on current costs and SEC pricing requirements, and forecasts of future production rates. Under the SEC regulations 210.4-10(a)(22)(v) and (26), proved reserves must be demonstrated to be economically producible based on existing economic conditions including the prices and costs at which economic productivity from a reservoir is to be determined as of the effective date of the report. With respect to the property interests we own, production and well tests from examined wells, normal direct costs of operating the wells or leases, other costs such as transportation and/or processing fees, production taxes, recompletion and development costs and product prices are based on the SEC regulations, geological maps, well logs, core analyses, and pressure measurements.
The reserve data set forth in the Cawley report represents only estimates, and should not be construed as being exact quantities. They may or may not be actually recovered, and if recovered, the actual revenues and costs could be more or less than the estimated amounts. Moreover, estimates of reserves may increase or decrease as a result of future operations.
Reservoir engineering is a subjective process of estimating underground accumulations of oil and natural gas that cannot be measured in an exact manner. There are numerous uncertainties inherent in estimating oil and natural gas reserves and their estimated values, including many factors beyond our control. The accuracy of any reserve estimate is a function of the quality of available data and of engineering and geologic interpretation and judgment. As a result, estimates of different engineers, including those used by us, may vary. In addition, estimates of reserves are subject to revision based upon actual production, results of future development and exploration activities, prevailing oil and natural gas prices, operating costs and other factors. The revisions may be material. Accordingly, reserve estimates are often different from the quantities of oil and natural gas that are ultimately recovered and are highly dependent upon the accuracy of the assumptions upon which they are based. See “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to our Business—Our estimated proved reserves are based on many assumptions that may prove to be inaccurate. Any material inaccuracies in these reserve estimates or underlying assumptions will materially affect the quantities and present value of our total reserves.”
Internal Controls Over Reserves Estimation Process
We utilize Cawley, a third-party reservoir engineering firm, as our independent reserves evaluator for 100% of our proved reserves base. In addition, we employ an internal reserve engineering department, which is led by our Chief Engineer, who is responsible for overseeing the preparation of our reserves estimates. Our Chief Engineer has a B.S. in petroleum engineering from Texas A&M University, over twenty years of oil and gas experience, including 15 years with a focus on reserve evaluation, and additional experience with acquisitions, operations and production engineering in multiple basins.
Our reserve engineering department meets with Cawley to review properties and discuss evaluation methods and assumptions used in the proved reserves estimates by Cawley, in accordance with our prescribed internal control procedures. As part of this process our reserve engineering department, including our Chief Engineer, reviews the technologies employed by Cawley in its preparation of our reserves estimates and confirms the adequacy of such technologies employed. Our internal controls over the reserves estimation process include verification of input data, as well as management review, such as, but not limited to the following:
| ∎ | comparison of historical expenses from the lease operating statements and workover authorizations for expenditure to the operating costs input; |
90
| ∎ | review of working interests and net revenue interests in our reserves database against our well ownership system; |
| ∎ | review of historical realized prices and Differentials from index prices as compared to the Differentials used in our reserves database; |
| ∎ | review of updated capital costs based on information from our operators and actual drilling and completion costs on recent activity; |
| ∎ | review of internal reserve estimates by well and by area by our internal reservoir engineer; |
| ∎ | discussion of material reserve variances among our internal reservoir engineer and our executive management; and |
| ∎ | review of a preliminary copy of the reserve report by executive management. |
Production, Price and Production Expenses
The price that we receive for the oil and natural gas produced from wells in which we hold interests is largely a function of market supply and demand. Demand is impacted by general economic conditions, weather and other seasonal conditions, including hurricanes and tropical storms. Over or under supply of oil or natural gas can result in substantial price volatility. Oil supply in the United States has grown over the past few years, and the supply of oil could impact oil prices in the United States if the supply outstrips domestic demand. Historically, commodity prices have been volatile, and we expect that volatility to continue in the future. A substantial or extended decline in oil or natural gas prices or poor drilling results could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, cash flows, quantities of oil and natural gas reserves that may be economically produced and our ability to access capital markets.
The table below sets forth information regarding our oil and natural gas production, realized prices and production costs for the periods indicated.
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Net Production | ||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
2,226 | 2,446 | 2,927 | |||||||||
| Central Rockies(1) |
210 | 153 | 136 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
2,436 | 2,599 | 3,063 | |||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
6,409 | 5,161 | 4,927 | |||||||||
| Central Rockies |
656 | 448 | 178 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
7,066 | 5,609 | 5,105 | |||||||||
| Total (MBoe) |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
3,295 | 3,306 | 3,748 | |||||||||
| Central Rockies |
319 | 228 | 166 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
3,614 | 3,534 | 3,914 | |||||||||
| Oil (Bbls) per day |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
6,097 | 6,683 | 8,021 | |||||||||
| Central Rockies |
576 | 418 | 372 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
6,673 | 7,101 | 8,393 | |||||||||
| Natural gas (Mcf) per day |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
17,560 | 14,101 | 13,498 | |||||||||
| Central Rockies |
1,797 | 1,224 | 489 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
19,357 | 15,325 | 13,987 | |||||||||
| Total (Boe) per day |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
9,024 | 9,033 | 10,270 | |||||||||
| Central Rockies |
875 | 622 | 454 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
9,899 | 9,655 | 10,724 | |||||||||
| (1) | Includes Denver-Julesburg and Powder River Basin wells. |
91
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Average Sales Prices: |
||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 62.34 | $ | 35.22 | $ | 51.29 | ||||||
| Effect of gain (loss) on realized oil derivative on average price (per Bbl) |
(5.37 | ) | 10.45 | 1.32 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Oil Net of Realized Oil Derivatives (per Bbl) |
56.97 | 45.67 | 52.61 | |||||||||
| Natural gas and NGLs (per Mcf) |
4.72 | 1.01 | 2.78 | |||||||||
| Effect of gain (loss) on realized natural gas derivatives on average price (per Mcf) |
(0.12 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Natural gas and NGLs net of realized natural gas derivative (per Mcf) |
4.60 | 1.01 | 2.78 | |||||||||
| Realized price on a Boe basis excluding realized commodity derivatives |
51.25 | 27.51 | 43.76 | |||||||||
| Effect of gain (loss) on realized commodity derivatives on average prices (per Boe) |
(3.85 | ) | 7.69 | 1.04 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Realized price on a Boe basis net of realized commodity derivatives |
47.40 | 35.20 | 44.80 | |||||||||
| Average Costs: |
||||||||||||
| Production expenses (per Boe) |
$ | 12.15 | $ | 11.81 | $ | 10.95 | ||||||
Drilling and Development Activity
The table below sets forth the number of gross and net productive and non-productive wells in which we owned an interest drilled in the periods indicated. The number of wells drilled refers to the number of wells completed at any time during the period, regardless of when drilling was initiated.
| NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| GROSS | NET | GROSS | NET | GROSS | NET | |||||||||||||||||||
| Exploratory Wells: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Productive Oil |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Productive Natural gas |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-productive |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Development Wells: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Productive Oil (1) |
243 | 6.55 | 241 | 3.96 | 384 | 11.78 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Productive Natural gas |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-productive |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total productive exploratory and development wells (1) |
243 | 6.55 | 241 | 3.96 | 384 | 11.78 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (1) | Includes royalty interests in 57 gross (0.08 net) wells drilled in 2021, 39 gross (0.11 net) wells drilled in 2020 and 66 gross (0.18 net) wells drilled in 2019. |
92
The table below sets forth summary information by location with respect to estimated productive oil wells as of August 31, 2022. Productive wells are classified as either oil or natural gas wells according to the predominant production stream. All of our productive wells as of August 31, 2022 were classified as oil wells, although they also produce natural gas.
| AS OF AUGUST 31, 2022 | ||||||||||||
| PRODUCTIVE WORKING INTEREST OIL WELLS |
AVERAGE WORKING INTEREST |
|||||||||||
| GROSS | NET | |||||||||||
| Combined Total: |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
5,120 | 118 | 2.3 | % | ||||||||
| Central Rockies (1) |
83 | 16 | 18.8 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
5,203 | 134 | 2.6 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| AS OF AUGUST 31, 2022 | ||||||||||||
| PRODUCTIVE ROYALTY INTEREST OIL WELLS |
AVERAGE ROYALTY INTEREST |
|||||||||||
| GROSS | NET | |||||||||||
| Combined Total: |
||||||||||||
| Williston Basin |
998 | 3 | 25 | % | ||||||||
| Central Rockies (1) |
— | — | — | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
998 | 3 | 25 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Includes Denver-Julesburg and Powder River Basin wells. |
As of August 31, 2022, we owned an interest in 292 gross (6.5 net) wells that were being drilled or completed, and an additional 460 gross (8.5 net) wells that had been permitted for development by our operating partners.
Acreage
The table below sets forth our estimated gross and net developed and undeveloped acreage by geographic area as of August 31, 2022.
| DEVELOPED ACREAGE | UNDEVELOPED ACREAGE |
TOTAL ACREAGE | ROYALTY ACRES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GROSS | NET | GROSS | NET | GROSS | NET | GROSS | NET | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Williston |
1,512,308 | 44,330 | 15,676 | 1,892 | 1,527,985 | 46,222 | 106,630 | 1,010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Rockies (1) |
7,127 | 110 | 9,600 | 87 | 16,727 | 197 | 640 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total |
1,519,435 | 44,440 | 25,276 | 1,979 | 1,544,712 | 46,419 | 107,270 | 1,011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Includes Denver-Julesburg and Powder River Basin acreage. |
Approximately 99% of our undeveloped acreage is held by production as of August 31, 2022, with 2,560 gross (279 net) acres and 1,000 gross (370 net) acres subject to potential expiration in 2022 and 2024, respectively.
Industry Operating Environment
We operate in a highly cyclical industry. Demand for oil and natural gas is cyclical and is subject to large and rapid fluctuations. This is primarily because the industry is driven by commodity demand and corresponding price increases. When oil and natural gas price increases occur, producers generally increase their capital expenditures, which generally results in greater revenues and profits. The increased capital expenditures also ultimately result in
93
greater production, which historically has resulted in increased supplies and reduced prices. For these reasons, our results of operations may fluctuate from quarter-to-quarter and from year-to-year, and these fluctuations may distort period-to-period comparisons of our results of operations.
The global energy mix is also transitioning to cleaner lower carbon sources and our business is not immune to these trends. In our view, energy transition will play out over the coming decades and oil and natural gas will still be a dominant source for affordable and reliable energy. We see the quality of our asset base, depth of inventory and competitive economics carrying us profitably through this transition.
We primarily engage in oil and natural gas development and production by participating on a proportionate basis alongside third-party interests in wells drilled and completed in spacing units that include our leasehold interests. In addition, we acquire wellbore interests in wells in which we do not hold the underlying leasehold interests from third parties unable or unwilling to participate in certain well proposals. We typically depend on our operators to propose, permit, and initiate the drilling and completion of wells. Prior to commencing drilling, our operators are required to provide all owners of working interests within the designated spacing unit the opportunity to participate in the drilling and completion costs and net revenues of the well to the extent of their pro-rata share of such interest within the spacing unit. We assess each drilling and completion opportunity on a case-by-case basis and participate in wells that are expected to meet a desired return based upon estimates of recoverable oil and natural gas, anticipated oil and natural gas prices, the expertise of the operator, and the anticipated completed well cost from each project, as well as other factors. Historically, we have participated pursuant to our working interest in a vast majority of the wells proposed to us. However, declines in oil prices typically reduce both the number of well proposals we receive and the proportion of well proposals in which we elect to participate. Our land, engineering and finance teams use our extensive database to make these economic decisions. Vitesse created customized data systems (vLuminis) that are integrated, centralized and utilized by our employees to evaluate development opportunities. These data systems maintain real time dashboards to monitor operators, rigs, well performance and costs. Given our large acreage footprint and substantial number of well participations, we believe we can make accurate economic drilling and completion decisions utilizing our data systems.
Historically, we have not managed our commodities marketing activities internally. Instead, our operators generally market and sell oil and natural gas produced from wells in which we have an interest. Our operators coordinate the transportation of our oil and natural gas production from our wells to appropriate pipelines or rail transport facilities pursuant to arrangements that they negotiate and maintain with various parties purchasing the production. We understand that our operating partners generally sell our production to a variety of purchasers at prevailing market prices under separately negotiated short-term contracts. Although we have historically relied on our operators for these activities, we may in the future seek to take a portion of our production in kind and internally manage the marketing activities for such production. The price at which our production is sold is generally tied to the spot market for oil or natural gas. The price at which our oil production is sold typically reflects a discount to the WTI benchmark price. This Differential primarily represents the transportation costs in moving the oil from wellhead to refinery and will fluctuate based on availability of pipeline, rail and other transportation methods. The price at which our natural gas production is sold may reflect either a discount or premium to the NYMEX benchmark price.
Although we plan to focus on a target asset class and deal size where we believe that competition and costs are reduced as compared to the broader oil and natural gas industry, the acquisition market for non-operated and operated properties remains intensely competitive, and we will compete with other oil and natural gas companies for acquisitions, some of which have substantially greater resources than us and may be able to pay more for properties.
There is currently only one public company with a focus on acquiring non-operated assets, with an enterprise value of approximately $3.1 billion as of June 30, 2022. Public companies that directly manage and operate assets are potentially net sellers of non-operated assets, which makes them potential partners and sources of deals for us.
Other sources of competition might come from new IPOs, which is a market that has been largely unavailable to non-operators, as evidenced by the fact that in the last 10 years there has not been a single traditional IPO of a
94
non-operated focused company. Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (“SPACs”) that seek to take advantage of the non-operated market dynamic are another source of potential competition. For example, on May 16, 2022, Grey Rock Investment Partners and Executive Network Partnering Corporation announced that they had entered into a definitive agreement to complete a business combination to form Granite Ridge Resources, Inc., a non-operated oil and natural gas company. New sources of capital like asset-backed securitizations and insurance company balance sheet investments have also made the non-operated sector a focus.
We believe our management is particularly suited to capitalize on this opportunity and generate attractive returns given our deep energy acquisition experience and relationships in the non-operated sector, which we believe will help us in deal-sourcing, asset selection, underwriting and financing.
Finally, the emerging impact of climate change activism, fuel conservation measures, governmental requirements for renewable energy resources, increasing demand for alternative forms of energy, and technological advances in energy generation devices may result in reduced demand for the oil and natural gas we produce.
Prior to completing an acquisition of non-operated working or royalty interests, we perform a title review on each tract to be acquired. Our title review is meant to confirm the quantum of non-operated working and royalty interest owned by a prospective seller, the property’s lease status and royalty amount as well as encumbrances or other related burdens.
In addition to our initial title work, operators often will conduct a thorough title examination prior to drilling a well. Should our title work uncover any further title defects, we will perform curative work with respect to such defects. We believe that the title to our assets is satisfactory in all material respects.
Our oil and natural gas properties are subject to customary royalty and other interests, liens under indebtedness, liens incident to operating agreements, liens for current taxes and other burdens, including other mineral encumbrances and restrictions. We expect that our indebtedness under our New Revolving Credit Facility, which will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, will also be secured by liens on substantially all our assets. We do not believe that any of these burdens materially interfere with the use of our properties or the operation of our business.
Winter weather events and conditions, such as ice storms, blizzards and freezing conditions, and lease stipulations can limit or temporarily halt the drilling and producing activities of our operators and other oil and natural gas operations. These constraints and the resulting shortages or high costs could delay or temporarily halt the operations of our operators and materially increase our operating and capital costs. Such seasonal anomalies can also pose challenges for meeting well drilling objectives and may increase competition for equipment, supplies and personnel during the spring and summer months, which could lead to shortages and increase costs or delay or temporarily halt our operators’ operations.
Regulation and Environmental Matters
Our operations are subject to various rules, regulations and limitations impacting the oil and natural gas acquisition, development and production industry as whole.
Regulation of Oil and Natural Gas Production
Our oil and natural gas development, production and related operations are subject to extensive rules and regulations promulgated by federal, state, tribal and local authorities and agencies. For example, North Dakota and Montana require permits for drilling operations, drilling bonds and reports concerning operations and impose other requirements relating to the development and production of oil and natural gas. Such states may also have statutes or regulations addressing conservation matters, including provisions for the unitization or pooling of oil and natural gas properties, limitations or prohibitions on the venting or flaring of natural gas, the location of wells, the method of drilling and casing wells, the surface use and restoration of properties upon which wells are drilled, the sourcing and disposal of water used in the process of drilling, completion and abandonment, the establishment of maximum rates of production from wells, and the regulation of spacing, plugging and abandonment of such wells. Moreover, the
95
current administration has indicated that it expects to impose additional federal regulations limiting access to and production from federal lands, although recent executive actions to pause drilling on federal lands have been subject to ongoing litigation. The effect of these regulations is to limit the amount of oil and natural gas that we can produce from our wells and to limit the number of wells or the locations at which we can drill. Moreover, many states impose a production or severance tax with respect to the production and sale of oil, natural gas and NGLs within their jurisdictions. Failure to comply with any such rules and regulations can result in substantial penalties. The regulatory burden on the oil and natural gas industry will most likely increase our cost of doing business and may affect our profitability. Because such rules and regulations are frequently amended or reinterpreted, we are unable to predict the future cost or impact of complying with such laws. Significant expenditures may be required to comply with governmental laws and regulations and may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Additionally, currently unforeseen environmental incidents may occur or past non-compliance with environmental laws or regulations may be discovered. Therefore, we are unable to predict the future costs or impact of compliance. Additional proposals and proceedings that affect the oil and natural gas industry are regularly considered by Congress, the states, FERC and the courts. We cannot predict when or whether any such proposals may become effective.
Regulation of Transportation of Oil
Sales of oil, condensate and NGLs are not currently regulated and are made at negotiated prices. Nevertheless, Congress could reenact price controls in the future. Our sales of oil are affected by the availability, terms and cost of transportation. The transportation of oil by common carrier pipelines is also subject to rate and access regulation. FERC regulates interstate oil pipeline transportation rates under the Interstate Commerce Act. In general, interstate oil pipeline rates must be cost-based, although settlement rates agreed to by all shippers are permitted and market-based rates may be permitted in certain circumstances. Effective January 1, 1995, FERC implemented regulations establishing an indexing system (based on inflation) for transportation rates for oil pipelines that allows a pipeline to increase its rates annually up to a prescribed ceiling, without making a cost-of-service filing. Every five years, FERC reviews the appropriateness of the index level in relation to changes in industry costs. On January 20, 2022, FERC established a new price index for the five-year period which commenced on July 1, 2021.
Intrastate oil pipeline transportation rates are subject to regulation by state regulatory commissions. The basis for intrastate oil pipeline regulation, and the degree of regulatory oversight and scrutiny given to intrastate oil pipeline rates varies from state to state. Insofar as effective interstate and intrastate rates are equally applicable to all comparable shippers, we believe that the regulation of oil transportation rates will not affect our operations in any way that is of material difference from those of our competitors who are similarly situated.
Further, interstate and intrastate common carrier oil pipelines must provide service on a non-discriminatory basis. Under this open access standard, common carriers must offer service to all similarly situated shippers requesting service on the same terms and under the same rates. When oil pipelines operate at full capacity, access is generally governed by pro-rationing provisions set forth in the pipelines’ published tariffs. Accordingly, we believe that access to oil pipeline transportation services generally will be available to us to the same extent as to our similarly situated competitors.
Regulation of Transportation and Sales of Natural Gas
Historically, the transportation and sale for resale of natural gas in interstate commerce has been regulated by FERC under the Natural Gas Act of 1938, the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978 and regulations issued under those statutes. In the past, the federal government has regulated the prices at which natural gas could be sold. While sales by producers of natural gas can currently be made at market prices, Congress could reenact price controls in the future.
Onshore gathering services, which occur upstream of FERC jurisdictional transmission services, are regulated by the states. Although FERC has set forth a general test for determining whether facilities perform a non-jurisdictional gathering function or a jurisdictional transmission function, FERC’s determinations as to the classification of facilities is done on a case-by-case basis. State regulation of natural gas gathering facilities generally includes various safety, environmental and, in some circumstances, nondiscriminatory take requirements. Although such regulation has not generally been affirmatively applied by state agencies, natural gas gathering may receive greater regulatory scrutiny in the future.
Intrastate natural gas transportation and facilities are also subject to regulation by state regulatory agencies, and certain transportation services provided by intrastate pipelines are also regulated by FERC. The basis for intrastate
96
regulation of natural gas transportation and the degree of regulatory oversight and scrutiny given to intrastate natural gas pipeline rates and services varies from state to state. Insofar as such regulation within a particular state will generally affect all intrastate natural gas shippers within the state on a comparable basis, we believe that the regulation of similarly situated intrastate natural gas transportation in any states in which we operate and ship natural gas on an intrastate basis will not affect our operations in any way that is of material difference from those of our competitors. Like the regulation of interstate transportation rates, the regulation of intrastate transportation rates affects the marketing of natural gas that we produce, as well as the revenues we receive for sales of our natural gas.
Environmental Matters
Our operations and properties are subject to extensive and changing federal, state and local laws and regulations relating to environmental protection, including the generation, storage, handling, emission, transportation and discharge of materials into the environment, and relating to safety and health. The recent trend in environmental legislation and regulation is generally toward stricter standards, and this trend will likely continue. These laws and regulations may:
| ∎ | require the acquisition of a permit or other authorization before construction or drilling commences and for certain other activities; |
| ∎ | limit or prohibit construction, drilling and other activities on certain lands lying within wilderness and other protected areas; and |
| ∎ | impose substantial liabilities for pollution resulting from our operations. |
The permits required for our operations may be subject to revocation, modification and renewal by issuing authorities. Governmental authorities have the power to enforce their rules and regulations, and violations can be subject to fines, injunctions, or both. In the opinion of management, we are in substantial compliance with current applicable environmental laws and regulations, and have no material commitments for capital expenditures to comply with existing environmental requirements. Nevertheless, changes in existing environmental laws and regulations or in interpretations thereof could have a significant impact on our company, as well as the oil and natural gas industry in general.
CERCLA, and comparable state statutes impose strict, joint and several liability on owners and operators of sites and on persons who disposed of or arranged for the disposal of “hazardous substances” found at such sites. It is not uncommon for the neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by the hazardous substances released into the environment. RCRA, and comparable state statutes, govern the disposal of “solid waste” and “hazardous waste” and authorize the imposition of substantial fines and penalties for noncompliance. Although CERCLA currently excludes petroleum from its definition of “hazardous substance,” state laws affecting our operations may impose clean-up liability relating to petroleum and petroleum related products. In addition, although the RCRA classifies certain oil field wastes as “non-hazardous,” such exploration and production wastes could be reclassified as hazardous wastes thereby making such wastes subject to more stringent handling and disposal requirements. Recent regulation and litigation that has been brought against others in the industry under the RCRA concern liability for earthquakes that were allegedly caused by injection of oil field wastes.
The ESA seeks to ensure that activities do not jeopardize endangered or threatened animal, fish and plant species, nor destroy or modify the critical habitat of such species. Under the ESA, exploration and production operations, as well as actions by federal agencies, may not significantly impair or jeopardize a covered species or its habitat. The ESA provides for criminal penalties for willful violations of the ESA. Other statutes that provide protection to animal and plant species and that may apply to our operators’ activities include, but are not necessarily limited to, the Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act, the Fishery Conservation and Management Act, the Migratory Bird Treaty Act and the National Historic Preservation Act. Although we believe that our operators are in substantial compliance with such statutes, any change in these statutes or any reclassification of a species as endangered or threatened could subject our company (directly or indirectly through our operators) to significant expenses to modify our operations or could force discontinuation of certain operations altogether.
The CAA controls air emissions from oil and natural gas production and natural gas processing operations, among other sources. The CAA regulations include NSPS for the oil and natural gas source category to address emissions of sulfur dioxide and VOCs, and a separate set of emission standards to address hazardous air pollutants frequently associated with oil and natural gas production and processing activities.
97
On November 2, 2021, EPA proposed to revise and add to the NSPS program rules. These rules, if adopted, could have a significant impact on the upstream and midstream oil and natural gas sectors. The proposed rule would impose further restrictions on methane and VOC emissions for new and modified facilities in the oil and natural gas sector. Methane is a greenhouse gas. The proposed rules also would regulate, for the first time under the NSPS program, existing oil and natural gas facilities. Specifically as it concerns existing sources, the EPA’s proposed new rule would require states to implement plans that meet or exceed federally established emission reduction guidelines for oil and natural gas facilities. Additionally, various states and groups of states have adopted or are considering adopting legislation, regulations or other regulatory initiatives that are focused on such areas as greenhouse gas cap and trade programs, carbon taxes, reporting and tracking programs, and restriction of emissions. At the international level, the United Nations-sponsored Paris Agreement calls for parties to set and achieve individually-determined greenhouse gas emission reduction goals every five years after 2020. While the United States withdrew from the Paris Agreement effective November 4, 2020, President Biden recommitted the United States to the Paris Agreement on January 20, 2021.
These regulations and proposals and any other new regulations requiring the installation of more sophisticated pollution control equipment or restrictions on operations could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The CWA imposes restrictions and controls on the discharge of produced waters and other pollutants into WOTUS. Permits must be obtained to discharge pollutants into state and federal waters and to conduct construction activities in waters and wetlands. The CWA and certain state regulations prohibit the discharge of produced water, sand, drilling fluids, drill cuttings, sediment and certain other substances related to the oil and natural gas industry into certain coastal and offshore waters without an individual or general National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System discharge permit. In addition, the CWA and analogous state laws require individual permits or coverage under general permits for discharges of storm water runoff from certain types of facilities. The meaning of WOTUS has been heavily litigated and the subject of rulemaking in recent years. Most recently, on January 24, 2022, the Supreme Court agreed to hear a case to determine the propriety of the “significant nexus” interpretation of the rule, which could further impact the scope of the definition of WOTUS. Regardless, the applicable WOTUS definition affects what CWA permitting or other regulatory obligations may be triggered during development and operation of our properties, and changes to the WOTUS definition could cause delays in development and/or increase the cost of development and operation of our properties. Some states also maintain groundwater protection programs that require permits for discharges or operations that may impact groundwater conditions.
The OPA amends and augments the oil spill provisions of the CWA and imposes certain duties and liabilities on certain “responsible parties” related to the prevention of oil spills and damages resulting from such spills in or threatening waters of the United States or adjoining shorelines. For example, operators of certain oil and natural gas facilities must develop, implement and maintain facility response plans, conduct annual spill training for certain employees and provide varying degrees of financial assurance. Owners or operators of a facility, vessel or pipeline that is a source of an oil discharge or that poses the substantial threat of discharge is one type of “responsible party” who is liable. The OPA applies joint and several liability, without regard to fault, to each liable party for oil removal costs and a variety of public and private damages. As such, a violation of the OPA has the potential to adversely affect our business.
The CAA, CWA and comparable state statutes provide for civil, criminal and administrative penalties for unauthorized discharges of oil and other pollutants and impose liability on parties responsible for those discharges, for the costs of cleaning up any environmental damage caused by the release and for natural resource damages resulting from the release.
The underground injection of oil and natural gas wastes are regulated by the Underground Injection Control program authorized by the SDWA. The primary objective of injection well operating requirements is to ensure the mechanical integrity of the injection apparatus and to prevent migration of fluids from the injection zone into underground sources of drinking water. Substantially all of the oil and natural gas production in which we have interest is developed from unconventional sources that require hydraulic fracturing as part of the completion process. Hydraulic fracturing involves the injection of water, sand and chemicals under pressure into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formation to stimulate gas production. Legislation to amend the SDWA to repeal the exemption for
98
hydraulic fracturing from the definition of “underground injection” and require federal permitting and regulatory control of hydraulic fracturing, as well as legislative proposals to require disclosure of the chemical constituents of the fluids used in the fracturing process, were proposed in recent sessions of Congress. Congress continues to consider legislation to amend the SDWA to address hydraulic fracturing operations. In addition, in 2020, the Supreme Court held that the CWA requires a discharge permit if the addition of pollutants through groundwater is the “functional equivalent” of a direct discharge from the point source into navigable waters. Costs may be associated with the treatment of wastewater and/or developing and implementing storm water pollution prevention plans. If in the future CWA permitting is required for saltwater injection wells as a result of the 2020 Supreme Court ruling, the costs of permitting and compliance for injection well operations by the companies that operate the Properties could increase.
Scrutiny of hydraulic fracturing activities continues in other ways. The federal government is currently undertaking several studies of hydraulic fracturing’s potential impacts. Several states, including Montana and North Dakota where our properties are located, have also proposed or adopted legislative or regulatory restrictions on hydraulic fracturing. A number of municipalities in other states, including Colorado, have enacted bans on hydraulic fracturing. In Colorado, the Colorado Supreme Court has ruled the municipal bans were preempted by state law. However, the Colorado legislature subsequently enacted “SB 101” that gave significant local control over oil and natural gas well head operations. Municipalities in Colorado have enacted local rules restricting oil and natural gas operations based on SB 101. We cannot predict whether any other legislation will ever be enacted and if so, what its provisions would be. If additional levels of regulation and permits were required through the adoption of new laws and regulations at the federal or state level, it could lead to delays, increased operating costs and process prohibitions that would materially adversely affect our revenue and results of operations.
The NEPA establishes a national environmental policy and goals for the protection, maintenance and enhancement of the environment and provides a process for implementing these goals within federal agencies. A major federal agency action having the potential to significantly impact the environment requires review under NEPA. Many of the activities of our third-party operators are covered under NEPA. Some activities are subject to robust NEPA review which could lead to delays and increased costs that could materially adversely affect our revenues and results of operations. Other activities are covered under categorical exclusions which results in a shorter NEPA review process. In April 2022, the Biden Administration finalized a rule to undue changes to NEPA enacted under the Trump Administration. The April 2022 rule promulgation is considered phase one of a two-phase review of the 2020 NEPA Rule that was announced by the Biden Administration to emphasize the need to review federal actions for climate change and environmental justice impacts, among other factors. These new and (if enacted) additional anticipated changes to the NEPA review process would affect the assessment of projects ranging from oil and gas leasing to development on public and Indian lands.
Significant studies and research have been devoted to climate change, and climate change has developed into a major political issue in the United States and globally. Certain research suggests that greenhouse gas emissions contribute to climate change and pose a threat to the environment. Recent scientific research and political debate has focused in part on carbon dioxide and methane incidental to oil and natural gas exploration and production.
In response to findings that emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other GHGs present an endangerment to public health and the environment, the EPA has adopted regulations under existing provisions of the CAA that, among other things, require preconstruction and operating permits for GHG emissions from certain large stationary sources that already emit conventional pollutants above a certain threshold. In addition, the EPA has adopted rules requiring the monitoring and reporting of GHG emissions from specified onshore and offshore oil and gas production sources in the United States on an annual basis, which may include operations on our properties.
Congress has from time to time considered legislation to reduce emissions of GHGs. Most recently, in August 2022, Congress passed, and President Biden signed, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 establishes a program designed to reduce methane emissions from certain oil and natural gas facilities, which includes a charge on methane emissions above certain thresholds. In addition, a number of state and regional efforts have emerged that are aimed at tracking or reducing GHG emissions by means of cap and trade programs. These
99
programs typically require major sources of GHG emissions to acquire and surrender emission allowances in return for emitting those GHGs. Although it is not possible at this time to predict how legislation or new regulations that may be adopted to address GHG emissions would impact us, any future laws and regulations imposing reporting obligations on, or limiting emissions of GHGs from, operators’ equipment and operations could require them to incur costs to reduce emissions of GHGs associated with their operations. For example, although EPA regulations implementing the methane charge requirements associated with the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 have not yet been developed, the future implementation of these requirements could result in direct costs for our operators based on methane emissions above set thresholds or require capital expenditure by our operators to reduce their emissions. In addition, substantial limitations on GHG emissions could adversely affect demand for the oil and gas produced from our properties. For a more detailed discussion of the risks associated with climate change legislation or regulation, see “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Legal and Regulatory Matters—The adoption of climate change legislation or regulations restricting emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases could result in increased operating costs and reduced demand for the oil and natural gas we produce.”
In addition, spurred by increasing concerns regarding climate change, the oil and natural gas industry faces growing demand for corporate transparency and a demonstrated commitment to sustainability goals. The industry could also be impacted by governmental initiatives aimed at encouraging fuel conservation and a shift to alternative energy sources. For more information, see “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to our Business—Increased attention to ESG matters may impact our business” and “—Fuel conservation measures and related governmental initiatives, technological advances and negative shift in market perception towards the oil and natural gas industry could reduce demand for oil and natural gas.”
Finally, climate changes may have significant physical effects, such as increased frequency and severity of storms, freezes, floods, drought, hurricanes and other climatic events; if any of these effects were to occur, they could have an adverse effect on the operations of our operating partners, and ultimately, our business.
As of August 31, 2022, we had 38 full time employees. We may hire additional personnel as appropriate. We also may use the services of independent consultants and contractors to perform various professional services. We are focused on attracting, engaging, developing, retaining and rewarding top talent. We strive to enhance the economic and social well-being of our employees and the communities in which we operate. We are committed to providing a welcoming, inclusive environment for our workforce, with excellent training and career development opportunities to enable employees to thrive and achieve their career goals.
Our principal executive offices are located at 9200 E Mineral Ave, Suite 200, Centennial, Colorado 80112. Our current office space consists of approximately 15,000 square feet of leased space. We believe our current office space is sufficient to meet our needs and that additional office space can be obtained if necessary.
From time to time we are subject to legal, administrative and environmental proceedings before various courts, arbitration panels and governmental agencies concerning claims arising in the ordinary course of business. These proceedings include certain contract disputes, additional environmental reviews and investigations, audits and pending judicial matters. Based on our current knowledge, we believe that the amount or range of reasonably possible losses will not, either individually or in the aggregate, materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The results of any litigation cannot be predicted with certainty, and an unfavorable resolution in any legal proceedings could materially affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Regardless of the outcome, litigation can have an adverse impact on us because of defense and settlement costs, diversion of management resources and other factors.
100
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion of our results of operations and financial condition together with our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements and the notes thereto included under the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements,” as well as the discussion in the section entitled “Business.” This discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. The forward-looking statements are not historical facts, but rather are based on current expectations, estimates, assumptions and projections about the oil and natural gas industry and our business and financial results. Our actual results could differ materially from the results contemplated by these forward-looking statements due to a number of factors, including those discussed in the sections entitled “Risk Factors” and “Cautionary Statement Concerning Forward-Looking Statements.”
Our business strategy going forward is focused on creating long-term stockholder value through the acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas assets at attractive rates of return, while maintaining a strong balance sheet and distributing a portion of our free cash flow to our stockholders in the form of a regular cash dividend on a quarterly basis. We invest in non-operated minority working and mineral interests in oil and natural gas properties with our core area of focus in the Bakken and Three Forks formations of Williston Basin of North Dakota and Montana, with the majority of horizontal drilling activity occurring in Dunn, McKenzie, Mountrail, and Williams Counties, North Dakota. Approximately 75% of our 46,222 net acres as of August 31, 2022 was in the above counties of the Bakken and Three Forks formations and approximately 99% of our acreage in the Williston Basin was held by production. As of August 31, 2022, we had a working interest in 5,120 gross (118.3 net) productive wells and 223 gross (4.4 net) wells that were being drilled or completed, and an additional 409 gross (8.4 net) wells that had been permitted for development by our operators. Our estimated proved reserves in North Dakota and Montana as of November 30, 2021 were 39,609 MBoe (70% oil), which represented 93% of our total estimated proved reserves and contributed average production of 9,394 Boe per day during the month ended November 30, 2021. We also have interests in wells in the Denver-Julesburg Basin located in Colorado and Wyoming and the Powder River Basin located in Wyoming.
Our financial and operating performance for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 included the following:
| ∎ | Oil and natural gas sales of $224.7 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022. |
| ∎ | Cash flows from operations of $108.4 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022. |
| ∎ | Net income of $55.5 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022, which includes a non-cash unrealized loss on derivatives of $7.9 million. |
| ∎ | Modest decline in outstanding indebtedness from $68.0 million at November 30, 2021 to $66.0 million at August 31, 2022. |
| ∎ | Acquisitions of working interests in wellbores of approximately $20.3 million that are expected to be completed in the next twelve months. |
| ∎ | Distributions of $42.0 million to our equity holders for the nine months ended August 31, 2022. |
Our financial and operating performance for the year ended November 30, 2021 included the following:
| ∎ | Oil and natural gas sales of $185.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2021. |
| ∎ | Cash flows from operations of $87.0 million for the year ended November 30, 2021. |
| ∎ | Net income of $18.1 million for the year ended November 30, 2021. |
| ∎ | Proved reserves of 42.5 MMBoe at November 30, 2021, as estimated by our third-party reserve engineers using SEC guidelines. |
| ∎ | Reduced outstanding indebtedness from $98.5 million at November 30, 2020 to $68.0 million at November 30, 2021. |
| ∎ | Paid a monthly distribution of $6.0 million to our equity holders in October and November of 2021. |
101
Industry Trends Impacting Our Business
Commodity prices are the most significant factor impacting our acquisition and divestiture strategy, as well as the decisions of our operators in conducting their operations. Prices for oil and natural gas can be highly volatile. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic and efforts to mitigate the spread of the disease, combined with OPEC actions in early 2020, led to spot and future prices of oil and natural gas falling to historic lows during the second quarter of 2020 and remaining depressed through much of 2020. Our operators in the Williston Basin responded by significantly decreasing drilling and completion activity, and by shutting in or curtailing production from a significant number of producing wells. Commodity prices, however, quickly reached pre-pandemic levels in the second half of 2021, and during the first nine months of 2022 only further accelerated upward, in part as a result of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine may have further global economic consequences, including disruptions of the global energy markets and the amplification of inflation and supply chain constraints, partially due to sanctions by the European Union, the United Kingdom and the United States on imports of oil and gas from Russia. On October 5, 2022, OPEC also announced a 2 MMBbl/d reduction in production quotas, the organization’s largest cut since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
As a result of such commodity price volatility, which we expect to continue for the remainder of 2022 and into 2023, our earnings and operating cash flows can vary substantially, and are subject to external factors over which the company has no control. While we do hedge a substantial portion of our production, we are still significantly subject to movements in commodity prices. Such volatility can make it difficult to predict future effects on our company and the decisions of our operators. Factors that we expect will continue to impact commodity prices include product demand connected with global economic conditions, industry production and inventory levels, the United States Department of Energy’s future planned repurchases (or additional possible releases) of oil from the strategic petroleum reserve, technology advancements, production quotas or other actions imposed by OPEC countries, actions of regulators, and regional supply interruptions or fears thereof that may be caused by military conflicts (including invasion), civil unrest, pandemic or political uncertainty. Any of the foregoing can have a substantial impact on the prices of oil and natural gas, which in turn impacts the decision of our operators to drill and extract resources. Despite such commodity price volatility, we expect that our cash flow from operations and borrowing availability under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility or New Revolving Credit Facility, as applicable, will allow us to meet our liquidity needs for the next twelve months.
We derive our revenues from the sale of oil and natural gas produced from our properties. Revenues are a function of the volume produced, the prevailing market price at the time of sale, oil quality, Btu content and transportation costs to market. We use derivative instruments to hedge future sales prices on a substantial, but varying, portion of our oil production. We currently do not hedge natural gas production due to the mismatch between our operators’ pricing formulas and settlement mechanics on natural gas hedges. We expect our derivative activities will help us achieve more predictable cash flows and reduce our exposure to downward price fluctuations. The use of derivative instruments has in the past, and may in the future, prevent us from realizing the full benefit of upward price movements but also mitigates the effects of declining price movements.
Principal Components of Our Cost Structure
Commodity price differentials. The price differential between our well head price for oil and the WTI benchmark price is primarily driven by the cost to transport oil via train, pipeline or truck to refineries. The price differential between our well head price for natural gas and the NYMEX benchmark price is primarily driven by gathering, processing and transportation costs.
Gain (loss) on commodity derivatives, net. We utilize commodity derivative financial instruments to reduce our exposure to fluctuations in the prices of oil and gas. Gain (loss) on commodity derivatives, net is comprised of (1) cash gains and losses we recognize on settled commodity derivatives during the period, and (2) non-cash mark-to-market gains and losses we incur on commodity derivative instruments outstanding at period-end.
Production expenses. Production expenses are daily costs incurred to bring oil and natural gas out of the ground and to the market, together with the daily costs incurred to maintain our producing properties. Such costs also include field personnel compensation, saltwater disposal, utilities, maintenance, repairs and servicing expenses related to our oil and natural gas properties.
102
Production taxes. Production taxes are paid on produced oil and natural gas based on a percentage of revenues from products sold at market prices (not hedged prices) or at fixed rates established by federal, state or local taxing authorities. We seek to take full advantage of all credits and exemptions in our various taxing jurisdictions. In general, the production taxes we pay correlate to the changes in oil and natural gas revenues.
Depreciation, depletion, amortization and accretion. Depreciation, depletion, amortization and accretion includes the systematic expensing of the capitalized costs incurred to acquire, explore and develop oil and natural gas properties. As a successful efforts company, costs associated with the acquisition, drilling, and equipping of successful exploratory wells and costs of successful and unsuccessful development wells are capitalized. Accretion expense relates to the passage of time of our asset retirement obligations.
General and administrative expenses. General and administrative expenses include overhead, including payroll and benefits for our corporate staff, costs of maintaining our headquarters, costs of managing our acquisition and development operations, franchise taxes, audit and other professional fees and legal compliance.
Interest expense. We finance a portion of our working capital requirements, capital expenditures and acquisitions with borrowings under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility. As a result, we incur interest expense that is affected by both fluctuations in interest rates and our financing decisions. We do not capitalize any portion of the interest paid on applicable borrowings. Given rising interest rates, we could incur increased interest expense in the future, which would be funded from cash flow from operations. Higher interest rates are not expected to have any material impact on our financial condition given our conservative debt levels, or direct impacts on our balance sheet. We include the amortization of deferred financing costs, commitment fees and annual agency fees as interest expense.
Impairment expense. Under the successful efforts method of accounting, we review our oil and natural gas properties for impairment whenever events and circumstances indicate that a decline in the recoverability of their carrying value may have occurred. Whenever we conclude the carrying value may not be recoverable, we estimate the expected undiscounted future net cash flows of our oil and natural gas properties using proved and risked probable and possible reserves based on our development plans and best estimate of future production, commodity pricing, reserve risking, gathering, processing and transportation deductions, production tax rates, lease operating expenses and future development costs. We compare such undiscounted future net cash flows to the carrying amount of the oil and natural gas properties in each depletion pool to determine if the carrying amount is recoverable. If the undiscounted future net cash flows exceed the carrying amount of the aggregated oil and natural gas properties, no impairment is recorded. If the carrying amount of the oil and natural gas properties exceeds the undiscounted future net cash flows, we will record an impairment expense to reduce the carrying value to fair value as of the balance sheet date. The factors used to determine fair value may include, but are not limited to, recent sales prices of comparable properties, indications from marketing activities, the present value of future revenues, net of estimated operating and development costs using estimates of reserves, future commodity pricing, future production estimates, anticipated capital expenditures and various discount rates commensurate with the risk and current market conditions associated with realizing the projected cash flows.
Income tax expense. Vitesse Energy is a limited liability company. Accordingly, no provision for income taxes has been recorded, as the income, deductions, expenses, and credits of Vitesse Energy are reported on the income tax returns of Vitesse Energy’s members.
Selected Factors That Affect Our Operating Results
Our revenues, cash flows from operations and future growth depend substantially upon:
| ∎ | the timing and success of drilling and production activities by our operating partners; |
| ∎ | the prices and the supply and demand for oil, natural gas and NGLs; |
| ∎ | the quantity of oil and natural gas production from the wells in which we participate; |
| ∎ | changes in the fair value of the derivative instruments we use to reduce our exposure to fluctuations in the price of oil; |
| ∎ | our ability to continue to identify and acquire high-quality acreage and drilling opportunities; and |
| ∎ | the level of our operating expenses. |
103
In addition to the factors that affect companies in our industry generally, the location of substantially all of our acreage and wells in the Williston, Denver-Julesburg and Powder River Basins subjects our operating results to factors specific to these regions. These factors include the potential adverse impact of weather on drilling, production and transportation activities, particularly during the winter and spring months, as well as infrastructure limitations, transportation capacity, regulatory matters and other factors that may specifically affect one or more of these regions.
The price of oil can vary depending on the market in which it is sold and the means of transportation used to transport the oil to market, particularly in the Williston Basin where a substantial majority of our revenues are derived. Additional pipeline infrastructure has increased takeaway capacity in the Williston Basin which has improved wellhead values in the region.
The price at which our oil production is sold typically reflects a discount to the NYMEX benchmark price. The price at which our natural gas production is sold may reflect either a discount or premium to the NYMEX benchmark price. Thus, our operating results are also affected by changes in the oil price differentials between the applicable benchmark and the sales prices we receive for our oil production. Our oil price differential to the NYMEX benchmark price during 2021 was $3.58 per barrel, as compared to $5.88 per barrel in 2020. Our net realized gas price during 2021 was $4.72 per Mcf, representing 129% realization relative to average Henry Hub pricing, compared to a net realized gas price of $1.01 per Mcf during 2020, representing a 50% realization relative to average Henry Hub pricing. Fluctuations in our price differentials and realizations are due to several factors such as gathering, processing and transportation costs, takeaway capacity relative to production levels, regional storage capacity, and seasonal refinery maintenance temporarily depressing demand.
Another significant factor affecting our operating results is drilling costs. The cost of drilling wells can vary significantly, driven in part by volatility in commodity prices that can substantially impact the level of drilling activity. Generally, higher oil prices have led to increased drilling activity, with the increased demand for drilling and completion services driving these costs higher. Lower oil prices have generally had the opposite effect. In addition, individual components of the cost can vary depending on numerous factors such as the length of the horizontal lateral, the number of fracture stimulation stages, and the type and amount of proppant. During 2021, the average authorization for expenditure cost for wells we elected to participate in was $7.0 million, compared to $7.3 million for the wells we elected to participate in during 2020.
The price that we receive for the oil and natural gas we produce is largely a function of market supply and demand. Because our oil and gas revenues are heavily weighted toward oil, we are more significantly impacted by changes in oil prices than by changes in the price of natural gas. World-wide supply in terms of output, especially production from properties within the United States, the production quota set by OPEC, the war between Russia and Ukraine and the strength of the U.S. dollar can adversely impact oil prices.
Historically, commodity prices have been volatile and we expect the volatility to continue in the future. Factors impacting the future oil supply balance are world-wide demand for oil, as well as the growth in domestic oil production.
Prices for various quantities of oil, natural gas and NGLs that we produce significantly impact our revenues and cash flows. The following table lists average NYMEX prices for oil and natural gas for the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019.
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| Average NYMEX Prices (1) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 65.97 | $ | 40.20 | $ | 56.20 | ||||||
| Natural Gas (per MMBtu) |
3.79 | 2.00 | 2.70 | |||||||||
| (1) | Based on average NYMEX closing prices. |
104
The average 2021 NYMEX oil price was $65.97 per barrel or 64% higher than the average NYMEX price per barrel in 2020. Our settled derivatives decreased our realized oil price per barrel by $5.37 in 2021 and increased our realized oil price per barrel by $10.45 in 2020. Our average 2021 realized oil price per barrel after reflecting settled derivatives was $56.97 compared to $45.67 in 2020. The average 2021 NYMEX natural gas price was $3.79 per Mcf, or 90% higher than the average NYMEX price per Mcf in 2020. Our settled derivatives decreased our realized natural gas price per Mcf by $0.12 in 2021 with no natural gas hedges in place in 2020. Our 2021 realized gas price per Mcf after reflecting settled derivatives was $4.60 compared to $1.01 in 2020, which was primarily driven by higher NYMEX pricing for natural gas and gas realizations, which was partially offset by a decrease in settled derivatives.
We employ a hedging program that mitigates the risk associated with fluctuations in commodity prices. For detailed information on our commodity hedging program, see “—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk” and Note 6 (“Derivative Instruments”) to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Note 6 (“Derivative Instruments”) to the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
Nine Months Ended August 31, 2022 Compared with Nine Months Ended August 31, 2021
The following table sets forth selected operating data for the periods indicated.
| NINE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31 |
INCREASE (DECREASE) |
|||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except per unit data) | 2022 | 2021 | AMOUNT | PERCENT | ||||||||||||
| Operating Results: |
||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 179,177 | $ | 106,986 | $ | 72,191 | 67 | % | ||||||||
| Natural gas |
45,510 | 17,496 | 28,014 | 160 | % | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 224,687 | $ | 124,482 | $ | 100,205 | 80 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||||||
| Production |
$ | 35,179 | $ | 32,591 | $ | 2,588 | 8 | % | ||||||||
| Production taxes |
17,828 | 10,082 | 7,746 | 77 | % | |||||||||||
| General and administrative |
11,496 | 7,704 | 3,792 | 49 | % | |||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
46,310 | 45,476 | 834 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
7,539 | 814 | 6,725 | 826 | % | |||||||||||
| Interest Expense |
$ | 2,847 | $ | 2,517 | $ | 329 | 13 | % | ||||||||
| Commodity Derivative Gain (Loss) |
$ | (47,990 | ) | $ | (32,934 | ) | $ | (15,056 | ) | 46 | % | |||||
| Production Data: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
1,869 | 1,830 | 39 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
5,304 | 5,191 | 112 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined volumes (MBoe) |
2,753 | 2,695 | 58 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| Daily combined volumes (Boe/d) |
10,048 | 9,836 | 211 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| Average Realized Prices before Hedging: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 95.86 | $ | 58.46 | $ | 37.40 | 64 | % | ||||||||
| Natural gas (per Mcf) |
8.58 | 3.37 | 5.21 | 155 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined (per Boe) |
81.61 | 46.19 | 35.43 | 77 | % | |||||||||||
| Average Realized Prices with Hedging: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 74.69 | $ | 54.84 | $ | 19.85 | 36 | % | ||||||||
| Natural gas (per Mcf) |
8.47 | 3.36 | 5.11 | 152 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined (per Boe) |
67.03 | 43.71 | 23.32 | 53 | % | |||||||||||
| Average Costs (per Boe): |
||||||||||||||||
| Production |
$ | 12.78 | $ | 12.09 | $ | 0.69 | 6 | % | ||||||||
| Production taxes |
6.48 | 3.74 | 2.73 | 73 | % | |||||||||||
| General and administrative |
4.18 | 2.86 | 1.32 | 46 | % | |||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
16.82 | 16.87 | (0.05 | ) | 0 | % | ||||||||||
105
Oil and Natural Gas Revenue and Volumes. Oil and natural gas revenue increased to $224.7 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $124.5 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. The increase in oil and natural gas revenue was due to an 77% increase in the average realized prices per Boe before hedging and a 2% increase in production volumes. The increase in average realized prices per Boe before hedging increased oil and natural gas revenue by approximately $95.5 million, while the increase in production volumes increased oil and natural gas revenue by approximately $4.7 million.
Our oil price differential to the WTI benchmark price for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 was $1.10 per barrel, as compared to $3.72 per barrel for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. Our net realized gas price for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 was $8.58 per Mcf, representing a 136% realization relative to average NYMEX pricing, compared to a net realized gas price of $3.37 per Mcf during the nine months ended August 31, 2021, representing a 109% realization relative to average NYMEX pricing. Fluctuations in our price differentials and realizations are due to several factors such as NGL value net of processing costs, gathering and transportation fees, takeaway capacity relative to production levels, regional storage capacity, and seasonal refinery maintenance temporarily depressing demand. The exact impact of each of these items is difficult to quantify as each of our operators pass through these costs in a different manner. Some operators may deduct these costs directly from our revenues, while other operators may invoice them to us as lease operating expenses.
Production Expense. Production expense generally includes lease operating, transportation and gathering expenses related to the operations of wells and are comprised of fixed, variable and semi-variable costs. Each operating partner reports these costs to us differently. Some operators may deduct these costs directly from our revenues, while other operators may invoice them to us as lease operating expenses. Production expense increased to $12.78 per Boe for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $12.09 per Boe for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. The increase per Boe for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 compared with the nine months ended August 31, 2021 was primarily related to higher expense related to workovers and lease maintenance costs related to a severe late winter snow storm that occurred in April 2022 and higher oil and natural gas prices driving up field labor and maintenance costs. Workover expenses were $1.7 million higher for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 as operators increased workovers to increase oil and gas production from existing wells to take advantage of increased oil and natural gas prices, as compared to the nine months ended August 31, 2021.
Production Tax Expense. Total production taxes increased to $17.8 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $10.1 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. Production taxes are primarily based on oil revenue and gas production excluding gains and losses associated with hedging activities. Production taxes as a percentage of oil and natural gas sales before hedging adjustments were 7.9% and 8.1% for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The decrease in the production tax rate for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 was due to a larger percentage of our revenue during the period coming from natural gas sales, which are taxed at a lower rate than oil sales in North Dakota.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense increased to $11.5 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $7.7 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. General and administrative expense on a per Boe basis increased to $4.18 for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $2.86 for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. We incurred approximately $3.0 million ($1.07 per Boe) of non-recurring costs related to becoming a public entity during the nine months ended August 31, 2022. The additional increase in general and administrative expense was due to increased employee costs and legal fees related to litigation against one of our operators for withholding excessive deductions against our revenues.
Depreciation, Depletion and Amortization (“DD&A”). DD&A increased slightly to $46.3 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 compared with $45.5 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. The increase of $0.8 million was the result of a 2% increase in production, partially offset by a slight decrease in the DD&A rate for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 compared with the nine months ended August 31, 2021. The increase in production accounted for a $1.0 million increase in DD&A expense while the decrease in the DD&A rate accounted for a $0.2 million decrease in DD&A expense.
Unit-based Compensation. Unit-based compensation expense is recorded for in-substance call options granted to the founding members of management which are classified as liabilities and recorded at estimated fair value at each period end. Unit-based compensation expense is also recognized for management incentive units granted to other employees
106
which are classified as liabilities until the holder has borne the risk of unit ownership. Unit-based compensation expense is recorded as these units vest and expense or contra-expense is recognized as the estimated fair value of the liability changes with market conditions. Unit-based compensation expense increased to $7.5 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $0.8 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021 primarily due to increased oil and gas prices causing the estimated fair value of the liabilities to increase.
Interest Expense. Interest expense increased slightly to $2.8 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 from $2.5 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. The slight increase for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 was due to a higher SOFR due to increased Federal Reserve rates, partially offset by a lower average outstanding debt balance on our Existing Revolving Credit Facility for the nine month period ended August 31, 2022 as compared to the nine month period ended August 31, 2021.
Commodity Derivative Gain (Loss). Commodity derivative loss was $48.0 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 compared with a loss of $32.9 million for the nine months ended August 31, 2021. Gain (loss) on commodity derivatives is comprised of (1) cash gains and losses we recognize on settled commodity derivative instruments during the period, and (2) unsettled gains and losses we incur on commodity derivative instruments outstanding at period-end. The increase in the commodity derivative loss of $15.1 million was primarily attributable to an increase in the average WTI oil price to $96.96 for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 compared to $62.18 for the nine months ended August 31, 2021.
The mark-to-market fair value of the unsettled commodity derivative instruments will generally be inversely related to the price movement of the underlying commodity. If commodity price trends reverse from period to period, prior unrealized gains may become unrealized losses and vice versa. These unrealized gains and losses will impact our net income in the period reported. The mark-to-market fair value can create non-cash volatility in our reported earnings during periods of commodity price volatility. We have experienced such volatility in the past and are likely to experience it in the future. Gains on our derivatives generally indicate lower oil revenues in the future, while losses indicate higher future oil revenues.
The table below summarizes our commodity derivative gains and losses that were recorded in the periods presented:
| NINE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31, |
||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Realized gain (loss) on commodity derivatives (1) |
$ | (40,138 | ) | $ | (6,671 | ) | ||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on commodity derivatives (1) |
(7,852 | ) | (26,263 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total commodity derivative gain (loss) |
$ | (47,990 | ) | $ | (32,934 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Realized and unrealized gains and losses on commodity derivatives are presented herein as separate line items but are combined for a total commodity derivative gain (loss) in the condensed consolidated statements of operations included in this Information Statement. Management believes the separate presentation of the realized and unrealized commodity derivative gains and losses is useful because the realized cash settlement portion provides a better understanding of our hedge position. |
For the nine months ended August 31, 2022, approximately 58% of our oil volumes and 11% of our natural gas volumes were subject to financial hedges, which resulted in a realized loss on oil derivatives of $39.6 million and a realized loss on natural gas derivatives of $0.6 million after settlements. For the nine months ended August 31, 2021, approximately 49% of our oil volumes and 3% of our natural gas volumes were covered by financial hedges, which resulted in a realized loss on oil derivatives of $6.6 million and a realized loss on natural gas derivatives of $0.1 million after settlements.
107
Year Ended November 30, 2021 Compared with Year Ended November 30, 2020
The following table sets forth selected operating data for the periods indicated.
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, |
INCREASE (DECREASE) |
|||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except per unit data) | 2021 | 2020 | AMOUNT | PERCENT | ||||||||||||
| Operating Results: |
||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 151,838 | $ | 91,542 | $ | 60,296 | 66 | % | ||||||||
| Natural gas |
33,340 | 5,688 | 27,652 | 486 | % | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 185,178 | $ | 97,230 | $ | 87,948 | 90 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||||||
| Production |
$ | 43,910 | $ | 41,731 | $ | 2,179 | 5 | % | ||||||||
| Production taxes |
14,535 | 9,173 | 5,362 | 58 | % | |||||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,581 | 9,196 | 1,385 | 15 | % | |||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
60,846 | 58,307 | 2,539 | 4 | % | |||||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties |
— | 13,200 | (13,200 | ) | *nm | |||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
1,409 | (544 | ) | 1,953 | *nm | |||||||||||
| Interest Expense |
$ | 3,207 | $ | 4,679 | $ | (1,472 | ) | (31 | )% | |||||||
| Commodity Derivative Gain (Loss) |
$ | (32,590 | ) | $ | 29,633 | $ | (62,223 | ) | (210 | )% | ||||||
| Production Data: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
2,436 | 2,599 | (163 | ) | (6 | )% | ||||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
7,065 | 5,609 | 1,456 | 26 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined volumes (MBoe) |
3,613 | 3,534 | 79 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| Daily combined volumes (Boe/d) |
9,899 | 9,655 | 244 | 3 | % | |||||||||||
| Average Realized Prices before Hedging: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 62.34 | $ | 35.22 | $ | 27.12 | 77 | % | ||||||||
| Natural gas (per Mcf) |
4.72 | 1.01 | 3.71 | 367 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined (per Boe) |
51.25 | 27.51 | 23.74 | 86 | % | |||||||||||
| Average Realized Prices with Hedging: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 56.97 | $ | 45.67 | $ | 11.30 | 25 | % | ||||||||
| Natural gas (per Mcf) |
4.60 | 1.01 | 3.59 | 355 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined (per Boe) |
47.40 | 35.20 | 12.20 | 35 | % | |||||||||||
| Average Costs (per Boe): |
||||||||||||||||
| Production |
$ | 12.15 | $ | 11.81 | $ | 0.34 | 3 | % | ||||||||
| Production taxes |
4.02 | 2.60 | 1.42 | 55 | % | |||||||||||
| General and administrative |
2.93 | 2.60 | 0.33 | 13 | % | |||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
16.84 | 16.50 | 0.34 | 2 | % | |||||||||||
| * | Not meaningful |
Oil and Natural Gas Revenue and Volumes. Oil and natural gas revenue increased to $185.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 from $97.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2020. The increase in oil and natural gas revenue was due to an 86% increase in the average realized prices per Boe before hedging, along with a 2% increase in production volumes for the year ended November 30, 2021. The increase in average realized prices per Boe before hedging increased oil and natural gas revenue by approximately $83.9 million, while the increase in production volumes increased oil and natural gas revenue by approximately $4.0 million.
Our oil price differential to the WTI benchmark price during the year ended November 30, 2021 was $3.58 per barrel, as compared to $5.88 per barrel during the year ended November 30, 2020. Our net realized natural gas price during the year ended November 30, 2021 was $4.72 per Mcf, representing a 129% realization relative to average NYMEX pricing, compared to a net realized natural gas price of $1.01 per Mcf during the year ended November 30, 2020, representing a 50% realization relative to average NYMEX pricing. Fluctuations in our price
108
differentials and realizations are due to several factors such as NGL value net of processing costs, gathering and transportation fees, takeaway capacity relative to production levels, regional storage capacity, and seasonal refinery maintenance temporarily depressing demand. The exact impact of each of these items is difficult to quantify as each of our operators pass through these costs in a different manner. Some operators may deduct these costs directly from our revenues while other operators may invoice them directly to us as lease operating expenses.
Production Expense. Production expense increased to $12.15 per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2021 from $11.81 per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2020. The slight increase per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2021 compared with the year ended November 30, 2020 was primarily related to higher expense related to workovers and higher costs related to added natural gas gathering and processing fees due to increased regulation regarding capturing natural gas. Workover expenses were $0.7 million higher for the year ended November 30, 2021 as operators increased workovers to increase oil and gas production from existing wells to take advantage of increased oil and natural gas prices, as compared to the year ended November 30, 2020.
Production Tax Expense. Total production taxes increased to $14.5 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 from $9.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2020. Production taxes are primarily based on oil revenue and gas production, excluding gains and losses associated with hedging activities. Production taxes as a percentage of oil and natural gas sales before hedging adjustments were 7.9% and 9.4% for the years ended November 30, 2021 and 2020, respectively. The decrease in the production tax rate for the year ended November 30, 2021 was due to a larger percentage of our revenue during that period coming from natural gas sales, which are taxed at a lower rate than oil sales in North Dakota.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense increased to $10.6 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 from $9.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2020. General and administrative expense on a per Boe basis increased slightly to $2.93 for the year ended November 30, 2021 from $2.60 for the year ended November 30, 2020. The increase in general and administrative expense on a per Boe basis was primarily related to employee costs, legal fees related to our litigation against one of our operators for withholding excessive deductions against our revenues and costs related to becoming a public entity.
DD&A. DD&A increased to $60.8 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 compared with $58.3 million for the year ended November 30, 2020. The increase of $2.5 million was the result of a 2% increase in production and a 2% increase in the DD&A rate for the year ended November 30, 2021 compared with the year ended November 30, 2020. The increase in production accounted for a $1.3 million increase in DD&A expense while the increase in the DD&A rate accounted for a $1.2 million increase in DD&A expense.
For the year ended November 30, 2021, the relationship of capital expenditures, proved reserves and production from certain producing fields yielded a depletion rate of $16.84 per Boe compared with $16.50 per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2020. The slight increase in the depletion rate of 2% was the result of end-of-period undeveloped reserve adjustments for the year ended November 30, 2021.
Unit-based Compensation. Unit-based compensation expense is recorded for in-substance call options granted to the founding members of management which are classified as liabilities and recorded at estimated fair value at each period end. Unit-based compensation expense is also recognized for management incentive units granted to other employees which are classified as liabilities until the holder has borne the risk of unit ownership. Unit-based compensation expense is recorded as these units vest and expense or contra-expense is recognized as the estimated fair value of the liability changes with market conditions. Unit-based compensation expense increased to $1.4 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 from negative $0.5 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 primarily due to increased oil and gas prices causing the estimated fair value of the liabilities to increase.
Interest Expense. Interest expense decreased to $3.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 from $4.7 million for the year ended November 30, 2020. The decrease for the year ended November 30, 2021 was due to a lower balance on our Existing Revolving Credit Facility as we reduced the outstanding debt balance from $98.5 million at November 30, 2020 to $68.0 million at November 30, 2021.
Commodity Derivative Gain (Loss). Commodity derivative loss was $32.6 million for the year ended November 30, 2021 compared with a gain of $29.6 million for the year ended November 30, 2020. Gain (Loss) on Commodity Derivatives is
109
comprised of (1) cash gains and losses we recognize on settled commodity derivative instruments during the period, and (2) unsettled gains and losses we incur on commodity derivative instruments outstanding at period-end.
The mark-to-market fair value of the unsettled commodity derivative instruments will generally be inversely related to the price movement of the underlying commodity. If commodity price trends reverse from period to period, prior unrealized gains may become unrealized losses and vice versa. These unrealized gains and losses will impact our net income in the period reported. The mark-to-market fair value can create non-cash volatility in our reported earnings during periods of commodity price volatility. We have experienced such volatility in the past and are likely to experience it in the future. Gains on our derivatives generally indicate lower oil revenues in the future while losses indicate higher future oil revenues.
The table below summarizes our commodity derivative gains and losses that were recorded in the periods presented.
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, |
||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Realized gain (loss) on commodity derivatives (1) |
$ | (13,903 | ) | $ | 27,160 | |||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on commodity derivatives (1) |
(18,687 | ) | 2,473 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total commodity derivative gain (loss) |
$ | (32,590 | ) | $ | 29,633 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Realized and unrealized gains and losses on commodity derivatives are presented herein as separate line items but are combined for a total commodity derivative gain (loss) in the consolidated statements of operations included in this Information Statement. Management believes the separate presentation of the realized and unrealized commodity derivative gains and losses is useful because the realized cash settlement portion provides a better understanding of our hedge position. |
In 2021, approximately 46% of our oil volumes and 8% of our natural gas volumes were subject to financial hedges, which resulted in a realized loss on oil derivatives of $13.1 million and a realized loss on natural gas derivatives of $0.8 million after settlements. In 2020, approximately 65% of our oil volumes and 0% of our natural gas volumes were covered by financial hedges, which resulted in a realized gain on oil derivatives of $27.2 million.
110
Year Ended November 30, 2020 Compared with Year Ended November 30, 2019
The following table sets forth selected operating data for the periods indicated.
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, |
INCREASE (DECREASE) |
|||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except per unit data) | 2020 | 2019 | AMOUNT | PERCENT | ||||||||||||
| Operating Results: |
||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 91,542 | $ | 157,112 | $ | (65,570 | ) | (42 | )% | |||||||
| Natural gas |
5,688 | 14,189 | (8,501 | ) | (60 | )% | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 97,230 | $ | 171,301 | $ | (74,071 | ) | (43 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||||||
| Production |
$ | 41,731 | $ | 42,875 | $ | (1,144 | ) | (3 | )% | |||||||
| Production taxes |
9,173 | 15,572 | (6,399 | ) | (41 | )% | ||||||||||
| General and administrative |
9,196 | 7,957 | 1,239 | 16 | % | |||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
58,307 | 64,721 | (6,414 | ) | (10 | )% | ||||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties |
13,200 | — | 13,200 | *nm | ||||||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
(544 | ) | 3,295 | (3,839 | ) | (117 | )% | |||||||||
| Interest Expense |
$ | 4,679 | $ | 4,825 | $ | (146 | ) | (3 | )% | |||||||
| Commodity Derivative Gain (Loss) |
$ | 29,633 | $ | 3,778 | $ | 25,855 | 684 | % | ||||||||
| Production Data: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (MBbls) |
2,599 | 3,063 | (464 | ) | (15 | )% | ||||||||||
| Natural gas (MMcf) |
5,609 | 5,105 | 504 | 10 | % | |||||||||||
| Combined volumes (MBoe) |
3,534 | 3,914 | (380 | ) | (10 | )% | ||||||||||
| Daily combined volumes (Boe/d) |
9,655 | 10,724 | (1,069 | ) | (10 | )% | ||||||||||
| Average Realized Prices before Hedging: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 35.22 | $ | 51.29 | $ | (16.06 | ) | (31 | )% | |||||||
| Natural gas (per Mcf) |
1.01 | 2.78 | (1.77 | ) | (64 | )% | ||||||||||
| Combined (per Boe) |
27.51 | 43.76 | (16.25 | ) | (37 | )% | ||||||||||
| Average Realized Prices with Hedging: |
||||||||||||||||
| Oil (per Bbl) |
$ | 45.67 | $ | 52.61 | $ | (6.94 | ) | (13 | )% | |||||||
| Natural gas (per Mcf) |
1.01 | 2.78 | (1.77 | ) | (64 | )% | ||||||||||
| Combined (per Boe) |
35.20 | 44.80 | (9.60 | ) | (21 | )% | ||||||||||
| Average Costs (per Boe): |
||||||||||||||||
| Production |
$ | 11.81 | $ | 10.95 | $ | 0.86 | 8 | % | ||||||||
| Production taxes |
2.60 | 3.98 | (1.38 | ) | (35 | )% | ||||||||||
| General and administrative |
2.60 | 2.03 | 0.57 | 28 | % | |||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
16.50 | 16.53 | (0.03 | ) | (0 | )% | ||||||||||
| * | Not meaningful |
Oil and Natural Gas Revenue and Volumes. Oil and natural gas revenue decreased to $97.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $171.3 million for the year ended November 30, 2019. The decrease in oil and natural gas revenue was due primarily to a 37% decrease in the average realized prices per Boe before hedging, along with a 10% decrease in production volumes. The decrease in average realized prices per Boe before hedging decreased oil and natural gas revenue by approximately $63.6 million, while the decrease in volumes decreased oil and natural gas revenue by approximately $10.5 million. The drop in realized prices before the effects of hedging as well as the drop in production were primarily related to the COVID-19 pandemic, as significantly lower demand for oil and gas resulted in lower oil and gas prices and the shut-in of production by many operators. In addition, new drilling and completions were dramatically reduced during the period, limiting production from new wells, which normally would increase production. The Williston Basin saw a reduction in the active drilling rig count from a pre-COVID-19 level of 55 active drilling rigs at November 30, 2019 to 14 active drilling rigs at November 30, 2020 based on reports issued by the North Dakota Oil and Gas Division of the North Dakota Industrial Commission.
111
Our oil price differential to the WTI benchmark price during year ended November 30, 2020 was $5.88 per barrel, as compared to $4.98 per barrel during year ended November 30, 2019. Our net realized natural gas price during 2020 was $1.01 per Mcf, representing 50% realization relative to average NYMEX pricing, compared to a net realized natural gas price of $2.78 per Mcf during year ended November 30, 2019, representing 103% realization relative to average NYMEX pricing. Fluctuations in our price differentials and realizations are due to several factors such as NGL value net of processing costs, gathering and transportation fees, takeaway capacity relative to production levels, regional storage capacity, and seasonal refinery maintenance temporarily depressing demand. The exact impact of each of these items is difficult to quantify as each of our operators pass through these costs in a different manner. Some operators may deduct these costs directly from our revenues while other operators may invoice them to us as lease operating expenses.
Production Expense. Production expense increased to $11.81 per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $10.95 per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2019. The increase per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2020 compared with the year ended November 30, 2019 was related to fixed production costs being spread over lower volumes as wells were constrained or shut in due to the COVID-19 pandemic and higher costs related to added natural gas gathering and processing fees due to increased regulation regarding capturing natural gas.
Production Tax Expense. Total production taxes decreased to $9.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $15.6 million for the year ended November 30, 2019. Production taxes are primarily based on oil revenue and gas production excluding gains and losses associated with hedging activities. The 41% drop in production taxes aligns with a drop in production revenues of 43% during the year ended November 30, 2020, while the production tax rate as a percentage of oil and natural gas sales before hedging adjustments remained consistent at 9.4% and 9.1% for the years ended November 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense increased to $9.2 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $8.0 million for the year ended November 30, 2019. General and administrative expense on a per Boe basis increased to $2.60 for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $2.03 for the year ended November 30, 2019. The increase was related to employee costs while the per Boe rate increase was related to fixed costs being spread over lower volumes.
DD&A. DD&A decreased to $58.3 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 compared with $64.7 million for the year ended November 30, 2019. The decrease for the year ended November 30, 2020 of $6.4 million was the result of a 10% decrease in production, which accounted for a $6.3 million decrease in DD&A expense, and a minimal decrease in the DD&A rate, which accounted for a $0.1 million decrease in DD&A expense, compared with the year ended November 30, 2019.
For the year ended November 30, 2020, the relationship of capital expenditures, proved reserves and production from certain producing fields yielded a depletion rate of $16.50 per Boe compared with $16.53 per Boe for the year ended November 30, 2019. The slight decrease in the depletion rate of 0.2% was the result of end-of-period reserve adjustments for the year ended November 30, 2020.
Unit-based Compensation. Unit-based compensation expense is recorded for in-substance call options granted to the founding members of management which are classified as liabilities and recorded at estimated fair value at each period end. Unit-based compensation expense is also recognized for management incentive units granted to other employees which are classified as liabilities until the holder has borne the risk of unit ownership. Unit-based compensation expense is recorded as these units vest and expense or contra-expense is recognized as the estimated fair value of the liability changes with market conditions. Unit-based compensation expense decreased to negative $0.5 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $3.3 million for the year ended November 30, 2019 primarily due to lower oil and gas prices causing the estimated fair value of the liabilities to decrease.
Interest Expense. Interest expense decreased to $4.7 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 from $4.8 million for the year ended November 30, 2019. The slight decrease for the year ended November 30, 2020 was due to a lower balance on our Existing Revolving Credit Facility as we reduced the outstanding debt balance from $104.0 million as of November 30, 2019 to $98.5 million as of November 30, 2020.
112
Commodity Derivative Gain (Loss). Commodity derivative gain was $29.6 million for the year ended November 30, 2020 compared with a gain of $3.8 million for the year ended November 30, 2019. Gain (Loss) on Commodity Derivatives is comprised of (1) cash gains and losses we recognize on settled commodity derivative instruments during the period, and (2) unsettled gains and losses we incur on commodity derivative instruments outstanding at period-end.
If commodity price trends reverse from period to period, prior unrealized gains may become unrealized losses and vice versa. These unrealized gains and losses will impact our net income in the period reported. The mark-to-market fair value can create non-cash volatility in our reported earnings during periods of commodity price volatility. We have experienced such volatility in the past and are likely to experience it in the future. Gains on our derivatives generally indicate lower oil revenues in the future while losses indicate higher future oil revenues.
The table below summarizes our commodity derivative gains and losses that were recorded in the periods presented.
| YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, |
||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Realized gain (loss) on commodity derivatives (1) |
$ | 27,160 | $ | 4,058 | ||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on commodity derivatives (1) |
2,473 | (280 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total commodity derivative gain (loss) |
$ | 29,633 | $ | 3,778 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Realized and unrealized gains and losses on commodity derivatives are presented herein as separate line items but are combined for a total commodity derivative gain (loss) in the consolidated statements of operations included in this Information Statement. Management believes the separate presentation of the realized and unrealized commodity derivative gains and losses is useful because the realized cash settlement portion provides a better understanding of our hedge position. |
In 2020, approximately 65% of our oil volumes and none of our natural gas volumes were subject to financial hedges, which resulted in a realized gain on oil derivatives of $27.2 million. In 2019, approximately 36% of our oil volumes and none of our natural gas volumes were covered by financial hedges, which resulted in a realized gain on oil derivatives of $4.1 million.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview. At August 31, 2022, we had $8.1 million of unrestricted cash on hand and $66.0 million of long-term debt. At November 30, 2021, we had $2.8 million of unrestricted cash on hand and $68.0 million of long-term debt, while at November 30, 2020, we had $1.7 million of unrestricted cash on hand and $98.5 million of long-term debt and at November 30, 2019, we had $1.8 million of unrestricted cash on hand and $104.0 million of long-term debt. We expect that our liquidity going forward will be primarily derived from cash flows from our operations, cash on hand and availability under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility or the New Revolving Credit Facility, as applicable, and that these sources of liquidity will be sufficient to provide us the ability to fund our material cash requirements, as described below, including our planned capital expenditures program, as well as distributions to our equity holders. We may need to fund acquisitions or other business opportunities that support our strategy through additional borrowings under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility or New Revolving Credit Facility, as applicable, or the issuance of equity or debt. Our primary uses of capital have been for the acquisition and development of our oil and natural gas properties. We continually monitor potential capital sources for opportunities to enhance liquidity or otherwise improve our financial position.
Working Capital. Our working capital balance fluctuates as a result of changes in commodity pricing and production volumes, the collection of receivables, capital expenditures related to our acquisition and development, and production operations and the impact of our outstanding commodity derivative instruments.
At August 31, 2022, we had a working capital surplus of $5.6 million as compared to a surplus of $4.2 million at November 30, 2021. Current assets increased by $16.5 million and current liabilities increased by $15.1 million at August 31, 2022, compared to November 30, 2021. The increase in current assets in 2022 was due to an increase
113
of $12.7 million in revenue receivable primarily due to our higher oil and natural gas revenue and a $5.3 million increase in the cash balance, which was partially offset by a decrease of $1.5 million in our commodity derivative assets due to change in fair value resulting from an increase in oil prices. The change in current liabilities in 2022 was primarily due to an increase of $9.2 million in accounts payable and accrued liabilities primarily as a result of increased development activity and an increase of $5.9 million in derivative instruments as a result of future oil price increases.
At November 30, 2021, we had a working capital surplus of $4.2 million, compared to a surplus of $6.7 million at November 30, 2020. Current assets increased by $7.3 million and current liabilities increased by $9.8 million at November 30, 2021, compared to November 30, 2020. The increase in current assets in 2021 as compared to 2020 was primarily due to an increase of $16.0 million in revenue receivable primarily due to our higher oil and natural gas revenue and an increased cash balance of $1.1 million, which was partially offset by a decrease of $7.7 million in our commodity derivative instruments due to the change in fair value as a result of higher oil prices and a $2.0 million decline in prepaid expenses. The change in current liabilities in 2021 as compared to 2020 was primarily due to an increase of $1.2 million in accounts payable and accrued liabilities primarily as a result of increased development activity and an increase of $8.7 million in derivative instruments as a result of forward oil price increases.
Cash Flows. Our cash flows for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 are presented below:
| NINE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31, |
YEAR ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by operating activities |
$ | 108,417 | $ | 86,971 | $ | 76,309 | $ | 101,194 | ||||||||
| Cash flows used in investing activities |
(57,317 | ) | (43,317 | ) | (70,808 | ) | (104,367 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash flows used in financing activities |
(45,816 | ) | (42,587 | ) | (5,528 | ) | (41 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash |
$ | 5,284 | $ | 1,067 | $ | (27 | ) | $ | (3,214 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
During the nine months ended August 31, 2022, we generated $108.4 million of cash from operations, an 88% increase from the same period in the prior year. During the year ended November 30, 2021, we generated $87.0 million of cash from operating activities, an increase of $10.7 million from the year ended November 30, 2020 but down from the year ended November 30, 2019 when we generated $101.2 million of cash from operating activities. Cash flows from operations are primarily affected by production volumes and commodity prices, net of the effects of settlements of our derivative contracts, and by changes in working capital. Any interim cash needs are funded by cash on hand, cash flows from operations or borrowings under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility. We typically enter into commodity derivative transactions covering a substantial, but varying, portion of its anticipated future oil and gas production for the next 12 to 24 months. See “—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk.”
One of the primary sources of variability in our cash provided by operating activities is commodity price volatility, which we are required by certain debt covenants to partially mitigate through the use of commodity derivative contracts. As of August 31, 2022, we had oil swaps covering the sale of approximately 43% of projected oil production at a weighted average price of $59.30 per Bbl for the remainder of 2022 and oil swaps covering the sale of approximately 33% of projected oil production at a weighted average price of $78.50 per Bbl for the fiscal year ending November 30, 2023. As of August 31, 2022, we had no natural gas derivative contracts. For more information on our outstanding derivatives, see Note 6 (“Derivative Instruments”) to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Note 6 (“Derivative Instruments”) to the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
Cash used in investing activities during the nine months ended August 31, 2022 was $57.3 million. Cash used in investing activities during the year ended November 30, 2021 was $43.3 million, compared to $70.8 million during
114
the year ended November 30, 2020 and $104.4 million during the fiscal year ended November 30, 2019, and primarily related to capital expenditures for acquisition and development costs. The annual sequential decreases in cash used in investing activities was primarily attributable to reduced development activity by our operators due to the COVID-19 pandemic, while increased activity during the nine months ended August 31, 2022 represent a recovery from these same factors. Our cash used in investing activities reflects actual cash spending, which can lag several months from when the related costs were accrued. As a result, our actual cash spending is not always reflective of current levels of development activity. Acquisition and development activities are discretionary. We monitor our capital expenditures on a regular basis, adjusting the amount up or down, and between projects, depending on projected commodity prices, cash flows and financial returns. We supplement development activity on our asset base with acquisitions of near-term drilling opportunities when development activity by our operators on our existing properties lags behind our development objectives. Our cash spending for acquisition activities was $6.2 million, $9.2 million and $5.1 million during the fiscal years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and $20.3 million in the nine months ended August 31, 2022.
Cash used in financing activities during the nine months ended August 31, 2022 was $45.8 million. Cash used in financing activities was $42.6 million and $5.5 million for the fiscal years ended November 30, 2021 and 2020, respectively. The cash used in financing activities in 2021 and 2020 was primarily related to $30.5 million and $5.5 million, respectively, of net repayments under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility. We made net repayments of $2.0 million under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility and paid distributions to our equity holders of $42 million during the nine months ended August 31, 2022. We paid distributions to our equity holders of $12.0 million during the year ended November 30, 2021.
Existing Revolving Credit Facility. In May 2015, Vitesse entered into a revolving credit facility with a syndicate of banks led by Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. (as Administrative Agent), which originally was scheduled to mature in May 2020. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility has been subsequently amended several times, and the maturity date has been extended to April 29, 2026. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility was most recently amended and restated in April 2022. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility permits borrowing on a revolving credit basis with availability equal to least of (1) the current aggregate elected commitments of $170 million, (2) the current borrowing base of $200 million and (3) the maximum credit amount of $500 million. The aggregate elected commitments of the lenders under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility may be increased up to a maximum credit amount of $500 million, subject to the satisfaction of certain customary conditions, including the willingness of the existing lenders to increase their commitments or of new lenders to provide additional commitments. The borrowing base under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility is subject to regular, semi-annual redeterminations on or about April 1 and October 1 of each year based on, among other things, the value of our proved oil and natural gas reserves, as determined by the lenders in their discretion. The borrowing base is subject to further adjustments for asset dispositions and liquidations of hedge agreements, among other things. As of August 31, 2022, under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility we had outstanding borrowings of $66.0 million and available borrowing capacity of $104.0 million. At our option, borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on SOFR (“Term SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the administrative agent’s prime rate, the federal funds rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day Term SOFR rate plus 1.0%), plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to Term SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the percentage of the current commitments being utilized. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility is guaranteed by all of our subsidiaries and is collateralized by a first priority lien on substantially all assets of Vitesse Energy and its subsidiaries, including a first priority lien on properties representing a minimum of 85% of the proved reserve value of our oil and natural gas properties. See Note 5 (“Credit Facility”) to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Note 5 (“Credit Facility”) to the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements” for further details regarding the Existing Revolving Credit Facility.
Material Cash Requirements. Our material short-term cash requirements include payments under our short-term lease agreements, recurring payroll and benefits obligations for our employees, capital and operating expenditures and other working capital needs. As commodity prices improve, our working capital requirements may increase as we spend additional capital, increase production and pay larger settlements on our outstanding commodity derivative contracts.
115
Our long-term material cash requirements from currently known obligations include anticipated repayment of outstanding borrowings and interest payment obligations under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility, settlements on our outstanding commodity derivative contracts, future obligations to plug, abandon and remediate our oil and gas properties at the end of their productive lives, and operating lease obligations. We cannot provide specific timing for repayments of outstanding borrowings on our Existing Revolving Credit Facility, or the associated interest payments, as the timing and amount of borrowings and repayments cannot be forecasted with certainty and are based on working capital requirements, commodity prices and acquisition and divestiture activity, among other factors. We cannot provide specific timing for other current and long-term liability obligations where we cannot forecast with certainty the amount and timing of such payments, including asset retirement obligations, as the plugging and abandonment of wells is at the discretion of the operators and any amounts we may be obligated to pay under our derivative contracts, as such payments are dependent on commodity prices in effect at the time of settlement. See Note 4 (“Fair Value Measurements”) to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Note 4 (“Fair Value Measurements”) to the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements” for further information on these contracts and their fair values as of November 30, 2021, which fair values represent the cash settlement amount required to terminate such instruments based on forward price curves for commodities as of that date.
Distributions. We paid cash distributions to our equity holders totaling $25.0 million during the year ended November 30, 2019, $0.0 during 2020, $12.0 million during the year ended November 30, 2021, and $42.0 million during the nine months ended August 31, 2022. While we believe that our future cash flows from operations can sustain further distributions, we do not currently intend to pay additional cash distributions pending completion of the Spin-Off. Future distributions are reliant on a variety of factors, including contractual restrictions, legal limitations (the most common of which are limitations set forth in a company’s organizational documents and insolvency), business developments and the judgment of our board of managers. Cash distributions to equity holders are subject to the terms of the Existing Revolving Credit Facility. Under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility, we are permitted to make cash distributions without limit to our equity holders if (i) no event of default or borrowing base deficiency (i.e., outstanding debt (including loans and letters of credit) exceeds the borrowing base) then exists or would result from such distribution and (ii) after giving effect to such distribution, (a) our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 70% of the least of (the following collectively referred to as “Commitments”): (1) $500 million, (2) our then-effective borrowing base, and (3) the then-effective aggregate amount of our lenders’ commitments and (b) as of the date of such distribution, the EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 1.50 to 1.00. If our total outstanding credit usage is between 70% and 80% of the Commitments, we may make distributions if, in addition to the foregoing conditions, (i) our EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 2.25 to 1.00, (ii) we have free cash flow, as defined under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, greater than $0 and (iii) we have delivered a certificate to our lenders attesting to the foregoing. The above restrictions have not limited our ability to pay distributions in the amounts declared by our Board. However, there can be no guarantee that we will make distributions or otherwise return capital to our investors in the future.
Capital Expenditures. For the year ending November 30, 2022, we are budgeting approximately $70 million to $80 million in total planned capital expenditures, including development expenditures and our acquisition activity. We expect to fund planned capital expenditures with cash generated from operations and, if required, borrowings under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility. The foregoing excludes larger acquisitions, which are typically not included in our annual capital expenditures budget. With our cash on hand, cash flow from operations, and borrowing capacity under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility, we believe that we will have sufficient cash flow and liquidity to fund our budgeted capital expenditures and operating expenses for at least the next twelve months. However, we may seek additional access to capital and liquidity. We cannot assure you, however, that any additional capital will be available to us on favorable terms or at all.
The amount, timing and allocation of capital expenditures are largely discretionary and subject to change based on a variety of factors. If oil and natural gas prices decline below our acceptable levels, or costs increase, we may choose to defer a portion of our budgeted capital expenditures until later periods to achieve the desired balance between sources and uses of liquidity and prioritize capital projects that we believe have the highest expected financial returns and potential to generate near-term cash flow. We may also increase our capital expenditures significantly to take advantage of opportunities we consider to be attractive. We will carefully monitor and may adjust our projected
116
capital expenditures in response to success or lack of success in drilling activities, changes in prices, availability of financing and joint venture opportunities, drilling and acquisition costs, industry conditions, the timing of regulatory approvals, the availability of rigs, change in service costs, contractual obligations, internally generated cash flow and other factors both within and outside our control. For additional information on the impact of changing prices and market conditions on our financial position, see “—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.”
Our recent capital commitments have been to fund acquisitions and development of oil and natural gas properties. We expect to fund our near-term capital requirements and working capital needs with cash flows from operations and available borrowing capacity under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility. Our capital expenditures could be curtailed if our cash flows decline. Because production from existing oil and natural gas wells declines over time, reductions of capital expenditures used to drill and complete new oil and natural gas wells would likely result in lower levels of oil and natural gas production in the future. Also, our obligations may change due to acquisitions, divestitures and continued growth. Our future success in growing proved reserves and production may be dependent on our ability to access outside sources of capital. If internally generated cash flow and borrowing capacity is not available under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility, we may issue equity or debt securities to fund capital expenditures, acquisitions, extend maturities or to repay debt.
Effects of Inflation and Pricing. The oil and natural gas industry is very cyclical and the demand for goods and services of oil field companies, suppliers and others associated with the industry put extreme pressure on the economic stability and pricing structure within the industry. Higher prices for oil and natural gas have resulted in increases in the costs of materials, services and personnel, which has led to approximately 10% higher drilling and completion costs in 2022 compared to 2021. Typically, as prices for oil and natural gas increase, so do all associated costs. However, the recent increase in oil and natural gas prices has more than offset such increased costs. Conversely, in a period of declining prices, associated cost declines are likely to lag and may not adjust downward in proportion. Material changes in prices also impact our current revenue stream, estimates of future reserves, borrowing base calculations of bank loans, impairment assessments of oil and natural gas properties, and values of properties in purchase and sale transactions. Such changes can impact the value of oil and natural gas companies and their ability to raise capital, borrow money and retain personnel.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
We prepare our financial statements and the accompanying notes in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, which require management to make estimates and assumptions about future events that affect the reported amounts in the financial statements and the accompanying notes. We identify certain accounting policies and estimates as critical based on, among other things, their impact on our financial condition, results of operations, and the degree of difficulty, subjectivity and complexity in their application. Critical accounting policies and estimates cover accounting matters that are inherently uncertain because the future resolution of such matters is unknown. Management routinely discusses the development, selection and disclosure of each of the critical accounting policies and estimates. The following is a discussion of our most critical accounting policies and estimates.
Proved Oil and Natural Gas Reserves
The determination of depreciation, depletion and amortization expense as well as impairments that may be recognized on our oil and natural gas properties are highly dependent on the estimates of the proved oil and natural gas reserves attributable to our properties. Our estimate of proved reserves is based on the quantities of oil and natural gas which geological and engineering data demonstrate, with reasonable certainty, to be recoverable in the future years from known reservoirs under existing economic and operating conditions. The accuracy of any reserve estimate is a function of the quality of available data, engineering and geological interpretation, and judgment. For example, we must estimate the amount and timing of future operating costs, production taxes and development costs, all of which may in fact vary considerably from actual results. In addition, as the prices of oil and natural gas and cost levels change from year to year, the economics of producing our reserves may change and therefore the estimate of proved reserves may also change. Approximately 35% of our proved oil and gas reserve volumes are categorized as proved undeveloped reserves. Any significant variance in these assumptions could materially affect the estimated quantity and value of our reserve, future cash flows from our reserves, and future development of our proved undeveloped reserves.
External petroleum engineers independently estimated all of the proved reserve quantities included in our financial statements for the year ended November 30, 2021, which were prepared in accordance with the rules promulgated by the SEC. In connection with our external petroleum engineers performing their independent reserve estimations,
117
we furnish them with the following information: (1) technical support data, (2) technical analysis of geologic and engineering support information, (3) economic and production data and (4) our well ownership interests.
Oil and Natural Gas Properties
We follow the successful efforts method of accounting for oil and gas activities. Under this method of accounting, costs associated with the acquisition, drilling, and equipping of successful exploratory wells and costs of successful and unsuccessful development wells are capitalized and depleted, net of estimated salvage values, using the units-of-production method on the basis of a reasonable aggregation of properties within a common geological structural feature or stratigraphic condition, such as a reservoir or field. The reserve base used to calculate depletion for leasehold acquisition costs and the cost to acquire proved properties is the sum of proved developed reserves and proved undeveloped reserves. With respect to well equipment costs, which include development costs and successful exploration drilling costs, the reserve base includes only proved developed reserves. Our proved oil and gas reserve information was computed by applying the average first-day-of-the- month oil and gas price during the 12-month period ended on the balance sheet date.
We review our oil and natural gas properties for impairment whenever events and circumstances indicate a decline in the recoverability of their carrying value. If we determined an evaluation for impairment is required, we estimate the expected future cash flows of our oil and natural gas properties and compare such cash flows to the carrying amount of the proved oil and natural gas properties to determine if the amount is recoverable. If the carrying amount exceeds the estimated undiscounted future cash flows, we will adjust the carrying value of proved oil and natural gas properties to estimated fair value. The factors used to estimate fair value include estimates of reserves, future commodity prices adjusted for basis differentials, future production estimates, anticipated capital expenditures, and a discount rate commensurate with the risk associated with realizing the projected cash flows. The discount rate is a rate that management believes is representative of current market conditions and includes estimates for a risk premium and other operational risks.
For the year ended November 30, 2021, we did not record any impairment expense. For the year ended November 30, 2020, we recorded a $13.2 million of impairment expense. For the year ended November 30, 2019, we did not record any impairment expense.
Unit-based Compensation
We account for unit-based compensation under accounting guidance related to share-based compensation, whereby the awards are recognized as liabilities, with changes in the estimated value of the awards recorded in earnings. For certain management incentive units, once the holders have borne the risk of unit ownership, the liability associated with those certain management incentive units is reclassified to temporary equity, and changes in the estimated fair value is recorded as an adjustment to members’ equity.
The fair value determination for unit-based compensation requires the use of highly subjective assumptions, including the market value of Vitesse, expected volatility, and expected term, among others. Changes in these inputs and assumptions can materially affect the measure of estimated fair value, which in turn can materially affect the amount of unit-based compensation expense (or reduction to expense) that we recognize in a given period. These assumptions are highly subjective and generally require significant analysis and judgment to develop. When estimating fair value, some of the assumptions will be based on, or determined from, external data and other assumptions may be derived from our historical experience. As we are a private entity whose units are not publicly traded, we consider the average volatility of comparable entities to develop an estimate of expected volatility which results in a reasonable estimate of fair value. Our estimate of the fair value of Vitesse is determined using estimates of discounted future cash flows, a market approach using multiples for publicly traded comparable entities, and relevant precedent transactions, among other factors.
The appropriate weight to place on historical experience, as well as on each estimate of fair value using the applicable approach, is a matter of judgment, based on relevant facts and circumstances. The market value of Vitesse can vary significantly based on changes in the market value of oil and natural gas prices. Variances in these factors can materially affect unit-based compensation expense in the periods presented. Additionally, changes in various assumptions may impact the fair value of unit-based compensation in different directions which may be material.
118
Recently Issued or Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
For discussion of recently issued or adopted accounting pronouncements, see Note 2 (“Significant Accounting Policies”) to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Note 2 (“Significant Accounting Policies”) to the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements.”
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We currently do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a material current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk
Commodity Price Risk
The price we receive for our oil and natural gas production heavily influences our revenue, profitability, access to capital and future rate of growth. Oil and natural gas are commodities, and, as a result, their prices are subject to wide fluctuations in response to relatively minor changes in supply and demand and other factors. Historically, the markets for oil and natural gas have been volatile, and we believe these markets will likely continue to be volatile in the future. The prices we receive for our production depend on numerous factors beyond our control. Our revenue generally would have increased or decreased along with any increases or decreases in oil or natural gas prices, but the exact impact on our income is indeterminable given the variety of expenses associated with producing and selling oil that also increase and decrease along with oil prices.
We enter into derivative contracts to achieve a more predictable cash flow by reducing our exposure to commodity price volatility. All derivative positions are carried at their fair value on the balance sheet and are marked-to-market at the end of each period. Any realized gains and losses on settled derivatives, as well as mark-to-market gains or losses, are aggregated and recorded to gain (loss) on derivative instruments, net on the statements of operations rather than as a component of other comprehensive income or other income (expense).
We generally use derivatives to economically hedge a significant, but varying portion of our anticipated future production. Any payments due to counterparties under our derivative contracts are funded by proceeds received from the sale of our production. Production receipts, however, lag payments to the counterparties. Any interim cash needs are funded by cash from operations or borrowings under our Existing Revolving Credit Facility.
The following table summarizes our open crude oil swap contracts as of August 31, 2022, by fiscal quarter.
| SETTLEMENT PERIOD |
OIL (barrels) | WEIGHTED AVERAGE PRICE ($) |
||||||
| Swaps-Oil |
||||||||
| 2022: |
||||||||
| Q4 |
345,000 | $ | 59.30 | |||||
| 2023: |
||||||||
| Q1 |
270,000 | $ | 78.50 | |||||
| Q2 |
270,000 | $ | 78.50 | |||||
| Q3 |
270,000 | $ | 78.50 | |||||
| Q4 |
270,000 | $ | 78.50 | |||||
| 2024: |
||||||||
| Q1 |
180,000 | $ | 75.97 | |||||
| Q2 |
180,000 | $ | 75.97 | |||||
| Q3 |
180,000 | $ | 75.97 | |||||
| Q4 |
180,000 | $ | 75.97 | |||||
See Note 4 (“Fair Value Measurements”) and Note 6 (“Derivative Instruments”) to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Note 4 (“Fair Value Measurements”) and Note 6 (“Derivative Instruments”) to the Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in the section entitled “Index to Financial Statements” for further details regarding our commodity derivatives, including basis swap contracts for both oil and natural gas, which are not included in the foregoing tables.
119
Interest Rate Risk
Our long-term debt is composed of borrowings that contain floating interest rates. Our Existing Revolving Credit Facility interest rate is a floating rate option that is designated by us within the parameters established by the underlying agreement. At our option, borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on SOFR (“Term SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the administrative agent’s prime rate, the Federal Funds Rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day Term SOFR rate plus 1.0%), plus a spread ranging from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to Term SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the borrowing base utilization percentage. All outstanding principal is due and payable upon termination of the Existing Revolving Credit Facility.
120
Executive Officers Following the Spin-Off
The following table and accompanying narrative presents information, as of January 6, 2023, regarding the individuals who are expected to serve as executive officers of Vitesse following the completion of the Spin-Off, including a five-year employment history. We are in the process of identifying the other persons who are expected to serve as our executive officers following the completion of the Spin-Off and will include information concerning those persons in an amendment to this Information Statement. None of Vitesse’s executive officers are currently executive officers or employees of Jefferies.
| NAME |
AGE | POSITION WITH VITESSE | ||||
| Bob Gerrity |
71 | Chief Executive Officer | ||||
| Brian Cree |
59 | President and Chief Operating Officer | ||||
| David Macosko |
61 | Chief Financial Officer | ||||
| Chris Humber |
49 | General Counsel and Secretary | ||||
Bob Gerrity. Mr. Gerrity was appointed the Chief Executive Officer of Vitesse in August 2022 and will continue in such position following the Spin-Off. Mr. Gerrity has decades of experience in the energy industry, beginning in Colorado in 1982. Mr. Gerrity invested his own capital in the beginning of what would become Vitesse and has personally participated in over 500 gross wells to date. Mr. Gerrity established and was Chief Executive Officer of Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation, which was one of the most active operators in the country in the early 1990s. Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation merged with Snyder Oil’s Wattenberg assets in 1996 to form Patina Oil & Gas Corporation, which eventually merged into Noble Energy, Inc. Mr. Gerrity founded and has served as the Chief Executive Officer of Vitesse Energy since its inception in 2014, and also has served as the Chief Executive Officer of Vitesse Oil since 2013.
Brian Cree. Mr. Cree was appointed the President and Chief Operating Officer of Vitesse in August 2022 and will continue as President following the Spin-Off. Mr. Cree has worked in the oil and natural gas industry for over 25 years. In 1987, he joined the predecessor of Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation and worked closely with Mr. Gerrity for almost nine years to grow and eventually merge Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation with Patina Oil & Gas Corporation in 1996. While at Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation, Mr. Cree held various financial and operational roles, including Chief Financial Officer, Senior Vice President of Operations and Chief Operating Officer, and served as a director on its board of directors. Mr. Cree served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer and as a director of Patina Oil & Gas Corporation from 1996 to 1999, following which time he spent close to ten years as the Chief Financial Officer and/or Chief Operating Officer at various companies focused on oil and gas software and the creation of a molecular memory technology and the use of biotechnology to create sustainable natural gas. One such company, Luca Technologies Inc., filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy relief in July of 2013. Mr. Cree has served as the President of Vitesse Energy since 2014 and the Chief Operating Officer of Vitesse Energy since 2020, and also previously served as the Chief Financial Officer of Vitesse Energy from 2014 to 2020. In addition, Mr. Cree has served as the President of Vitesse Oil since 2013 and the Chief Operating Officer of Vitesse Oil since 2020, and also previously served as the Chief Financial Officer of Vitesse Oil from 2013 to 2020. Mr. Cree served as Vice Chairman of the Colorado Oil and Gas Conservation Commission, a position appointed by the Governor of Colorado, from 1999 through 2007. He received a B.A. in Accounting from the University of Northern Iowa.
David Macosko. Mr. Macosko was appointed the Chief Financial Officer of Vitesse in August 2022 and will continue in such position following the Spin-Off. Mr. Macosko served at HighPoint Resources Corporation (formerly, Bill Barrett Corporation), a publicly traded oil and gas exploration and production company, in various roles from 2003 to May 2020, including as its Senior Vice President Accounting and Principal Accounting Officer from 2010. In March of 2021, after Mr. Macosko ceased his tenure, HighPoint Resources Corporation filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy relief. Prior to that, Mr. Macosko served in various business oriented and accounting capacities at senior levels with other publicly traded oil and gas companies, including Vice President of Business Operations at Gerrity Oil & Gas Corporation and Patina Oil & Gas Corporation. Mr. Macosko has served as the Chief Financial Officer of Vitesse
121
Energy since 2020 and as the Chief Financial Officer of Vitesse Oil during the same period. Mr. Macosko received a B.S./B.A. in Accounting from West Virginia University.
Chris Humber. Mr. Humber was appointed the General Counsel and Secretary of Vitesse in September 2022 and will continue in such position following the Spin-Off. He served as Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary of Sundance Energy Inc. from July 2020, until its sale to SilverBow Resources, Inc. in June 2022. Sundance Energy Inc. filed for bankruptcy relief under Chapter 11 in March of 2021 and emerged from bankruptcy in April 2021. Previously, Mr. Humber served as Jagged Peak Energy Inc.’s Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary from August 2016 through the company’s February 2017 initial public offering until the company’s merger with Parsley Energy, Inc. in January 2020. Prior to that, he served as the Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary of Bonanza Creek Energy, Inc. from its initial public offering in December 2011 until March 2016. Bonanza Creek Energy, Inc. filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy relief in January 2017. Prior to that time, Mr. Humber was a practicing attorney focusing on mergers and acquisitions, corporate finance, and securities matters for public and private companies as a partner with the law firm Kendall, Koenig & Oelsner PC in Denver, Colorado and an associate with the law firms Hogan & Hartson LLP (now Hogan Lovells US LLP) in Denver, Colorado and Arnold & Porter LLP in Washington, D.C. and McLean, Virginia. Mr. Humber has a J.D. from Emory University School of Law and a Bachelor of Arts in Biology from the University of Colorado at Boulder.
Board of Directors Following the Spin-Off
The following table and accompanying narrative presents information, as of January 6, 2023, regarding the individuals who are expected to serve on our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off and until their respective successors are duly elected and qualified, including a five-year employment history and any directorships held by our directors in public companies.
| NAME |
AGE | POSITION WITH VITESSE | ||||
| Linda Adamany |
70 | Director | ||||
| Brian Friedman |
67 | Director | ||||
| Bob Gerrity |
71 | Director and Chief Executive Officer | ||||
| Daniel O’Leary |
67 | Director | ||||
| Cathleen Osborn |
70 | Director | ||||
| Randy Stein |
69 | Director | ||||
| Joseph Steinberg |
78 | Director | ||||
Linda Adamany. Ms. Adamany will serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. Ms. Adamany has been a director on the Jefferies Board since 2014, a director of Jefferies Group LLC (“Jefferies Group”), previously Jefferies’ largest subsidiary, from November 2018 until November 1, 2022 (when Jefferies Group merged into Jefferies), and a director of Jefferies International Limited since March 2021. Ms. Adamany is the Lead Director, chairs the Nominating and Corporate Governance and Risk and Liquidity Oversight Committees, and serves as a member of the Audit, and ESG/DEI Committees of the Jefferies Board. She also serves as Chair of the Remuneration Committee and a member of the Audit, Risk and Nominations and Corporate Governance Committees of Jefferies International Limited. Ms. Adamany also has served as a director of Coeur Mining Inc. since March 2013 and is a member of its Environmental, Health, Safety and Social Responsibility Committee and Chair of its Audit Committee, and as a director of BlackRock Institutional Trust Company, N.A. since March 2018, where she is a member of its Audit and Risk Committees.
From October 2017 through April 2019, Ms. Adamany served as a director and member of both the Audit Committee and the Safety, Assurance and Business Ethics Committee of Wood plc, a global leader in the delivery of project, engineering and technical services to energy and industrial markets. Prior to that time, from October 2012 until October 2017, Ms. Adamany served as a member of the board of directors of AMEC Foster Wheeler plc, and chaired its Health, Safety, Security, Environment and Ethics Committee and served as a member of its Audit Committee, Nominations and Governance Committee and Compensation Committee. Ms. Adamany also served as a member of the board of directors of National Grid plc from October 2006 until October 2012, where she was a member of the Audit, Environment and Safety, Nominations and Governance and Remuneration Committees. Ms. Adamany’s career reflects 32 years of diverse executive experience in global businesses, including 27 years at BP plc spanning from 1980 to
122
2007, where she held a variety of leadership roles in both business and functional support areas, including Refining and Marketing, Exploration and Production, Chemicals, Shipping, Supply and Trading, Logistics, Information Technology, Supply Chain Management, Strategy and Human Resources. Ms. Adamany is a C.P.A. and holds a B.S. in Business Administration with a major in Accounting, magna cum laude, from John Carroll University, where she also was the recipient of the Arthur Anderson prize awarded to the top accounting graduate.
We believe Ms. Adamany’s experience serving on the boards of directors and committees of other public companies, including an ethics committee and audit committee as chair, as well as her compensation and corporate governance committees experience, provide her with the necessary experience, qualification and skills to serve as a director of Vitesse.
Brian Friedman. Mr. Friedman will serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. Mr. Friedman has served as a director and the President of Jefferies since March 2013, and as a director and executive officer of Jefferies Group from July 2005 until November 1, 2022 (when Jefferies Group merged into Jefferies), as well as Chairman of the Executive Committee of Jefferies Group from 2002 until November 1, 2022. Since 1997, Mr. Friedman also has served as President of Jefferies Capital Partners (formerly, FS Private Investments), a private equity fund management company controlled by Mr. Friedman. Mr. Friedman was previously employed by Furman Selz LLC and its successors, including serving as Head of Investment Banking and a member of its Management and Operating Committees. Prior to his 17 years with Furman Selz LLC and its successors, Mr. Friedman was an attorney with Wachtell, Lipton, Rosen & Katz.
Mr. Friedman has previously served on a number of boards of private and public portfolio companies and was on the board of Fiesta Restaurant Group from 2011 through April 2021 and as a board member of HomeFed Corporation from 2014 to July 2019.
Mr. Friedman is also engaged in a range of philanthropic efforts personally and through his family foundation and serves as the Co-Chairman of the board of Strive International, a workforce training effort, and Vice President of the HC Leukemia Foundation. He also serves as the Co-Chair of the Global Diversity Council at Jefferies. Mr. Friedman received a J.D. from Columbia Law School and a B.S. in Economics and M.S. in Accounting from The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania.
We believe that Mr. Friedman’s business, financial, and management expertise, as well as his experience serving on the boards of public companies gives him the necessary experience, qualifications and skills to serve as a director of Vitesse.
Bob Gerrity. Mr. Gerrity is currently a member of our Board and will continue to serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. For Mr. Gerrity’s biography, see “—Executive Officers Following the Spin-Off.” We believe that Mr. Gerrity’s experience in the energy industry and long history with Vitesse Energy provide him with the necessary skills to serve as a director and Chief Executive Officer of Vitesse.
Daniel O’Leary. Mr. O’Leary will serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. He has served on the board of Hillman Solutions Corp. since 2021 and currently serves on its Audit and Nominating and ESG Committees. Mr. O’Leary has served on the board of Custom Ecology, Inc. since 2021 as its Non-Executive Chairman. Additionally, he served as a director on the board of Sprint Industrial from 2017 to 2019.
Mr. O’Leary is an independent consultant who served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Edgen Murray Corporation, a distributor for energy infrastructure components, specialized oil and gas parts and equipment, from 2003 to 2021, and guided a management buyout that grew the company through a series of acquisitions and growth initiatives during that time. He was appointed Chairman of the board of Edgen Murray Corporation in 2006 and served in that role until March 2021. Edgen Murray Corporation completed its initial public offering in May 2012 and was acquired in 2013 by Sumitomo Corporation. Mr. O’Leary has served on various boards within Sumitomo Corporation and its subsidiaries. Mr. O’Leary received a B.S. in Education from Tulsa University.
We believe Mr. O’Leary’s management, operational and business experience, combined with his long career principally in the oil and gas and energy infrastructure markets, provide him with the necessary experience, qualifications and skills to serve as a director of Vitesse.
123
Cathleen Osborn. Ms. Osborn will serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. Ms. Osborn is currently a consultant working in the area of oil and natural gas transactions.
Ms. Osborn is a corporate attorney with nearly 30 years of experience working in the energy industry. Previously, Ms. Osborn served as Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary of SRC Energy Inc., an oil and gas company, from August 2015 until the company’s merger with PDC Energy, Inc. in 2020. Prior to that, Ms. Osborn was Deputy General Counsel of Whiting Petroleum Corporation, an oil and gas company, from 2014 to August 2015, and General Counsel of Kodiak Oil & Gas Corporation, an oil and gas company, from 2011 until it was merged with Whiting Petroleum Corporation in 2014. Ms. Osborn received her B.A. and J.D. from the University of Denver.
We believe that Ms. Osborn’s experience leading the in-house legal departments at several public oil and gas companies provides her with the necessary experience, qualifications and skills to serve as a director of Vitesse.
Randy Stein. Mr. Stein will serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. Mr. Stein is a self-employed tax, accounting, and general business consultant, having retired from PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP in 2000. Mr. Stein was employed for 20 years with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, most recently as principal in charge of the Denver, Colorado tax practice.
Mr. Stein currently serves on the board of Club Oil & Gas Inc., a private company that invests in oil and natural gas and real estate interests. Mr. Stein previously served as a director and Chairman of the Audit Committee of Denbury Resources Inc. from 2005 to 2020, HighPoint Resources Corporation (formerly, Bill Barrett Corporation) from 2004 to 2021 and Westport Resources Inc. from 2000 to 2004, all public oil and gas companies. In addition, Mr. Stein served from 2001 through 2005 as a director of Koala Corporation, a Denver-based public company engaged in the design, production, and marketing of family convenience products. Mr. Stein also was previously employed as an executive director of a Denver based independent oil and gas company. Mr. Stein received a B.S. in Accounting from Florida State University.
We believe that Mr. Stein’s experience serving on multiple public company boards of directors, including his multiple positions as Audit Committee Chair, as well as his experience in the energy industry, provide him with the necessary experience, qualifications and skills to serve as a director of Vitesse.
Joseph Steinberg. Mr. Steinberg will serve as a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off. He has served as a director on the Jefferies Board since December 1978 and as its Chairman since March 2013. Mr. Steinberg has served on the board of Crimson Wine Group, Ltd. since 2013.
Previously, Mr. Steinberg served as a director overseeing Jefferies’ investments in HomeFed Corporation from 1998 to 2019, HRG Group from 2014 to 2018, and Spectrum Brands Holdings, Inc. from 2018 to 2019, and as a director of Fidelity & Guaranty Life from 2015 to 2017 and of Pershing Square Tontine Holdings, Ltd. from 2020 to 2022. Mr. Steinberg received an M.B.A. from Harvard Business School and an A.B. in Government from New York University.
We believe that Mr. Steinberg’s experience serving on public company boards of directors provide him with the necessary experience, qualifications and skills to serve as a director of Vitesse.
The initial directors who will serve on our Board after the Spin-Off are expected to begin their terms at the time of the Distribution, with the exception of one independent director who is expected to begin his or her term prior to the date on which “when-issued” trading of our common stock commences and is expected to serve on our Audit Committee, our Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee and our Compensation Committee.
The Board is expected to affirmatively determine that Mses. Adamany and Osborn and Messrs. O’Leary and Stein qualify as independent under the rules of the NYSE and the Exchange Act, as applicable.
The Board will assess on a regular basis, and at least annually, the independence of directors and will make a determination as to which members are independent.
124
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, Vitesse was not an independent, publicly-traded company and did not have a compensation committee or any other committee serving a similar function. Decisions as to the compensation of those who served as our executive officers for that fiscal year are described in more detail under the section entitled “Executive Compensation—Historical Compensation Paid or Awarded Under Vitesse Energy Plans and Arrangements and Certain Compensation Being Granted or Paid in Connection with the Spin-Off.”
Effective upon the completion of the Spin-Off, our Board is expected to have an Audit Committee, Compensation Committee and Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee. The Board committees are expected to act in an advisory capacity to the full Board, except that the Compensation Committee is expected to have direct responsibility for the Chief Executive Officer’s and the President’s goals, performance and compensation along with compensation of other executive officers, and the Audit Committee is expected to have direct responsibility for appointing, replacing, compensating and overseeing the outside auditor. Our Board is expected to adopt a written charter for each of the standing committees that clearly establishes the committees’ respective roles and responsibilities, which will be posted to our website prior to the Distribution Date. In addition, each committee is expected to have the authority to retain independent outside professional advisors or experts as it deems advisable or necessary, including the sole authority to retain and terminate any such advisors, to carry out its duties.
Audit Committee
The Audit Committee is expected to be established in accordance with Section 3(a)(58)(A) and Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act. The responsibilities of our Audit Committee will be more fully described in our Audit Committee charter. We anticipate that our Audit Committee, among other duties, will:
| ∎ | assist the Board in its oversight of (i) the conduct of our financial reporting process, including by overviewing the integrity of the financial reports and other financial information provided by us to any governmental or regulatory body or the public, (ii) the performance of Vitesse’s accounting, internal control over financial reporting and internal audit functions and (iii) the performance of our outside auditor, including their qualifications and independence, and the annual independent audit of our financial statements; |
| ∎ | review the annual audit and the annual audit report of the outside auditor; |
| ∎ | review financial reports, internal controls and financial reporting and accounting risk exposures; |
| ∎ | prior to public release, discuss with management and the outside auditor, as appropriate, earnings press releases and financial information and earnings guidance provided to analysts and to rating agencies; |
| ∎ | review periodically with management the code of business conduct and ethics and other compliance and ethics programs; |
| ∎ | review accounting policies and system of internal controls; |
| ∎ | appoint, evaluate, compensate and oversee the work of the outside auditor; |
| ∎ | consider and pre-approve, as appropriate, all auditing and non-auditing services provided by the outside auditor; |
| ∎ | review our internal audit plan, including approval of the risk assessment methodology used in its development and the responsibilities, budget and staffing of both the outside and internal auditors; |
| ∎ | review legal and regulatory matters that may have a material impact on our financial statements and internal controls; |
| ∎ | confer with our independent petroleum reservoir engineering firm and review with management, including our internal reserves personnel, and the independent petroleum reservoir engineering firm the preparation of our oil and gas reserves report, the process by which our oil and gas reserves are estimated and reported and the associated disclosure; and |
| ∎ | retain independent outside professional advisors, as needed. |
The Audit Committee is expected to have at least three members and is expected to consist entirely of independent directors, each of whom will meet the independence requirements set forth in the listing standards of the NYSE and Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act. Each member of the Audit Committee will be financially literate, and at least
125
one member of the Audit Committee will have accounting and related financial management expertise and satisfy the criteria to be an “audit committee financial expert” under the rules and regulations of the SEC, as those qualifications are interpreted by our Board in its business judgment. Upon completion of the Spin-Off, we expect our
Audit Committee will consist of Mr. Stein, Ms. Adamany, Mr. O’Leary and Ms. Osborn, with Mr. Stein serving as chair.
Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee
The responsibilities of our Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee will be more fully described in our Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee charter, and we anticipate that our Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee, among other duties, will:
| ∎ | identify, screen and review individuals qualified to serve as directors, consistent with criteria approved by the Board and the commitment of Vitesse and the Board to a standard of Board inclusiveness, and recommend to the Board the nominees for election or re-election at the next annual meeting of stockholders and for filling any Board vacancies; |
| ∎ | oversee the evaluation of the Board and individual directors; |
| ∎ | establish and recommend to the Board Vitesse’s Corporate Governance Guidelines, as well as oversee the implementation and effectiveness of and recommend modifications as appropriate to such guidelines; |
| ∎ | review and recommend to the Board for approval any changes in the compensation of non-employee directors; |
| ∎ | oversee and provide input to management on Vitesse’s risks, policies, strategies and programs related to matters of sustainability, corporate social responsibility, corporate culture and corporate governance; |
| ∎ | consider and provide input to management on social, political and environmental trends in public policy, regulation and legislation and consider additional corporate social responsibility actions in response to such issues; |
| ∎ | review the goals established from time to time for Vitesse’s performance with respect to matters of sustainability and corporate social responsibility and monitor Vitesse’s progress against those goals and Vitesse’s Corporate Social Responsibility Principles (the “CSR Principles”); |
| ∎ | review Vitesse’s sustainability and corporate social responsibility reports as may be issued from time to time; |
| ∎ | as requested by the Board, make recommendations to the Board with respect to matters affecting corporate ESG responsibilities and related corporate conduct consistent with Vitesse’s CSR Principles; |
| ∎ | receive periodic reports from management regarding relationships with key external stakeholders that may have a significant impact on Vitesse’s ESG initiatives as well as business activities and performance; |
| ∎ | review Vitesse’s charitable giving policies and programs and receive reports from management on Vitesse’s charitable contributions; |
| ∎ | review stockholder proposals relating to corporate governance, public policy, sustainability and corporate social responsibility issues; |
| ∎ | review and approve annually (and periodically when material changes are proposed) the CSR Principles; and |
| ∎ | retain independent outside professional advisors, as needed. |
The Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee is expected to consist entirely of independent directors, each of whom will meet the independence requirements set forth in the listing standards of the NYSE. Upon completion of the Spin-Off, we expect our Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee will consist of Mr. O’Leary, Ms. Adamany and Mr. Stein, with Mr. O’Leary serving as chair.
126
Compensation Committee
The responsibilities of our Compensation Committee will be more fully described in our Compensation Committee charter, and we anticipate that our Compensation Committee, among other duties, will:
| ∎ | oversee senior management in establishing Vitesse’s general compensation philosophy and overseeing the development and implementation of compensation programs; |
| ∎ | review and approve corporate goals and objectives relevant to the compensation of Vitesse’s executive officers, evaluate the performance of the executive officers in light of those goals and objectives, and set the executive officers’ compensation level based on this evaluation; |
| ∎ | oversee the Chief Executive Officer and the President in formulating the compensation programs applicable to the senior management of Vitesse, including periodic review of perquisites and expense account policies applicable to senior management; |
| ∎ | make recommendations to the Board with respect to our incentive compensation plans and equity-based plans that are subject to Board approval, review and approve awards and grants made pursuant to these plans and discharge any other responsibilities imposed on the Committee by any of these plans; |
| ∎ | review our compensation policies and practices for executive officers and employees generally; |
| ∎ | assist the Board in its oversight of, and discuss with management as appropriate, our policies and strategies relating to human capital management, including recruiting, retention, and diversity; |
| ∎ | prepare compensation disclosure to be included in our annual proxy statement; |
| ∎ | evaluate whether the work of any compensation consultant has raised any conflict of interest; |
| ∎ | make a recommendation to the Board regarding the frequency of the advisory vote on compensation of our named executive officers; and |
| ∎ | retain independent outside professional advisors, as needed. |
The Compensation Committee is expected to consist entirely of independent directors, each of whom will meet the independence requirements set forth in the listing standards of the NYSE and Rule 10C-1 under the Exchange Act and will be “non-employee directors” (within the meaning of Rule 16b-3 under the Exchange Act). Upon completion of the Spin-Off, we expect our Compensation Committee will consist of Ms. Adamany, Mr. O’Leary and Ms. Osborn, with Ms. Adamany serving as chair.
We strive to maintain sound governance standards, to be reflected in our Governance Guidelines, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, our systematic approach to risk management, and our commitment to transparent financial reporting and strong internal controls. The following documents will be made available on the Corporate Governance section of our website in connection with the Spin-Off, where you will be able to access information about corporate governance at Vitesse:
| ∎ | Governance Guidelines; |
| ∎ | Code of Business Conduct and Ethics; and |
| ∎ | information about how to communicate concerns to the Board and management. |
The information on our website is not, and shall not be deemed to be, a part of this Information Statement or incorporated into any other filings we make with the SEC.
Criteria for Board Membership
We believe our Board should be composed of directors who have had high-level executive experience, have been directors on other boards, or worked extensively with public company boards and have been tested through economic downturns and crises. Industry experience, regional relationships and broad diversity of experience and backgrounds are also factors in Board nominee selection. The Board’s Governance Guidelines will confirm that we believe that it is desirable for Board members to possess diverse characteristics of gender, race, ethnicity and age, and we will consider those factors in Board evaluation and in the identification of candidates for Board membership. We believe this type of composition enables the Board to oversee the management of the business and affairs of Vitesse effectively.
127
The Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee is expected to consider candidates who have been properly nominated by stockholders, as well as candidates who have been identified by Board members and Vitesse personnel. In addition, the Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee may use a search firm to assist in the search for candidates and nominees and to evaluate the nominees’ skills against the Board’s criteria. Based on its review of all candidates, the Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee is expected to recommend a slate of director nominees for election at the annual meeting of stockholders. The slate of nominees may include both incumbent and new nominees.
Potential candidates are expected to be reviewed and evaluated by the Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee, and selected candidates are expected to go on to be interviewed by one or more Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee members. An invitation to join the Board is expected be extended by the Board itself, through the Executive Chairman and the Chair of the Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee.
Board Leadership Structure
The Nominating, Governance and Environmental and Social Responsibility Committee is expected to routinely review our governance practices and board leadership structure.
As of the completion of the Spin-Off, it is expected that Bob Gerrity will serve as Executive Chairman. Under our Governance Guidelines, the Board is expected to designate an independent director to serve as a Lead Director when the Chairman is not independent. It is expected that Mr. O’Leary will be elected to serve as Lead Director by a majority of the independent directors promptly following the completion of the Spin-Off.
We have not yet paid any compensation or made any determinations with respect to the compensation of the individuals who will be directors on our Board. Following the Distribution, compensation of directors on our Board will be reviewed and recommended by our Board and Compensation Committee. Directors who are also employees of Vitesse are not expected to receive any additional compensation for their services as directors.
128
The following discussion relates to the compensation of our principal executive officer and our two other most highly compensated executive officers, as determined under the rules of the SEC, based on compensation paid to or earned by such individuals for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021, and the one-month transition period from December 1, 2021 to December 31, 2021 (such period accounting for the transition from a November 30 fiscal year-end to a December 31 fiscal year-end, the “Transition Period”). See “Summary—Recent Developments” for more information concerning the change to our fiscal year end. These executive officers, whom we refer to as our “Named Executive Officers,” or our “NEOS” are:
| ∎ | Bob Gerrity, who currently serves as our Chief Executive Officer; |
| ∎ | Brian Cree, who currently serves as our President and Chief Operating Officer; and |
| ∎ | David Macosko, who currently serves as Chief Financial Officer. |
Messrs. Gerrity and Macosko are expected to serve in the same positions at Vitesse following the Spin-Off. Mr. Cree will serve as our President following the Spin-Off.
Historical Compensation Paid or Awarded Under Vitesse Energy Plans and Arrangements and Certain Compensation Being Granted or Paid in Connection with the Spin-Off
This discussion relates to the compensation paid to or earned by the NEOs while Vitesse Energy was majority owned by Jefferies. The amounts and forms of historical compensation reported herein, including the Executive Employment Agreements (as defined below) and NEO compensation for the years ended December 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021 and the Transition Period, do not reflect the NEOs’ compensation or terms of employment following the Spin-Off because their historical compensation was determined by Jefferies. The compensation to be granted or paid to each NEO in connection with or following the Spin-Off, as described in the following paragraph, was determined by Jefferies and approved by our Board, which was composed of Mr. Gerrity as the sole director. Future compensation levels not reported herein will be determined based on the compensation policies, programs and procedures to be established by our Board and Compensation Committee following the Spin-Off.
In connection with the Spin-Off, the Executive Employment Agreements will be terminated and we will adopt an Employee Severance Plan, the form of which is attached as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, which will, among other things, provide for severance payments to eligible employees upon certain terminations of employment (as reflected in the Employee Severance Plan) in an amount equal to one month’s base salary per year of service, with a minimum of two months’ base salary and up to a maximum of six months’ base salary or 12 months’ base salary for employees above a specified age. In connection with the Spin-Off, we will also adopt the VTS LTIP pursuant to which the Board or the Committee (as defined below) may issue up to 3,960,000 shares of our common stock (representing 12% of our shares calculated on a fully diluted basis immediately following the Spin-Off) pursuant to the grant of nonstatutory stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock awards, dividend equivalents, other stock-based awards, cash awards, substitute awards, or any combination of the foregoing. Immediately following the Spin-Off, Messrs. Gerrity, Cree and Macosko will each receive an award of time-vested restricted stock units with respect to 1,650,000, 726,000 and 180,875 shares of Vitesse common stock, respectively. Of Messrs. Gerrity’s and Cree’s restricted stock units, 1,500,000 and 363,000, respectively, will be granted pursuant to the Form of RSU Award Agreement (Executive – Retirement), the form of which is attached as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, which provides that such restricted stock units will vest in three equal annual installments, subject to continued employment through such dates, provided, that if either of Messrs. Gerrity or Cree voluntarily resigns (due to being retirement eligible), is terminated without cause, resigns for good reason, dies or is terminated due to disability, subject to compliance with restrictive covenants, including non-competition restrictions, through the remainder of the vesting period, the restricted stock units will vest in accordance with their original vesting schedule. The remaining 150,000 and 363,000 restricted stock units of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will be granted pursuant to the Form of RSU Award Agreement (Executive – Three-Year Vesting), the form of which is attached as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, which provides that such restricted stock units will vest in three equal annual installments, subject to continued employment through such dates, provided, that if Messrs. Gerrity’s or Cree’s employment is terminated without cause, due to a resignation for good reason, or due to
129
death or disability, the restricted stock units will vest. Mr. Macosko’s restricted stock units will be granted pursuant to the Form of RSU Award Agreement (Employee – Four- Year Vesting), the form of which is attached as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, which provides that such restricted stock units will vest over a four-year period, subject to continued employment through such dates, as follows: 50% two years following the date of grant, 25% three years following the date of grant and 25% four years following the date of grant. If Mr. Macosko’s employment is terminated due to his disability or upon Mr. Macosko’s death, or if Mr. Macosko’s employment is terminated without cause or due to his resignation for good reason within the two years following a change in control, Mr. Macosko’s restricted stock units will vest. The restricted stock unit grants of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree are conditioned on the termination of their Executive Employment Agreements and, in connection with the termination of their Executive Employment Agreements, Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will also each receive payment of their earned but unpaid annual bonus of $1,175,000 and $725,000, respectively, for the fiscal year 2022 if not previously paid and pursuant to the letter evidencing the termination of the Executive Employment Agreements, the form of which is attached as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, Messrs. Gerrity’s and Cree’s annual base salary will become $550,000 and $425,000, respectively, and their annual target bonuses will be 100% and 85% of base salary, respectively.
The following section provides compensation information pursuant to the scaled disclosure rules applicable to “emerging growth companies” under the rules of the SEC, including reduced narrative and tabular disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation.
The table below summarizes the total compensation earned by each of the Named Executive Officers for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021, and the Transition Period.
| NAME AND PRINCIPAL POSITION |
FISCAL YEAR | SALARY ($) | BONUS ($) (1) |
ALL OTHER COMPENSA- TION ($) |
TOTAL ($) | |||||||||||||
| 2022 | 500,000 | 1,175,000 | 30,720 | 1,705,720 | ||||||||||||||
| Bob Gerrity, Chief Executive Officer |
Transition Period | 41,667 | — | 2,560 | 44,227 | |||||||||||||
| 2021 | 500,000 | 1,050,000 | 41,675 | 1,591,675 | ||||||||||||||
| Brian Cree, President and Chief Operating Officer |
2022 | 400,000 | 725,000 | 18,174 | 1,143,174 | |||||||||||||
| Transition Period | 33,333 | — | 1,515 | 34,848 | ||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 400,000 | 650,000 | 14,513 | 1,064,513 | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 315,000 | 230,000 | 17,796 | 562,796 | ||||||||||||||
| David Macosko, Chief Financial Officer |
Transition Period | 26,250 | — | 1,483 | 27,733 | |||||||||||||
| 2021 | 315,000 | 230,000 | 11,106 | 556,106 | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | For Messrs. Gerrity and Cree, the amounts in this column represent the annual bonuses payable pursuant to the Executive Employment Agreements. For Mr. Macosko, the amount in this column represents the discretionary bonus to be paid to Mr. Macosko in 2023 in recognition of his contributions to the Company in 2022 and the discretionary bonus paid in 2022 in recognition of his contributions to the Company in 2021. The annual bonuses in respect of calendar year 2021 are reflected in the fiscal year ended November 30, 2021 and the annual bonuses in respect of calendar year 2022 are reflected in the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022. See “—Annual Bonuses.” |
Each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree entered into an employment agreement with Vitesse Management Company LLC, Vitesse Oil and Vitesse Energy (for purposes herein, collectively referred to as the “Company”), effective as of February 18, 2020 (individually, the “Gerrity Employment Agreement,” or the “Cree Employment Agreement,” and collectively, the “Executive Employment Agreements”).
In addition to setting Messrs. Gerrity’s and Cree’s annual base salaries and annual cash bonuses, the Executive Employment Agreements include certain restrictive covenants that apply to Messrs. Gerrity and Cree and provide Messrs. Gerrity and Cree with severance benefits under certain circumstances. See “—Potential Payments Upon Termination.”
Mr. Macosko is an at-will employee and is not party to an employment agreement.
130
The Executive Employment Agreements provided Messrs. Gerrity and Cree with a guaranteed annual bonus for the calendar year ended December 31, 2022 of $1,175,00 and $725,000, respectively, and December 31, 2021 of $1,050,000 and $650,000, respectively.
The Company determined that, because of Mr. Macosko’s contributions to the Company in each of the 2022 and 2021 calendar years and his individual performance, Mr. Macosko should receive a bonus of $230,000 with regard to each year. Payment of such bonuses was entirely in the Company’s discretion.
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
| OPTION AWARDS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAME |
GRANT DATE | NUMBER OF SECURITIES UNDERLYING UNEXERCISED OPTIONS (#) EXERCISABLE |
NUMBER OF SECURITIES UNDERLYING UNEXERCISED OPTIONS (#) UNEXERCISABLE |
OPTION EXERCISE PRICE ($) (3) |
EXPIRATION DATE |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Bob Gerrity |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitesse Energy MIUs |
(1) | 05/15/2014 | 450,000 | — | 0.00 | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitesse Oil MIUs |
(1) | 10/15/2013 | 450,000 | — | 0.00 | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brian Cree |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitesse Energy MIUs |
(1) | 5/15/2014 | 225,000 | — | 0.00 | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitesse Oil MIUs |
(1) | 10/15/2013 | 225,000 | — | 0.00 | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| David Macosko |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitesse Energy MIUs |
(1) (2) | 6/1/2020 | 25,000 | 25,000 | 0.00 | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Reflects information regarding Vitesse Energy MIUs and Vitesse Oil MIUs granted to our NEOs that were outstanding as of December 31, 2022. The Vitesse Energy MIUs represent membership interests in Vitesse Energy and the Vitesse Oil MIUs represent membership interests in Vitesse Oil. The Vitesse Energy MIUs and the Vitesse Oil MIUs are intended to constitute “profits interests” for federal income tax purposes. Despite the fact that neither the Vitesse Energy MIUs nor the Vitesse Oil MIUs require the payment of an exercise price, they are most similar economically to stock options. Accordingly, they are classified as “options” under the definition provided under applicable SEC rules and guidance. For more information on the Vitesse Energy MIUs and the Vitesse Oil MIUs, see “—Vitesse Energy Management Incentive Plan” and “—Vitesse Oil Management Incentive Plan.” Pursuant to the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, all of the Vitesse Energy MIUs held by each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will be transferred to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to each such NEO. In addition, all of the Vitesse Oil MIUs held by each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree are expected to be canceled and cease to exist because the Vitesse Oil MIUs are not expected to have any value when settled as part of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. For more information, see “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions” and “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons.” |
| (2) | Mr. Macosko’s unvested Vitesse Energy MIUs vest one-half on each of June 1, 2023 and 2024. Pursuant to the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, all of the vested Vitesse Energy MIUs held by Mr. Macosko will be transferred to Vitesse in exchange for newly issued shares of Vitesse common stock. For more information, see “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions.” |
| (3) | Represents the deemed exercise prices of the Vitesse Energy MIUs and the Vitesse Oil MIUs pursuant to the terms of the limited liability company agreement of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil, respectively. |
Vitesse Energy Management Incentive Plan
The members of Vitesse Energy adopted the Vitesse Energy Management Incentive Plan (the “Vitesse Energy MIP”) under which Vitesse Energy MIUs, which are intended to constitute “profits interests” for federal income tax purposes, may be granted. The Vitesse Energy MIUs granted to the NEOs generally are subject to a four-year vesting period. All of the Vitesse Energy MIUs held by each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree were fully vested as of December 31, 2022 and 50% of the Vitesse Energy MIUs held by Mr. Macosko were vested as of December 31, 2022. Vitesse Energy MIUs, whether vested or unvested, generally are subject to forfeiture for no consideration if a holder of Vitesse Energy MIUs defaults in his or her obligation to make a capital contribution to Vitesse Energy and such default is not cured within a specified period of time or if his or her employment is terminated for cause.
131
Vitesse Oil Management Incentive Plan
The members of Vitesse Oil adopted the Vitesse Oil Management Incentive Plan, (the “Vitesse Oil MIP”) under which Vitesse Oil MIUs, which are intended to constitute “profits interests” for federal income tax purposes, may be granted. The Vitesse Oil MIP and Vitesse Oil MIUs are substantially similar to the Vitesse Energy MIP and the Vitesse Energy MIUs.
Potential Payments Upon Termination
Separation Benefits in the Executive Employment Agreements
The Executive Employment Agreements provide that, upon a termination of either of Messrs. Gerrity’s or Cree’s employment for any reason, Messrs. Gerrity or Cree, as applicable, will be entitled to (1) payment of any base salary earned, accrued vacation time and accrued but unpaid business expense reimbursements (for expenses reimbursable pursuant to the Executive Employment Agreements) through the date of termination (the “Accrued Obligation”) and (2) payment of any earned but unpaid annual bonus for the year completed prior to the year in which such termination occurs (the “Prior Year Bonus”). The Executive Employment Agreements also entitle each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree to payment of any vested benefits to which they are entitled under any employee benefit plans and compensation arrangements in which they participate at the time of their termination (the “Benefit Obligation”).
Pursuant to the Executive Employment Agreements, Messrs. Gerrity and Cree are subject to restrictive covenants, including perpetual confidentiality and non-disparagement restrictions, and non-competition, non-solicitation (of both employees and customers) and non-interference restrictions (collectively, the “Restrictive Covenants”). The non-competition, non-solicitation and non-interference restrictions continue for six months following termination of employment if either of Messrs. Gerrity’s or Cree’s employment is terminated by the Company without Cause (as defined in the Executive Employment Agreements), by Messrs. Gerrity or Cree for Good Reason (as defined in the Executive Employment Agreements), or as a result of the Company’s nonrenewal of the Term of the Executive Employment Agreements and continue for twelve months following termination of employment for any other reason. Payment of any compensation or benefits owed to Messrs. Gerrity or Cree may be terminated in connection with their violation of any of the Restrictive Covenants.
Termination by the Company without Cause, by Messrs. Gerrity or Cree for Good Reason, or due to Death or Disability while Messrs. Gerrity or Cree are Performing the Duties set forth in the Executive Employment Agreements
In the event of either of Messrs. Gerrity’s or Cree’s termination of employment by the Company without Cause, by Messrs. Gerrity or Cree for Good Reason or Messrs. Gerrity’s or Cree’s death or termination of employment as a result of their disability, in each case, while performing their duties set forth in the Executive Employment Agreements, in addition to the Accrued Obligation, Prior Year Bonus and Benefit Obligation, Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will receive the Current Year Pro-Rata Bonus, paid within 30 days of termination and, subject to the execution of a release in favor of the Company and its affiliates, and their officers, directors, managers, employees and agents within 50 days following termination and nonrevocation thereafter, Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will also be entitled to the sum of their (1) base salary and (2) annual bonuses for the remainder of the initial term of the Executive Employment Agreements, which extends to December 31, 2023.
Vitesse Energy, Inc. Long-Term Incentive Plan
Prior to the Spin-Off, our Board intends to approve a long-term incentive plan, to become effective subject to and contingent upon the Spin-Off, which we refer to as the “VTS LTIP.” The following summary describes what we anticipate will be the material terms of the VTS LTIP, although the ultimate terms may vary depending on the plan actually adopted by the Board.
Participants. Any of our employees or consultants and any member of our Board, whether or not employed by us, will be eligible to participate in the VTS LTIP. An eligible employee, consultant or director becomes a participant if he or she is selected to receive and receives a VTS LTIP award by the plan administrator.
Plan Administration. Our Board will administer the VTS LTIP with respect to awards made to members of our Board who are not our employees. The committee designated by the Board, which we refer to as the “Committee,” will administer the VTS LTIP with respect to awards made to our employees and consultants. The Committee may delegate to our Chief Executive Officer, our President or a Committee member, all or part of its authority and duties as to awards made to individuals who are not subject to Section 16 of the Exchange Act.
132
The plan administrator will have the authority, among others, to select eligible persons to receive awards; determine the terms and conditions of, and all other matters relating to, awards; approve award agreements and the rules and regulations for the administration of the plan; construe and interpret the plan and award agreements; amend the terms of any award, including to accelerate vesting of any award; interpret, administer or reconcile inconsistencies in the plan; and make all other determinations as the plan administrator may deem necessary or advisable for the administration of the plan.
Aggregate Number of Plan Shares. The maximum aggregate number of shares of our common stock that may be issued or acquired and delivered (including in respect of the exercise of incentive stock options) under the VTS LTIP will be 3,960,000, (which represents approximately 12% of our shares of common stock calculated on a fully diluted basis immediately following the Spin-Off), with such shares subject to adjustment to reflect any extraordinary cash dividend, stock dividend, split or combination of our common stock. The total aggregate value of awards and cash compensation that may be issued or acquired and delivered to any non-employee director cannot exceed $750,000 per fiscal year; provided, that, for any calendar year in which a non-employee member of the Board (i) first commences service on the Board, (ii) serves on a special committee of the Board, or (iii) serves as lead director or chairman of the Board, additional awards may be granted to such non-employee member of the Board in excess of such limit. If any award granted under the VTS LTIP is settled in cash, expires or is forfeited, exchanged, canceled, or otherwise terminated without the actual delivery of shares (awards of restricted stock will not be considered “delivered shares” for this purpose), will again be available for awards. Notwithstanding the foregoing, (i) the number of shares tendered or withheld in payment of any exercise or purchase price of an option or SAR or taxes relating to any award, (ii) shares that were subject to an option or an SAR but were not issued or delivered as a result of the net settlement or net exercise of such option or SAR and (iii) shares repurchased on the open market with the proceeds of an option’s exercise price, will not, in each case, be available for awards. However, awards granted in substitution or exchange for awards previously granted by a company acquired by us or any subsidiary or with which we or any subsidiary combines, will not reduce the shares authorized for issuance under the VTS LTIP nor will any shares subject to such substitute awards be added to the shares available for issuance under the VTS LTIP (whether are not such substitute awards are later cancelled, forfeited or otherwise terminated).
Stock Option Awards. The exercise price of an option will be fixed by the plan administrator but cannot be less than the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The options will be subject to such terms, including the exercise price and the conditions and timing of vesting, exercise and expiration, as may be determined by the plan administrator. The maximum period in which an option may be exercised cannot exceed ten years from the date of grant. The option price may be paid in cash (or cash equivalent) or by such other method as the plan administrator may permit in its sole discretion, including by exchanging shares of our common stock valued at the fair market value at the time the option is exercised and by means of a “net exercise” procedure effected by withholding the minimum number of shares otherwise deliverable in respect of an option that are needed to pay the exercise price and all applicable required withholding taxes. Options granted under the VTS LTIP may be either non-qualified options or incentive stock options.
Stock Appreciation Rights Awards. Stock appreciation rights, which we refer to as “SARs,” entitle the holder, upon exercise, to receive an amount equal to the appreciation of the shares subject to such award between the grant date and the exercise date. The exercise price of a SAR will be fixed by the plan administrator but cannot be less than the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The maximum period in which a SAR may be exercised cannot exceed ten years from the date of grant. SARs may be granted as standalone awards or in connection with a stock option. SARs granted in connection with a stock option will be subject to the same terms and conditions as the underlying stock option, including with respect to exercisability. SARs may be settled in cash, shares of our common stock or a combination of the two, as determined by the plan administrator in its discretion.
Restricted Stock Awards. Restricted stock awards are a grant of shares of our common stock, which may be forfeitable or restricted for a certain period of time. Holders of restricted stock awards will generally have all of the rights of a stockholder (including voting and dividend rights) prior to the time the shares of our common stock become non-forfeitable or transferable. The vesting of restricted stock awards may also be subject to the achievement of performance goals as determined by the plan administrator.
133
Restricted Stock Unit Awards. Restricted stock unit awards are contractual promises to deliver shares of our common stock in the future, which may be forfeitable for a certain period of time. The vesting of restricted stock unit awards may also be subject to the achievement of performance goals as determined by the plan administrator. The restricted stock unit awards may receive dividend equivalents on the shares of our common stock, which may be paid in cash or shares that may be forfeited if the underlying restricted stock unit awards are forfeited. The restricted stock unit awards may be settled in cash, shares of our common stock or a combination of the two, as determined by the plan administrator in its discretion.
Performance Awards. Performance awards include performance share awards and performance unit awards that are granted subject to vesting or payment, as applicable, based on the attainment of specified performance objectives prescribed by the plan administrator during a performance period. Once earned, a performance award may be settled in cash, shares of our common stock or a combination of the two, as determined by the plan administrator in its discretion. Performance share awards may receive dividend equivalents, however no such dividend equivalents may be paid before the underlying performance share awards are earned and vested.
Other Stock-Based Awards. The plan administrator will be authorized to grant other stock-based awards in such amounts and subject to such terms and conditions as the plan administrator may determine.
Cash Awards. The plan administrator will be authorized to grant cash awards on a free-standing basis or in connection with any other award in the amount and terms as the plan administrator may determine.
Substitute Awards. The plan administrator may grant awards in substitution or exchange for any other award granted under the VTS LTIP or under any other of our plans or plans of our affiliates.
Changes in Capitalization. In the event of certain changes to our capitalization that result in subdivision or consolidation of the shares of stock (e.g., by reclassification, stock split, reverse stock split, or the issuance of a distribution on Stock payable in stock) or any other corporate transaction that would be considered an equity restructuring, appropriate adjustments will be made by the Committee as to the number, kind, and price of shares subject to outstanding awards, the number and kind of shares available for issuance under the plan, and any limitations on the number of awards that may be granted to particular classes of eligible persons.
Term and Amendments. The VTS LTIP will have a term of ten years. Our Board may amend the plan or terminate it at any time, subject to shareholder approval of any amendment to materially increase the aggregate number of shares of common stock that may be issued or delivered under the plan; provided, that, the Board may not materially affect the rights of any participant without their prior written approval.
134
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
Following the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions and immediately prior to the Spin-Off, Jefferies will beneficially own 94.37% of our total issued and outstanding common stock. After the Spin-Off, Jefferies will not own any shares of our common stock.
The following tables provide information regarding the anticipated beneficial ownership of our common stock immediately following the Spin-Off. Except as otherwise noted below, we based the share amounts on (1) each person’s beneficial ownership of Jefferies common stock on December 16, 2022, giving effect to a distribution ratio pursuant to which, for every 8.49668 shares of Jefferies common stock he, she or it held, one share of our common stock will be distributed, and (2) each person’s expected beneficial ownership of our common stock immediately prior to the Distribution as a result of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. Immediately following the Spin-Off, we estimate that approximately 28,202,019 shares of our common stock will be issued and outstanding, based on (1) the number of shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on December 16, 2022 and (2) the expected number of shares of Vitesse common stock outstanding (other than shares held by Jefferies) immediately prior to the Distribution as a result of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. The actual number of shares of our common stock outstanding following the Spin-Off will be determined on December 27, 2022.
To the extent our directors and executive officers own Jefferies common stock at the Record Date of the Spin-Off, they will participate in the Distribution on the same terms as other holders of Jefferies common stock.
Share Ownership Information for Directors and Officers
The following table shows the number of shares of Vitesse common stock expected to be beneficially owned by our current directors, named executive officers and directors and executive officers as a group immediately following the Spin-Off based on the assumptions set forth above. Except as otherwise noted in the footnotes below, each person identified in the table below has sole voting and investment power with respect to the securities he or she holds. Except as otherwise noted in the footnotes below, the address of each director and executive officer shown in the table below is 9200 E. Mineral Ave. Suite 200, Centennial, Colorado 80112.
| DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS |
COMMON STOCK(1) | PERCENT OF CLASS | ||||||
| Linda Adamany(2) |
7,535 | * | % | |||||
| Brian Cree(3) |
— | — | % | |||||
| Brian Friedman(4) |
866,705 | 3.0 | % | |||||
| Bob Gerrity(3) |
144,099 | * | % | |||||
| David Macosko(3) |
17,125 | * | % | |||||
| Chris Humber |
— | — | % | |||||
| Cathleen Osborn |
— | — | % | |||||
| Daniel O’Leary |
— | — | % | |||||
| Randy Stein |
— | — | % | |||||
| Joseph Steinberg(5) |
2,592,767 | 9.2 | % | |||||
| All directors and executive officers as a group (10 persons)(6) |
3,628,231 | 12.7 | % | |||||
| * | Less than 1% of the total shares of Vitesse common stock expected to be outstanding. |
| (1) | Share totals are rounded to the nearest whole share. In the Distribution, share totals may be slightly reduced due to disposition of fractional shares. |
| (2) | Ms. Adamany’s beneficial ownership includes 1,746 shares of restricted stock as to which she has sole voting power but no investment power. |
| (3) | Beneficial ownership totals of Messrs. Cree, Gerrity and Macosko do not include shares underlying time-vested restricted stock units that will not vest within 60 days after December 16, 2022. For more information concerning such restricted stock units, see “Executive Compensation—Historical Compensation Paid or Awarded Under Vitesse Energy Plans and Arrangements and Certain Compensation Being Granted or Paid in Connection with the Spin-Off.” Mr. Gerrity’s beneficial ownership reflects 144,099 shares held by Gerrity Bakken as to which Mr. Gerrity would have sole voting and investment power. |
135
| (4) | Mr. Friedman’s beneficial ownership includes (i) 196,647 shares underlying exercisable options; (ii) 4,254 shares held by the trustee of the Jefferies profit-sharing plan, as to which Mr. Friedman would have shared voting power but no investment power; (iii) 156,289 shares deliverable upon settlement of restricted stock units to be settled by issuance of shares within 60 days after December 16, 2022 and (iv) 195,027 shares held by certain entities over which Mr. Friedman would have sole voting and investment power. Assuming that Mr. Friedman were to meet vesting and performance requirements of the Transitional Plan awards and that the awards were to be fully exercisable or due for settlement, he would beneficially own 1,528,064 shares of Vitesse common stock (5.2% of the outstanding class). |
| (5) | Mr. Steinberg’s beneficial ownership includes (i) 12,590 shares held by Mr. Steinberg’s spouse over which Mr. Steinberg may be deemed to have shared voting and investment power, (ii) 2,283,150 shares held by corporations wholly owned by Mr. Steinberg, family trusts or corporations wholly owned by family trusts as to which Mr. Steinberg would have sole voting and investment power, and (iii) 9,976 shares held in a charitable trust over which Mr. Steinberg may be deemed to have shared voting and investment power. |
| (6) | Includes Mr. Friedman’s rights to acquire 196,647 shares underlying exercisable options and 156,289 shares deliverable upon settlement of restricted stock units within more than 60 days after December 16, 2022. Does not include shares underlying time-vested restricted stock units granted to Messrs. Cree, Gerrity and Macosko that will not vest within 60 days after December 16, 2022. |
The following table shows all holders known to Vitesse that are expected to be beneficial owners of more than five percent of the outstanding shares of Vitesse common stock immediately following the completion of the Spin-Off based on the assumptions set forth above. Except as otherwise noted in the footnotes below, each person or entity identified in the table has sole voting and investment power with respect to the securities he, she or it holds.
| NAME OF BENEFICIAL OWNER |
COMMON STOCK |
PERCENT OF CLASS |
||||||
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. |
2,601,529 | (1) | 9.2 | % | ||||
| BlackRock, Inc. |
2,147,786 | (2) | 7.6 | % | ||||
| Joseph Steinberg |
2,592,767 | (3) | 9.2 | % | ||||
| (1) | The Vanguard Group, 100 Vanguard Blvd., Malvern, Pennsylvania 19355, reported shared voting power over 109,385 shares of Jefferies common stock, sole dispositive power over 21,834,050 shares of Jefferies common stock, shared dispositive power over 270,310 shares of Jefferies common stock and sole voting power over no shares of Jefferies common stock as of December 31, 2021 in its amended Schedule 13G filed on February 10, 2022. |
| (2) | BlackRock, Inc., 55 East 52nd Street, New York, New York 10055, reported sole voting power over 17,348,307 shares of Jefferies common stock, sole dispositive power over 18,249,052 shares of Jefferies common stock and no shared voting or dispositive power over any shares of Jefferies common stock as of December 31, 2021 in its amended Schedule 13G filed on February 1, 2022. |
| (3) | Mr. Steinberg’s address is c/o Jefferies Financial Group Inc., 520 Madison Avenue, New York, New York 10022. Mr. Steinberg’s beneficial ownership includes (i) 12,590 shares held by Mr. Steinberg’s spouse over which Mr. Steinberg may be deemed to have shared voting and investment power, (ii) 2,283,150 shares held by corporations wholly owned by Mr. Steinberg, family trusts or corporations wholly owned by family trusts as to which Mr. Steinberg would have sole voting and investment power, and (iii) 9,976 shares held in a charitable trust over which Mr. Steinberg may be deemed to have shared voting and investment power. |
136
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Agreements Related to the Spin-Off
Following the Spin-Off, we and Jefferies will operate independently, and neither will have any ownership interest in the other. In order to govern the ongoing relationships among us, the Jefferies Parties, Jefferies Capital Partners, 3B Energy, Gerrity Bakken and Messrs. Gerrity and Cree after the Spin-Off and to facilitate an orderly transition, we intend to enter into a series of agreements to effect the Spin-Off, to provide a framework for the relationship among the parties after the separation and to provide for various rights and obligations following the Spin-Off, in each case, pursuant to which we and the Jefferies Parties will agree to indemnify each other against certain liabilities arising from our respective businesses. The following summarizes the terms of the material agreements into which we expect to enter.
Separation and Distribution Agreement
We intend to enter into a Separation and Distribution Agreement that will set forth our agreements with the Jefferies Parties, Jefferies Capital Partners, 3B Energy, Gerrity Bakken and Messrs. Gerrity and Cree regarding the principal actions to be taken in connection with the Spin-Off. It will also set forth other agreements that govern aspects of the parties’ relationships.
Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. The Separation and Distribution Agreement will describe certain actions relating to the Spin-Off that will occur prior to the Distribution, which are described in further detail under “The Spin-Off—Pre-Spin-Off Transactions.”
The Distribution. The Separation and Distribution Agreement will govern Jefferies’ and our respective rights and obligations regarding the proposed Distribution. Prior to the Distribution, Jefferies will deliver all the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock held by Jefferies to the distribution agent. Following the Distribution Date, the distribution agent will electronically deliver such shares of our common stock to Jefferies shareholders based on the distribution ratio. The Jefferies Board will have the sole and absolute discretion to determine the terms of, and whether to proceed with, the Distribution.
Conditions. The Separation and Distribution Agreement will also provide that several conditions must be satisfied or waived by Jefferies in its sole and absolute discretion before the Distribution can occur. For further information about these conditions, see the section entitled “The Spin-Off—Conditions to the Spin-Off.” The Jefferies Board may, in its sole and absolute discretion, determine the Record Date, the Distribution Date and the terms of the Spin-Off and may at any time prior to the completion of the Spin-Off decide to abandon or modify the Spin-Off.
Further Assurances. The parties will use commercially reasonable efforts to take all actions and to do all things reasonably necessary, proper or advisable under applicable laws, regulations and agreements to consummate the Distribution.
Exchange of Information. We and Jefferies will agree to provide each other with information to comply with reporting, disclosure, filing or other requirements of any governmental authority, for use in judicial, regulatory, administrative, tax and other proceedings and to satisfy audit, accounting, claims defense, regulatory filings, litigation, tax and other similar requests. The parties will also agree to use commercially reasonable efforts to retain such information in accordance with Jefferies’ policies as in effect on the Distribution Date or policies reasonably adopted by another party after the Distribution Date.
Releases. The parties will provide for a full and complete release and discharge of all liabilities existing or arising from or based on facts existing before the Distribution Date, between or among each of us or any of our affiliates, 3B Energy, Gerrity Bakken and Messrs. Gerrity and Cree, and Jefferies Capital Partners, on the one hand, and the Jefferies Parties, on the other hand, except as set forth in the Separation and Distribution Agreement.
These releases will not extend to obligations or liabilities under any agreements governing the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions and the Tax Matters Agreement and the Vitesse Energy, Inc. Transitional Equity Award Adjustment Plan, among others.
Indemnification. We and Jefferies will agree to provide cross-indemnification provisions principally designed to place financial responsibility for the liabilities of our business with us and financial responsibility for obligations and
137
liabilities of Jefferies’ business (other than our business) with Jefferies.
Specifically, Vitesse and its subsidiaries will agree to indemnify, defend and hold harmless the Jefferies Parties and their respective affiliates, directors, officers, employees and agents, and each of the heirs, executors, successors and assigns of any of the foregoing (collectively, the “Jefferies Indemnified Parties”), from and against all expenses or losses incurred or suffered by one or more of the Jefferies Indemnified Parties in connection with, relating to, arising out of or due to any of the following items:
| ∎ | any claim that the information included in our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, that was supplied by Vitesse, is or was false or misleading with respect to any material fact or omits or omitted to state any material fact required to be stated therein or necessary in order to make the statements therein, in light of the circumstances under which they were made, not misleading, regardless of whether the occurrence, action or other event giving rise to the applicable matter took place prior to or subsequent to the Distribution; |
| ∎ | the conduct of Vitesse and its subsidiaries on and after the Distribution; |
| ∎ | the businesses of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil not being operated in the ordinary course prior to the Distribution as a result of any action or failure to act by (i) Vitesse or its subsidiaries, (ii) any person who served or is serving as a director, officer or employee of Vitesse or its subsidiaries after the Distribution, or (iii) any person whose employment and job responsibilities would have resulted in such person serving as a director, officer or employee of Vitesse or its subsidiaries after the Distribution had such person not retired or his employment been terminated voluntarily or involuntarily prior to the Distribution (the persons listed in clauses (ii) and (iii), the “Vitesse Persons”); or |
| ∎ | the breach by Vitesse or its subsidiaries of any covenant or agreement set forth in the Separation and Distribution Agreement or any agreement or instrument contemplated by such agreement (other than the Tax Matters Agreement). |
Jefferies will agree to indemnify, defend and hold harmless Vitesse and its subsidiaries and their respective affiliates, directors, officers, employees and agents, and each of the heirs, executors, successors and assigns of any of the foregoing (collectively, the “SpinCo Indemnified Parties”), from and against all expenses or losses incurred or suffered by one or more of the SpinCo Indemnified Parties in connection with, relating to, arising out of or due to any of the following items:
| ∎ | any claim that the information included in our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part, that was supplied by Jefferies, is or was false or misleading with respect to any material fact or omits or omitted to state any material fact required to be stated therein or necessary in order to make the statements therein, in light of the circumstances under which they were made, not misleading, regardless of whether the occurrence, action or other event giving rise to the applicable matter took place prior to or subsequent to the Distribution; |
| ∎ | the businesses, assets and liabilities held by Jefferies at the time of the Distribution; |
| ∎ | the businesses of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil not being operated in the ordinary course prior to the Distribution as a result of any action or failure to act by Jefferies or its subsidiaries or any person who served or is serving as a director, officer or employee of Jefferies or its subsidiaries prior to, on or after the Distribution, other than the Vitesse Persons; or |
| ∎ | the breach by Jefferies or its subsidiaries of any covenant or agreement set forth in the Separation and Distribution Agreement or any agreement or instrument contemplated by such agreement (other than the Tax Matters Agreement). |
The Separation and Distribution Agreement will also establish procedures with respect to claims subject to indemnification and related matters.
Termination. The Jefferies Board, in its sole and absolute discretion, may terminate the Separation and Distribution Agreement at any time prior to the Distribution.
138
This summary does not purport to be complete and you are encouraged to read the form of the Separation and Distribution Agreement, which is filed as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is part, for greater detail with respect to these provisions.
Tax Matters Agreement
We intend to enter into a Tax Matters Agreement with Jefferies that will govern the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of Jefferies and us after the Spin-Off with respect to all tax matters, including taxes arising in the ordinary course of business, and taxes, if any, incurred as a result of any failure of the Distribution (or certain related transactions) to qualify as tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The Tax Matters Agreement will also set forth the respective obligations of the parties with respect to the filing of tax returns, the administration of tax contests and assistance and cooperation on tax matters.
In general, the Tax Matters Agreement will govern the rights and obligations that we and Jefferies have after the Distribution with respect to taxes. Under the Tax Matters Agreement, Jefferies generally will be responsible for income taxes attributable to the portion of items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit of Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil allocated by Vitesse Energy and Vitesse Oil to Jefferies (directly or through other entities) that are reported on partnership tax returns of Vitesse Energy or Vitesse Oil for tax periods ending on or before the Distribution. We will generally be responsible for any such income taxes to the extent that such taxes arise on audit following the Distribution, for any income taxes attributable to tax items not reported on partnership tax returns for tax periods ending on or before the Distribution, and for all non-income taxes attributable to our business.
The Tax Matters Agreement will further provide that:
| • | without duplication of our payment obligations described in the prior paragraph, we will generally indemnify Jefferies against (i) taxes allocated to us under the Tax Matters Agreement (as described above) and (ii) any liability or damage resulting from a breach by us or any of our affiliates of a covenant or representation made in the Tax Matters Agreement; and |
| • | Jefferies will indemnify us against taxes for which Jefferies is responsible under the Tax Matters Agreement (as described above). |
In addition to the indemnification obligations described above, the indemnifying party will generally be required to indemnify the indemnified party against any interest, penalties, additions to tax, losses, assessments, settlements or judgments arising out of or incident to the event giving rise to the indemnification obligation, along with costs incurred in any related contest or proceeding. Indemnification obligations of the parties under the Tax Matters Agreement are not subject to any cap.
Further, the Tax Matters Agreement generally will prohibit us and our affiliates from taking certain actions that could cause the Spin-Off or other related transactions to fail to qualify for their intended tax treatment, including:
| • | during the time period ending two years following the Distribution (or otherwise pursuant to a “plan” within the meaning of Section 355(e) of the Code), we may not cause or permit certain business combinations or transactions to occur; |
| • | during the time period ending two years following the Distribution, we may not discontinue the active conduct of our business (within the meaning of Section 355(b)(2) of the Code); |
| • | during the time period ending two years following the Distribution, issue shares of stock in a manner that could reasonably be expected to have adverse consequences under Section 355(e) of the Code; |
| • | during the time period ending two years following the Distribution, we may not redeem or otherwise acquire any of our common stock, other than pursuant to certain open-market repurchases; |
| • | during the time period ending two years following the Distribution, we may not amend our certificate of incorporation (or other organizational documents) or take any other action, whether through a stockholder vote or otherwise, affecting the voting rights of our common stock; and |
| • | more generally, we may not take any action that could reasonably be expected to cause the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, to fail to qualify as tax-free transactions under Section 368(a)(1)(D) and Section 355 of the Code. |
139
In the event that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, fails to qualify for the intended tax treatment, in whole or in part, and Jefferies is subject to tax as a result of such failure, the Tax Matters Agreement will determine whether Jefferies must be indemnified for any such tax by us. As a general matter, under the terms of the Tax Matters Agreement, we are required to indemnify Jefferies for any tax-related losses in connection with the Distribution and certain related transactions, due to any action by us or any of our subsidiaries. Therefore, in the event that the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, fail to qualify for their intended tax treatment due to any action by us or any of our subsidiaries, we will generally be required to indemnify Jefferies for the resulting taxes.
This summary does not purport to be complete and you are encouraged to read the form of the Tax Matters Agreement, which is filed as an exhibit to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is part, for greater detail with respect to these provisions.
Transitional Equity Award Adjustment Plan
The Vitesse Energy, Inc. Transitional Equity Award Adjustment Plan (the “Transitional Plan”) will generally provide for the treatment of those Jefferies outstanding compensatory equity awards that are to be adjusted into equity incentive awards denominated in shares of both our common stock and Jefferies common stock in connection with the Spin-Off. Other Jefferies equity awards will be adjusted by Jefferies without our issuance of equity awards, and thus will be outside of the scope of the Transitional Plan. All adjusted awards will be subject to generally the same vesting, exercisability, expiration, settlement and other material terms and conditions as applied to the applicable original Jefferies award immediately before the Spin-Off, except that equity awards relating to Vitesse will be subject to accelerated vesting, exercisability and in some cases settlement in the event of a change in control of Vitesse.
Each Jefferies stock option that will not remain an option to purchase shares of only Jefferies common stock will be converted into both a post-Spin-Off option to purchase shares of Jefferies common stock and an option to purchase shares of Vitesse common stock. The exercise price of such Jefferies stock option and the exercise price and number of shares subject to such Vitesse stock option will be adjusted so that (i) the aggregate intrinsic value of such post-Spin-Off Jefferies stock option and Vitesse stock option immediately after the Spin-Off equals the aggregate intrinsic value of the Jefferies stock option as measured immediately before the Spin-Off and (ii) the aggregate exercise price of the such post-Spin-Off Jefferies stock option and Vitesse stock option equals the aggregate exercise price of the Jefferies stock option immediately before the Spin-Off, subject to rounding.
Each Jefferies restricted stock unit award and performance stock unit award (other than those that will remain awards denominated in shares of only Jefferies stock, which includes the portion of any performance stock unit award that may be earned above the designated target level), including any additional stock units accrued as a result of dividend equivalents, will be adjusted by the grant of a Vitesse restricted stock unit award and a Vitesse performance stock unit award, respectively. The number of Vitesse awards to be granted in respect of these Jefferies awards will equal the number of Vitesse shares that would have been distributed in the Spin-Off if the Jefferies award had been shares of outstanding Jefferies common stock at the effective time of the Spin-Off, subject to rounding.
A holder of a Jefferies restricted stock award will receive shares of our common stock in the Distribution, which shares will be subject to the provisions of the Transitional Plan, including generally the same risk of forfeiture and other conditions as applied to the original Jefferies restricted stock award.
The new Vitesse equity awards issued as an adjustment to Jefferies equity awards will be issued pursuant to the Transitional Plan, the form of which will be filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part. The Transitional Plan will govern the terms and conditions of the new Vitesse awards issued as an adjustment to Jefferies awards at the effective time of the Spin-Off, but will not be used to make any grants following the Spin-Off.
Other Transactions and Relationships with Related Persons
Vitesse has engaged Jefferies LLC, an affiliate of Jefferies, as a financial advisor with respect to the Spin-Off. Jefferies LLC will provide Vitesse with financial and/or capital markets advice and assistance in connection with the Spin-Off, in exchange for a fee of $3.0 million and reimbursement of the reasonable out-of-pocket expenses, including the reasonable fees and expenses of the outside counsel of Jefferies LLC, ancillary expenses and the fees
140
and expenses of any other independent experts retained by Jefferies LLC with Vitesse’s consent, but not to exceed $50,000. Vitesse has agreed to indemnify Jefferies LLC and its affiliates and representatives against certain liabilities arising out of or in connection with Jefferies LLC’s services, or to contribute to payments such persons may be required to make in respect thereof.
Brian Friedman, who will be a member of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off, is an indirect limited partner of Jefferies Capital Partners and the President of Jefferies. As a result of the transfer of Vitesse Oil to Vitesse and the series of distributions contemplated by the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, Mr. Friedman will hold approximately 0.9% of the issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately prior to the Distribution, and will hold approximately 1.8% of the issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately following the Distribution. In addition, as a result of the adjustment of Mr. Friedman’s outstanding Jefferies compensatory equity awards upon the effectiveness of the Distribution, he will receive Vitesse stock options, Vitesse restricted stock units and Vitesse performance stock units that, assuming full exercise of the stock options (including portions that will not be immediately exercisable) and the settlement of all restricted stock units and performance stock units (the latter at the target level based on Jefferies performance), would represent an additional 3.4% of the issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse. The intrinsic value of the Vitesse equity awards to be granted as an adjustment to Mr. Friedman’s Jefferies equity awards at the effective time of the Distribution cannot currently be determined, but is estimated to be approximately $16.3 million as of December 16, 2022. However, all compensation expense relating to the adjustment to Jefferies equity awards by issuance of Vitesse equity awards is borne by Jefferies and not by Vitesse.
Bob Gerrity, who is a member of our Board and our Chief Executive Officer, and Brian Cree, who is our President and Chief Operating Officer, collectively hold 100% of the equity interests in 3B Energy. Pursuant to the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, 3B Energy will transfer all of its Vitesse Energy equity interests to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for prior loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to 3B Energy. As of December 1, 2022, the outstanding principal amount of such prior loans was $11,370,926 ($20,111,012 with accrued interest). In addition, each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree will transfer each of their Vitesse Energy MIUs to Vitesse Energy Finance as repayment for prior loans from Vitesse Energy Finance to each of Messrs. Gerrity and Cree. As of December 1, 2022, the outstanding principal amounts of such prior loans were $6,666,667 and $3,333,333, respectively ($6,850,000 and $3,425,000, respectively, with accrued interest).
Mr. Gerrity holds 100% of the equity interests of Gerrity Bakken. As a result of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, Mr. Gerrity will hold less than 1% of the issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately prior to and immediately following the Distribution.
David Macosko, our Chief Financial Officer, holds an aggregate of 50,000 Vitesse Energy MIUs. As a result of the transfer of Vitesse Energy to Vitesse and the series of distributions contemplated by the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, Mr. Macosko will hold less than 1% of the issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately prior to the Distribution.
On July 1, 2016, Vitesse Management Company LLC (“Vitesse Management”), an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Vitesse Energy, entered into a services agreement with JETX Energy, LLC (“JETX”), an indirect majority owned subsidiary of Jefferies. Pursuant to this services agreement, Vitesse agreed to provide JETX certain administrative services and supervise, administer and manage the business affairs and operations of JETX and its subsidiaries for a service provider fee of $0.2 million per month. The term of this services agreement extends for an unlimited amount of time, but is subject to termination by either Vitesse Management or JETX upon providing written consent or certain final exit events specified therein. During the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and the year ended November 30, 2021, Vitesse Energy received service provider fees of $1.8 million and $2.4 million, respectively, pursuant to the services agreement.
On July 1, 2016, Vitesse Energy adopted an Employee Participation Plan (as amended to date, the “Employee Participation Plan”). Pursuant to the Employee Participation Plan, Eligible Employees (as defined in the Employee Participation Plan) were invited to purchase and own working interests in new oil and gas wells in which Vitesse Energy decided to invest. Vitesse Energy terminated the Employee Participation Plan and repurchased working interests from EPP Participants (as defined in the Employee Participation Plan) for an aggregate of $4,935,000 on
141
November 30, 2022. Messrs. Gerrity, Cree and Macosko received $1,187,609, $783,452 and $181,372, respectively, as consideration for the repurchase of the working interests that each received under the Employee Participation Plan.
Adam Cree, the son of Brian Cree, our President and Chief Operating Officer, is a non-executive employee of the Company. For the year ended November 30, 2021, Mr. Adam Cree earned $191,667 in his capacity as a non-executive employee of the Company.
Dane Roybal, the stepson of Bob Gerrity, our Chief Executive Officer, is a non-executive employee of the Company. For the year ended November 30, 2021, Mr. Roybal earned $254,167 in his capacity as a non-executive employee of the Company. Mr. Roybal also holds an aggregate of 50,000 Vitesse Energy MIUs. As a result of the transfer of Vitesse Energy to Vitesse and the series of distributions contemplated by the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, Mr. Roybal will hold less than 1% of the issued and outstanding common stock of Vitesse immediately prior to the Distribution.
Linda Adamany, Brian Friedman and Joseph Steinberg, who will be members of our Board upon the completion of the Spin-Off, also serve on the Jefferies Board and will receive shares of Vitesse in the Distribution. They may be required to recuse themselves from deliberations relating to these arrangements and other arrangements between us and Jefferies in the future, due to potential conflicts of interest.
Policy and Procedures Governing Related Person Transactions
Prior to the completion of the Spin-Off, our Board will adopt a written policy regarding the review, approval and ratification of transactions with related persons as set forth in our Audit Committee Charter and the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics.
We anticipate that this policy will provide that our Audit Committee review each of Vitesse’s transactions in which any “related person” had, has or will have a direct or indirect material interest. In general, “related persons” are our directors, director nominees, executive officers and shareholders beneficially owning more than 5% of our outstanding common stock and immediate family members or certain affiliated entities of any of the foregoing persons. We expect that our Audit Committee will approve or ratify only those transactions that are fair and reasonable to Vitesse and in Vitesse and its shareholders’ best interests.
Anything that could present a conflict of interest for a director may also present a conflict of interest if it is related to a member of his or her immediate family. Because potential conflicts of interest may not always be clear cut, directors, individuals subject to Section 16 of the Exchange Act and senior executive officers will be expected to disclose any material transaction or relationship that involves, or may involve, a conflict of interest or potential conflict of interest with Vitesse promptly to the chair of Vitesse’s Audit Committee, who may consult with legal counsel, as appropriate.
142
DESCRIPTION OF OUR INDEBTEDNESS
The summaries below do not purport to be complete and you are encouraged to read the Existing Revolving Credit Facility and the form of the New Revolving Credit Facility, which are filed as exhibits to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is part, for greater detail with respect to these agreements.
Existing Revolving Credit Facility
Vitesse Energy has a secured Existing Revolving Credit Facility with Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and a syndicate of banks, as lenders. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility will mature on April 29, 2026. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility permits borrowing on a revolving credit basis with availability equal to the least of (1) the current aggregate elected commitments of $170 million, (2) the current borrowing base of $200 million and (3) the maximum credit amount of $500 million. The aggregate elected commitments of the lenders under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility may be increased up to a maximum credit amount of $500 million, subject to the satisfaction of certain customary conditions, including the willingness of the existing lenders to increase their commitments or of new lenders to provide additional commitments. In connection with the closing of the Existing Revolving Credit Facility in April 2022, the borrowing base was set at $200 million. Our borrowing base under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility is subject to regular, semi-annual redeterminations on or about April 1 and October 1 of each year based on, among other things, the value of our proved oil and natural gas reserves, as determined by the lenders in their discretion. As of August 31, 2022, under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility we had outstanding borrowings of $66.0 million and $104.0 million of available borrowing capacity. At our option, borrowings under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on SOFR (“Term SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the administrative agent’s prime rate, the federal funds rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day Term SOFR rate plus 1.0%), plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to Term SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the current commitment utilization percentage. The Existing Revolving Credit Facility is guaranteed by all of our subsidiaries and is collateralized by a first priority lien on substantially all assets of Vitesse Energy and its subsidiaries, including a first priority lien on properties representing a minimum of 85% of the proved reserve value of our oil and natural gas properties.
The credit agreement governing the Existing Revolving Credit Facility (the “Credit Agreement”) contains various affirmative, negative and financial maintenance covenants. These covenants limit our ability to, among other things, incur or guarantee additional debt, make distributions to our equity holders, make certain investments and acquisitions, incur certain liens or permit them to exist, enter into certain types of transactions with affiliates, merge or consolidate with another company and transfer, sell or otherwise dispose of assets.
Under the Credit Agreement, we are permitted to make cash distributions without limit to our equity holders if (i) no event of default or borrowing base deficiency (i.e., outstanding debt (including loans and letters of credit) exceeds the borrowing base) then exists or would result from such distribution and (ii) after giving effect to such distribution, (a) our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 70% of the least of (the following collectively referred to as “Commitments”): (1) $500 million, (2) our then-effective borrowing base, and (3) the then-effective aggregate amount of our lenders’ commitments and (b) as of the date of such distribution, the EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 1.50 to 1.00. If our total outstanding credit usage is between 70% and 80% of the Commitments, we may make distributions if, in addition to the foregoing conditions, (i) our EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 2.25 to 1.00, (ii) we have free cash flow, as defined under the Credit Agreement, greater than $0 and (iii) we have delivered a certificate to our lenders attesting to the foregoing.
The Credit Agreement also contains covenants requiring us to maintain the following financial ratios tested on a quarterly basis: (1) a consolidated Total Funded Debt to consolidated EBITDAX ratio (in each case, as defined in the Credit Agreement) of not greater than 3.0 to 1.0; and (2) a ratio of consolidated current assets to consolidated current liabilities of not less than 1.0 to 1.0. The Credit Agreement also contains customary events of default, including non-payment, breach of covenants, materially incorrect representations, cross default, bankruptcy and change in control. If an event of default exists under the Credit Agreement, the lenders will be able to terminate the lending commitments, accelerate the maturity of the Credit Agreement and exercise other rights and remedies with respect to the collateral.
Vitesse intends to enter into the secured New Revolving Credit Facility in connection with the Spin-Off. The New Revolving Credit Facility will amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility of Vitesse Energy. As the terms
143
of the New Revolving Credit Facility are finalized, we will provide any update to the description below and also file a form of the New Revolving Credit Facility in a subsequent amendment to the Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is a part.
Vitesse expects Vitesse Energy, as predecessor borrower under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, to assign the liens and Vitesse Energy’s existing rights, liabilities and obligations under the Existing Revolving Credit Facility to Vitesse. Vitesse then expects to amend and restate the Existing Revolving Credit Facility by entering into the New Revolving Credit Facility with Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and a syndicate of banks, as lenders. The New Revolving Credit Facility will mature on April 29, 2026. The New Revolving Credit Facility will permit borrowing on a revolving credit basis with availability equal to the least of (1) the anticipated aggregate elected commitments of $170 million, (2) the anticipated borrowing base of $265 million and (3) the maximum credit amount of $500 million. We anticipate that the aggregate elected commitments of the lenders under the New Revolving Credit Facility will allow increases up to a maximum credit amount of $500 million, subject to the satisfaction of certain customary conditions, including the willingness of the existing lenders to increase their commitments or of new lenders to provide additional commitments. Our borrowing base under the New Revolving Credit Facility is expected to be subject to regular, semi-annual redeterminations on or about April 1 and October 1 of each year based on, among other things, the value of our proved oil and natural gas reserves, as determined by the lenders in their discretion. We expect that, at our option, borrowings under the New Revolving Credit Facility will to bear interest at a rate unchanged from the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, which is either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on SOFR (“Term SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the administrative agent’s prime rate, the federal funds rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day Term SOFR rate plus 1.00%), plus an applicable margin expected to range from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to Term SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the current commitment utilization percentage. Consistent with the Existing Revolving Credit Facility, the New Revolving Credit Facility will be guaranteed by all of our subsidiaries and will be collateralized by a first priority lien on substantially all assets of Vitesse and its subsidiaries, including a first priority lien on properties representing a minimum of 85% of the total present value of our proved oil and natural gas properties.
The credit agreement governing the New Revolving Credit Facility (the “New Credit Agreement”) will contain various affirmative, negative and financial maintenance covenants. These covenants are expected to limit our ability to, among other things, incur or guarantee additional debt, make distributions to our equity holders, make certain investments and acquisitions, incur certain liens or permit them to exist, enter into certain types of transactions with affiliates, merge or consolidate with another company and transfer, sell or otherwise dispose of assets.
Under the New Credit Agreement, we anticipate we will be permitted to make cash distributions without limit to our equity holders if (i) no event of default or borrowing base deficiency (i.e., outstanding debt (including loans and letters of credit) exceeds the borrowing base) then exists or would result from such distribution and (ii) after giving effect to such distribution, (a) our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 80% of the least of (the following collectively referred to as “Commitments”): (1) $500 million, (2) our then-effective borrowing base, and (3) the then-effective aggregate amount of the aggregate elected commitments and (b) as of the date of such distribution, the EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 1.50 to 1.00. If our EBITDAX Ratio does not exceed 2.25 to 1.00, and if our total outstanding credit usage does not exceed 80% of the Commitments, we may also make distributions if our free cash flow (as defined under the New Revolving Credit Facility) is greater than $0 and we have delivered a certificate to our lenders attesting to the foregoing.
We also expect the New Credit Agreement will contain covenants requiring us to maintain the following financial ratios tested on a quarterly basis: (1) a consolidated Total Funded Debt to consolidated EBITDAX ratio (in each case, as defined in the Credit Agreement) of not greater than 3.0 to 1.0; and (2) a ratio of consolidated current assets to consolidated current liabilities of not less than 1.0 to 1.0. These financial covenants are consistent with the Existing Revolving Credit Facility. The New Credit Agreement will contain customary events of default, including non-payment, breach of covenants, materially incorrect representations, cross default, bankruptcy and change in control. If an event of default exists under the New Credit Agreement, the lenders will be able to terminate the lending commitments, accelerate the maturity of the Credit Agreement and exercise other rights and remedies with respect to the collateral.
144
DESCRIPTION OF OUR CAPITAL STOCK
Prior to the Distribution Date, Jefferies will approve and adopt our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, and our Board will approve and adopt our Amended and Restated Bylaws. The following summarizes information concerning our capital stock, including material provisions of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, our Amended and Restated Bylaws and certain provisions of Delaware law. This summary does not purport to be complete and you are encouraged to read the forms of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and our Amended and Restated Bylaws, which are filed as exhibits to our Registration Statement on Form 10, of which this Information Statement is part, for greater detail with respect to these provisions. As used in this “Description of Our Capital Stock,” “Vitesse,” “we,” “our” and “us” refer to Vitesse Energy, Inc. and not any of its consolidated subsidiaries after giving effect to the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions.
Immediately following the Spin-Off, our authorized capital stock will consist of 95,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share and 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.01 per share.
Shares Outstanding. Immediately following the Spin-Off, we estimate that approximately 28,202,019 shares of our common stock will be issued and outstanding, based on (1) the number of shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on December 27, 2022 and (2) the expected number of shares of our common stock outstanding (other than shares held by Jefferies) immediately prior to the Distribution as a result of the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions. The actual number of shares of our common stock outstanding immediately following the Spin-Off will depend on the actual number of shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding on the Record Date, and will reflect any issuance of new shares or exercise of outstanding options pursuant to Jefferies’ equity plans on or prior to the Record Date.
Dividends. Holders of shares of our common stock will be entitled to receive dividends when, as and if declared by our Board at its discretion out of funds legally available for that purpose, subject to the preferential rights of any preferred stock that may be outstanding. Following the Distribution, we expect that Vitesse will initially pay quarterly cash dividends and dividend equivalents totaling approximately $66.0 million per fiscal year. Notwithstanding this current expectation, the timing, declaration, amount of and payment of any dividends will be within the discretion of our Board and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our operating subsidiaries, covenants associated with certain of our debt service obligations, legal requirements or limitations, industry practice, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board. Moreover, if as expected we determine to initially pay a dividend following the Distribution, there can be no assurance that we will continue to pay dividends in the same amounts or at all thereafter. We have not adopted, and do not currently expect to adopt, a separate written dividend policy to reflect our Board’s policy. See the sections entitled “Dividend Policy” and “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Common Stock—Although we expect to pay dividends, we cannot provide assurance that we will pay dividends on our common stock, and our indebtedness may limit our ability to pay dividends on our common stock” and “—Our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is restricted by applicable laws and regulations and may be limited by requirements under our New Revolving Credit Facility.”
Voting Rights. The holders of our common stock will be entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters submitted to a vote of the stockholders.
Other Rights. Subject to the preferential liquidation rights of any preferred stock that may be outstanding, upon our liquidation, dissolution or winding-up, the holders of our common stock will be entitled to share ratably in our assets legally available for distribution to our stockholders.
Fully Paid. The issued and outstanding shares of our common stock are fully paid and non-assessable. Any additional shares of common stock that we may issue in the future will also be fully paid and non-assessable.
The holders of our common stock will not have preemptive rights or preferential rights to subscribe for shares of our capital stock.
145
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will authorize our Board to designate and issue from time to time one or more series of preferred stock without stockholder approval. Our Board may fix and determine the designation, relative rights, preferences and limitations of the shares of each such series of preferred stock. There are no present plans to issue any shares of preferred stock.
Certain Provisions of Delaware Law, Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws
Certain provisions in our proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and our proposed Amended and Restated Bylaws summarized below may be deemed to have an anti-takeover effect and may delay, deter or prevent a tender offer or takeover attempt that a stockholder might consider to be in its best interests, including attempts that might result in a premium being paid over the market price for the shares held by stockholders. These provisions are intended to enhance the likelihood of continuity and stability in the composition of our Board and in the policies formulated by our Board and to discourage certain types of transactions that may involve an actual or threatened change of control. These include provisions that:
| ∎ | prevent our stockholders from calling a special meeting or acting by written consent; |
| ∎ | require advance notice of any stockholder nomination for the election of directors or any stockholder proposal; |
| ∎ | provide for a plurality voting standard in contested director elections; |
| ∎ | authorize only our Board to fill director vacancies and newly created directorships; |
| ∎ | authorize our Board to adopt, amend or repeal our Amended and Restated Bylaws without stockholder approval; and |
| ∎ | authorize our Board to issue one or more series of “blank check” preferred stock. |
Section 203 of the DGCL, prohibits a Delaware corporation from engaging in a business combination with any interested stockholder for a period of three years following the date the person became an interested stockholder, subject to certain exceptions. In general, Section 203 of the DGCL defines an “interested stockholder” as an entity or person who, together with the entity’s or person’s affiliates, beneficially owns, or is an affiliate of the corporation and within three years prior to the time of determination of interested stockholder status did own, 15% or more of the outstanding voting stock of the corporation. A Delaware corporation may “opt out” of these provisions with an express provision in its certificate of incorporation. We have not opted out of Section 203 of the DGCL in our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation.
Limitation on Liability of Directors and Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Under Delaware law, a corporation may indemnify any individual made a party or threatened to be made a party to any type of proceeding, other than an action by or in the right of the corporation, because he or she is or was an officer, director, employee or agent of the corporation or was serving at the request of the corporation as an officer, director, employee or agent of another corporation or entity against expenses, judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred in connection with such proceeding if (1) he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation or (2) in the case of a criminal proceeding, he or she had no reasonable cause to believe that his or her conduct was unlawful. A corporation may indemnify any individual made a party or threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action or suit brought by or in the right of the corporation because he or she was an officer, director, employee or agent of the corporation, or is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation or other entity, against expenses actually and reasonably incurred in connection with such action or suit if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, provided that such indemnification will be denied if the individual is found liable to the corporation unless, in such a case, the court determines the person is nonetheless entitled to indemnification for such expenses. A corporation must indemnify a present or former director or officer who successfully defends himself or herself in a proceeding to which he or she was a party because he or
146
she was a director or officer of the corporation against expenses actually and reasonably incurred by him or her. Expenses incurred by an officer or director, or any employees or agents as deemed appropriate by the board of directors, in defending civil or criminal proceedings may be paid by the corporation in advance of the final disposition of such proceedings upon receipt of an undertaking by or on behalf of such director, officer, employee or agent to repay such amount if it shall ultimately be determined that he or she is not entitled to be indemnified by the corporation. The Delaware law regarding indemnification and expense advancement is not exclusive of any other rights which may be granted by our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation or our Amended and Restated Bylaws, a vote of stockholders or disinterested directors, agreement or otherwise.
Under Delaware law, termination of any proceeding by conviction or upon a plea of nolo contendere or its equivalent does not, of itself, create a presumption that such person is prohibited from being indemnified.
Delaware law permits a corporation to adopt a provision in its certificate of incorporation eliminating or limiting the personal liability of a director or officer in his or her capacity as such, to the corporation or its stockholders for monetary damages for breach of fiduciary duty as a director or officer, except that such provision may not limit the liability of (1) a director or officer for any breach of the director’s or officer’s duty of loyalty to the corporation or its stockholders, (2) a director or officer for acts or omissions not in good faith or that involve intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law, (3) a director for unlawful payment of dividends or stock purchases or redemptions, (4) a director or officer for any transaction from which the director or officer derived an improper personal benefit, or (5) an officer in any action by or in right of the corporation. Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, to the fullest extent permitted under Delaware law, no Vitesse director or officer shall be liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages for breach of fiduciary duty as a director or officer.
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will allow indemnification by Vitesse to the fullest extent permitted by law. Our Amended and Restated Bylaws will require indemnification, to the fullest extent permitted by law, of any person who was or is made a party or is threatened to be made a party to or is otherwise involved in any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative, or investigative (a “proceeding”) by reason of the fact that such person (or a person for whom such person is the legal representative) (i) is or was a director or officer of Vitesse (or any of its direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiaries), or (ii) while a director or officer of Vitesse, is or was serving at the request of Vitesse as a director, officer, employee, trustee, or agent of another corporation or of a partnership, limited liability company, joint venture, trust, other enterprise, or nonprofit entity, including service with respect to an employee benefit plan (a “Covered Person”), against all liability, loss, and reasonable expenses (including, without limitation, reasonable attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines, ERISA excise taxes and penalties, and amounts paid in settlement) incurred or suffered by such Covered Person in connection with such proceeding; provided that the foregoing shall not apply to a Covered Person with respect to a proceeding that was commenced by such Covered Person except under certain circumstances.
In addition, our Amended and Restated Bylaws will provide that Vitesse must pay the reasonable expenses (including reasonable attorneys’ fees) incurred by a Covered Person in defending any proceeding in advance of its final disposition; provided, however, that to the extent required by applicable law, such payment of expenses in advance of the final disposition of the proceeding shall be made only upon receipt of an undertaking by the Covered Person to repay all amounts advanced if it should be ultimately determined by final judicial decision from which there is no further right to appeal that the Covered Person is not entitled to be indemnified.
The indemnification rights to be provided in our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws will not be exclusive of any other right to which persons seeking indemnification may otherwise be entitled.
As permitted by Delaware law, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will authorize us to purchase and maintain insurance to protect any current or former director or officer against claims and liabilities that such persons may incur in such capacities.
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, in all cases to the fullest extent permitted by law, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of
147
Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for (1) any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of Vitesse, (2) any action or proceeding asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any current or former director, officer or other employee or stockholder of Vitesse to Vitesse or Vitesse stockholders, (3) any action or proceeding asserting a claim arising pursuant to, or seeking to enforce any right, obligation or remedy under, any provision of Delaware law or Vitesse’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation or Vitesse’s Amended and Restated Bylaws (with respect to each, as may be amended from time to time), (4) any action or proceeding asserting a claim governed by the internal affairs doctrine or any other action asserting an “internal corporate claim” as that term is defined in Section 115 of the DGCL or (5) any action or proceeding as to which the DGCL confers jurisdiction on the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware. However, if and only if the Court of Chancery of Delaware does not have jurisdiction, the action or proceeding may be brought in any other state or U.S. federal court located within the State of Delaware. Further, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will provide that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, to the fullest extent permitted by law, the U.S. federal district courts will be the sole and exclusive forum for any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under U.S. federal securities laws.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
In connection with its incorporation, on August 5, 2022, Vitesse issued 1,000 shares of its common stock at par value to Vitesse Energy Finance pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. Vitesse did not register the issuance of these shares under the Securities Act because such issuance did not constitute a public offering.
In connection with the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, Vitesse Energy Finance and holders of vested Vitesse Energy MIUs (other than Messrs. Gerrity and Cree) will transfer their respective equity interests in Vitesse Energy to Vitesse in exchange for 25,918,163 shares and 163,544 shares, respectively, of common stock of Vitesse. The transfers are expected to be consummated shortly before the Distribution. Shares of Vitesse common stock will be issued to Vitesse Energy Finance and such holders of vested Vitesse Energy MIUs as consideration for their respective ownership interests in Vitesse Energy pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. Vitesse does not plan to register the issuance under the Securities Act because this issuance will not constitute a public offering.
In connection with the Pre-Spin-Off Transactions, Jefferies Capital Partners and Gerrity Bakken will transfer their respective equity interests in Vitesse Oil to Vitesse in exchange for 1,976,213 shares and 144,099 shares, respectively, of common stock of Vitesse. The transfers are expected to be consummated concurrently with the transfer of Vitesse Energy to Vitesse and shortly before the Distribution. Shares of Vitesse common stock will be issued to Jefferies Capital Partners and Gerrity Bakken as consideration for their respective ownership interests in Vitesse Oil pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. Vitesse does not plan to register the issuances under the Securities Act because these issuances will not constitute a public offering.
The transfer agent and registrar for our common stock will be American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC.
New York Stock Exchange Listing
We intend to list our common stock on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “VTS.”
148
COMPARISON OF RIGHTS OF JEFFERIES SHAREHOLDERS AND VITESSE STOCKHOLDERS
The rights of Jefferies shareholders are currently governed by the NYBCL and Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated by-laws. The rights of Vitesse stockholders will be governed by the DGCL and Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws.
This section of this Information Statement describes certain material differences between the rights of Jefferies shareholders and Vitesse stockholders upon the completion of the Spin-Off.
This section does not include a complete description of all differences among the rights of Jefferies shareholders and Vitesse stockholders, nor does it include a complete description of the specific rights of these shareholders or stockholders, as applicable. Furthermore, the identification of some of the differences in the rights of these shareholders or stockholders, as applicable, as material is not intended to indicate that other differences do not exist.
You are urged to read carefully the relevant provisions of the NYBCL and the DGCL, as well as Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated by-laws and Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws. Copies of Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation and Jefferies’ amended and restated by-laws and Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws have been (or will be) filed with the SEC. See “Where You Can Find More Information.”
| JEFFERIES |
VITESSE | |||
| Authorized Capital Stock | Jefferies is authorized to issue 606,000,000 shares of capital stock, consisting of 600,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $1 per share, and 6,000,000 shares of preferred stock.
As of July 8, 2022, there were 232,452,897 shares of Jefferies common stock outstanding and 125,000 shares of mandatorily redeemable cumulative convertible preferred shares outstanding. |
Vitesse is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of capital stock, consisting of 95,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, and 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock. | ||
| Voting | Each holder of Jefferies common stock is entitled to one vote for each share held of record on the applicable record date for all matters submitted to a vote of shareholders.
Jefferies stockholders do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. |
Vitesse’s stockholders entitled to vote on a matter are entitled to one vote per share, except as otherwise provided in the DGCL or Vitesse’s certificate of incorporation.
Vitesse’s stockholders do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. | ||
| Class Voting | The NYBCL provides that holders of the outstanding shares of a class (or series) of shares are entitled to vote as a separate class in addition to the vote of all outstanding shares entitled to vote with respect to extraordinary transactions such as a | Section 242 of the DGCL provides that holders of the outstanding shares of a class of stock are entitled to vote as a separate class with respect to any amendment to the certificate of incorporation that would (i) alter | ||
149
| JEFFERIES |
VITESSE | |||
| plan of merger or consolidation or share exchanges or certificate of incorporation that would (i) limit such class’s voting rights, (ii) alter certain powers, preferences or rights of that class so as to adversely affect the holders of such class, or (iii) authorize any class or series of shares ranking prior to such series or class. | or change the powers, preferences or special rights of the shares of that class so as to adversely affect the holders of such class or (ii) increase or decrease the aggregate number of authorized shares or the par value of the shares of such class. | |||
| Rights of Preferred Stock | Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation expressly authorizes the Jefferies Board, subject to limitations prescribed by law and Jefferies’ restated certificate of incorporation, to provide for the issuance from time to time in one or more series of any number of shares of preferred stock and, by filing a certificate pursuant to the NYBCL, to establish the number of shares to be included in each such series, and to fix the designation, relative rights, preferences, qualifications and limitations of the shares of each such series. | Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation expressly authorizes the Board, subject to limitations prescribed by law and the provisions of Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, to provide for the issuance from time to time in one or more series of any number of shares of preferred stock and, by filing a certificate pursuant to the DGCL, to establish the number of shares to be included in each such series, and to fix the powers, designations, preferences and relative, participating, optional or other special rights, if any, and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions of the shares of each such series. | ||
| Dividends | Under Section 510 of the NYBCL, a corporation may declare and pay dividends on its outstanding shares either (i) out of surplus, so that the net assets of the corporation remaining after such declaration or payment shall at least equal the amount of its stated capital, or (ii) in case there shall be no such surplus, out of its net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend is declared and/or the preceding fiscal year.
The holders of Jefferies preferred stock have a priority over the holders of the common stock with respect to dividends. |
Vitesse may pay dividends out of statutory surplus (as defined and computed in accordance with the DGCL) or net profits (if no surplus), as and when declared by the Board. Vitesse stockholders will be entitled to receive and share equally in such dividends as may be declared by the Board out of funds legally available. | ||
150
| JEFFERIES |
VITESSE | |||
| Number of Directors | Jefferies’ amended and restated bylaws provide that the number of directors will be fixed by the Jefferies Board from time to time, but shall not be less than three. | Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Bylaws provide that the number of directors will be fixed by the Board from time to time, but shall not be less than three. | ||
| Elections of Directors | Jefferies’ amended and restated bylaws provide that a nominee for director will be elected if the votes cast for such nominee’s election exceed the number of against votes in respect of such nominee’s election; provided, however, that directors will be elected by a plurality of the votes cast at any meeting of shareholders for which the number of director nominees exceeds the number of directors to be elected.
Pursuant to Jefferies’ amended and restated bylaws, the directors other than those elected by the holders of preferred stock are elected for a one-year term, which expires at each annual meeting of stockholders when their successors are elected and qualified. |
Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Bylaws provide that, subject to the rights of the holders of any series of preferred stock to elect directors under specified circumstances, election of directors at all meetings of the stockholders at which directors are to be elected will be elected by the vote of the majority of the votes cast with respect to such director’s election by the holders of shares entitled to vote thereon; provided, that in a contested election, directors will be elected by the vote of a plurality of votes cast by holders entitled to vote.
Pursuant to Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, subject to the rights of holders of any series of preferred stock with respect to the election of directors, directors will be elected at each annual meeting of stockholders for a term to last until the next annual meeting of stockholders. | ||
| Removal of Directors |
Under Section 705 of the NYBCL, vacancies occurring on the board of directors by reason of the removal of directors without cause may be filled only by a vote of the shareholders unless the certificate of incorporation or bylaws provide otherwise.
Section 706 of the NYBCL, subject to certain conditions, provides that any or all of the directors may be removed for cause by vote of the shareholders, and, if the certificate of incorporation or the specific provisions of a bylaw adopted by the shareholders so provides, |
Under Section 141(k) of the DGCL, in a corporation with a declassified board of directors, any director or the entire board of directors may be removed, with or without cause, by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least a majority of the outstanding shares of stock entitled to vote at an election of directors, unless the certificate of incorporation provides otherwise.
The proposed Vitesse Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation provides that, subject to the rights of holders of | ||
151
| JEFFERIES |
VITESSE | |||
| directors may be removed by action of the board of directors. |
any series of preferred stock with respect to the election of directors, a director may be removed at any time, with or without cause, and upon the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding voting power of all then outstanding shares of capital stock entitled to vote generally in the election of directors. | |||
| Action by Written Consent | Under Section 615 of the NYBCL, any action by a shareholder by vote may be taken without a meeting on written consent, signed by the holders of all outstanding shares entitled to vote. | Pursuant to Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, except as otherwise expressly provided by the terms of any series of preferred stock permitting the holders of such series of preferred stock to act by written consent, any action required or permitted to be taken by the stockholders of Vitesse must be effected at a duly called annual or special meeting of stockholders of the Vitesse, and the ability of the stockholders to consent in writing to the taking of any action is specifically denied. | ||
| Special Meetings | Special meetings of shareholders of Jefferies may be called only by the Jefferies Board. | Special meetings of stockholders of Vitesse may be called only by the chairperson, the chief executive officer or the affirmative vote of the majority of our Board. | ||
| Advance Notice Requirements for Stockholder Nominations and Other Proposals | In order to properly submit any business to an annual meeting of shareholders, a shareholder must give timely notice in writing to the secretary of Jefferies of such shareholder’s intention to present such business. To be considered timely, a shareholder’s notice must be delivered and received at the principal executive office of Jefferies, not less than 120 days and not more than 150 days prior to the first anniversary date of Jefferies’ proxy statement in connection with the last annual meeting or if no annual meeting was held in the previous year, or if the date of the applicable annual | In addition to any other applicable requirements, for business to be properly brought before an annual meeting by a stockholder (including director nominations), such stockholder must have given timely notice thereof in proper written form to the Secretary of Vitesse. To be timely, a stockholder’s notice must be received by the Secretary at the principal executive offices of Vitesse not less than 120 days nor more than 150 days prior to the first anniversary of Vitesse’s proxy statement in connection with the preceding year’s annual meeting; provided, however, that | ||
152
| JEFFERIES |
VITESSE | |||
| meeting has been changed by more than 30 days from the first anniversary date of Jefferies’ proxy statement in connection with the last annual meeting, not less than the tenth day following the date on which public announcement of the date following the date on which Jefferies publicly announces the date of the applicable annual meeting. Similar notice requirements apply for director nominations made by shareholders. | in the event that the annual meeting is convened more than 30 days before or more than 60 days after the first anniversary of the date of the preceding year’s annual meeting, or if no annual meeting was held in the preceding year, notice by the stockholder to be timely must be so received no more than 190 days prior to such annual meeting nor less than the later of (A) 160 days prior to such annual meeting and (B) ten days after the day on which public disclosure of the date of the meeting was made. | |||
| Amendments to the Certificate of Incorporation | Under Section 803 of the NYBCL, subject to limited exceptions, amendments to the certificate of incorporation must be approved by vote of a majority of all outstanding shares entitled to vote on the proposed amendment at a meeting of shareholders, except that certificate of incorporation provisions requiring a greater or class vote may only be amended by such greater or class vote. Jefferies does not have supermajority voting requirements. In addition, Section 804 of the NYBCL provides that an amendment that negatively affects in certain ways holders of shares of a class or series requires authorization by a majority of the votes of all outstanding shares of the affected class or series. | Under Section 242 of the DGCL, unless the certificate of incorporation requires a greater vote, a proposed amendment to the certificate of incorporation must be approved by the affirmative vote of a majority of the voting power of the outstanding stock entitled to vote thereon and a majority of the outstanding stock of each class entitled to vote thereon as a class. Vitesse’s proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation does not have supermajority voting requirements. | ||
| Amendments to Bylaws | Jefferies’ bylaws may be adopted, amended or repealed either by the board of directors by vote of a majority of the directors present at the time of the vote if a quorum is then present or by vote of the holders of the shares at the time entitled to vote in the election of any directors. If any of Jefferies’ bylaws regulating an impending election of directors is adopted, amended or repealed by the board of directors, there must be set forth in the notice of the next meeting of shareholders for the election of directors the bylaws so adopted, amended or repealed, together with a concise statement of the changes made. | Vitesse’s proposed bylaws may be adopted, amended, altered or repealed by its board of directors or by the stockholders of Vitesse by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least a majority of the voting power of all then outstanding shares of the capital stock of Vitesse entitled to vote generally in the election of directors, voting together as a single class. | ||
153
| JEFFERIES |
VITESSE | |||
| State Anti-Takeover Statutes | Section 912 of the NYBCL generally provides that a New York corporation may not engage in a business combination with an interested shareholder for a period of five years following the interested shareholder’s becoming such. Such a business combination would be permitted where it is approved by the board of directors before the interested shareholder’s becoming such, or within thirty days thereafter, if a good faith proposal regarding a business combination is made in writing.
Covered business combinations include certain mergers and consolidations, dispositions or pledges of assets or stock, issuances of stock, plans for liquidation or dissolution, reclassifications of securities, recapitalizations and similar transactions. An interested shareholder is generally a stockholder owning at least 20% of a corporation’s outstanding voting stock.
In addition, New York corporations may not engage at any time with any interested shareholder in a business combination other than: (i) a business combination approved by the board of directors before the stock acquisition; (ii) a business combination approved by the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding voting stock not beneficially owned by the interested shareholder at a meeting for that purpose no earlier than five years after the stock acquisition; or (iii) a business combination in which the interested shareholder pays a formula price designed to ensure that all other shareholders receive at least the highest price per share that is paid by the interested shareholder and that meets certain other requirements. |
Section 203 of the DGCL, prohibits a Delaware corporation from engaging in a business combination with any interested stockholder for a period of three years following the date the person became an interested stockholder, unless (i) prior to such time the board of directors approved either the business combination or the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder; (ii) upon consummation of the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction commenced; or (iii) at or subsequent to such time the business combination is approved by the board of directors and authorized at an annual or special meeting of stockholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of at least 66 2/3% of the outstanding voting stock which is not owned by the interested stockholder.
In general, Section 203 of the DGCL defines an “interested stockholder” as an entity or person who, together with the entity’s or person’s affiliates, beneficially owns, or is an affiliate of the corporation and within three years prior to the time of determination of interested stockholder status did own, 15% or more of the outstanding voting stock of the corporation. A Delaware corporation may “opt out” of these provisions with an express provision in its certificate of incorporation. We have not opted out of Section 203 of the DGCL in our proposed Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. |
154
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed a Registration Statement on Form 10 with the SEC with respect to the shares of our common stock that Jefferies shareholders will receive in the Distribution, as contemplated by this Information Statement. This Information Statement is a part of, and does not contain all the information set forth in, the Registration Statement and the other exhibits and schedules to the Registration Statement. For further information with respect to us and our common stock, please refer to the Registration Statement, including its other exhibits and schedules. Statements we make in this Information Statement relating to any contract or other document are not necessarily complete, and you should refer to the exhibits attached to the Registration Statement for copies of the actual contract or document.
As a result of the Spin-Off, we will become subject to the information and reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, and, in accordance with the Exchange Act, we will file periodic reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. The SEC maintains a website, www.sec.gov, that contains periodic reports, proxy statements and information statements and other information regarding issuers, like us, that file electronically with the SEC. The Registration Statement, including its exhibits and schedules, and the periodic reports, proxy statements and information statements and other information that we file electronically with the SEC will be available for inspection and copying at the SEC’s website.
You can also find a copy of the Registration Statement and our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports, in each case, filed with or furnished to the SEC pursuant to the Exchange Act, on our website, www.vitesse-vts.com (which we expect to be operational on or prior to the Distribution Date), which we will make available free of charge as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC.
Information contained on, or connected to, any website we refer to in this Information Statement does not and will not constitute a part of this Information Statement or the Registration Statement of which this Information Statement is a part.
We intend to furnish holders of our common stock with annual reports containing financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP and audited and reported on, with an opinion expressed, by an independent registered public accounting firm.
You should rely only on the information contained in this Information Statement or to which this Information Statement has referred you. We have not authorized any person to provide you with different information or to make any representation not contained in this Information Statement.
155
| Vitesse Energy, Inc. Audited Financial Statement |
||||
| F-2 | ||||
| F-3 | ||||
| F-4 | ||||
| Vitesse Energy, LLC Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements |
||||
| Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets as of August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021 |
F-5 | |||
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Nine Months Ended August 31, 2022 and 2021 |
F-6 | |||
| F-7 | ||||
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Nine Months Ended August 31, 2022 and 2021 |
F-8 | |||
| F-9 | ||||
| Vitesse Energy, LLC Audited Consolidated Financial Statements |
||||
| F-20 | ||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of November 30, 2021 and 2020 |
F-21 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Years Ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 |
F-22 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Members’ Equity for Years Ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 |
F-23 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 |
F-24 | |||
| F-25 | ||||
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors of Vitesse Energy, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statement
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of Vitesse Energy, Inc. (the “Company”) as of August 31, 2022, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statement”). In our opinion, the financial statement presents fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of August 31, 2022, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
This financial statement is the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on this financial statement based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB and in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statement is free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statement, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statement. Our audit also included assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statement. We believe that our audit of the financial statement provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Denver, Colorado
December 28, 2022
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2022.
F-2
VITESSE ENERGY, INC.
Balance Sheet as of August 31, 2022
(in whole dollars)
| Assets |
||||
| Cash |
$ | — | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total Assets |
$ | — | ||
| Liabilities and Stockholder’s Equity |
||||
| Liabilities |
$ | — | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total Liabilities |
$ | — | ||
| Commitments and Contingencies |
||||
| Stockholder’s Equity |
||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value, 1,000 shares authorized; 1,000 shares issued and outstanding at August 31, 2022 |
$ | 10 | ||
| Stock subscription receivable |
(10 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total Stockholder’s Equity |
$ | — | ||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholder’s Equity |
$ | — | ||
|
|
|
See notes to balance sheet
F-3
VITESSE ENERGY, INC.
Note 1—Background and Nature of Operations
Vitesse Energy, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated as a corporation under the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware on August 5, 2022. The Company was formed for the purpose of effecting a “spin-off” transaction by Jefferies Financial Group Inc. (“Jefferies”). Prior to the spin-off, the Company will acquire all of the issued and outstanding equity interests of Vitesse Energy, LLC (“Vitesse Energy”) and Vitesse Oil, LLC, which together represent substantially all of those businesses or investments of Jefferies that acquire, develop, manage and monetize non-operated oil and natural gas working, royalty and mineral interests in the United States. Immediately prior to the completion of the spin-off, the Company will succeed to the operations of its predecessor, Vitesse Energy, and will become an independent, publicly traded company.
Note 2—Basis of Presentation and Accounting
The balance sheet is presented in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). Separate statements of operations, comprehensive income, changes in stockholder’s equity, and cash flows have not been presented because there have been no operations since the Company was formed.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the balance sheet. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Note 3—Stockholder’s Equity
As of August 31, 2022, the Company had 1,000 issued and outstanding shares of common stock, which were held by Vitesse Energy Finance LLC, an affiliate of Jefferies.
Note 4—Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated subsequent events through December 28, 2022, the date of issuance. Subsequent to August 31, 2022, in order to effectuate the “spin-off” transaction described in Note 1 above, the Company filed a registration statement on Form 10 and amendments thereto, with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
F-4
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets (Unaudited)
| (In thousands) | AUGUST 31, 2022 |
NOVEMBER 30, 2021 |
||||||
| Assets |
| |||||||
| Current Assets |
||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 8,085 | $ | 2,801 | ||||
| Revenue receivable |
44,737 | 31,959 | ||||||
| Commodity derivatives (Note 6) |
— | 1,513 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
136 | 148 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
52,958 | 36,421 | ||||||
| Oil and Gas Properties—Using the successful efforts method of accounting (Note 2) |
||||||||
| Proved oil and gas properties |
953,699 | 890,788 | ||||||
| Less accumulated DD&A and impairment |
(360,299 | ) | (314,292 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total oil and gas properties |
593,400 | 576,496 | ||||||
| Other Property and Equipment—Net |
148 | 223 | ||||||
| Other Assets |
||||||||
| Other noncurrent assets |
2,238 | 988 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total other assets |
2,238 | 988 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 648,744 | $ | 614,128 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities, Redeemable Units, and Members’ Equity |
| |||||||
| Current Liabilities |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 8,474 | $ | 4,593 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities (Note 7) |
23,984 | 18,617 | ||||||
| Commodity derivatives (Note 6) |
14,565 | 8,672 | ||||||
| Other current liabilities |
299 | 318 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
47,322 | 32,200 | ||||||
| Long-term Liabilities |
||||||||
| Revolving credit facility (Note 5) |
66,000 | 68,000 | ||||||
| Unit-based compensation (Note 10) |
15,891 | 8,352 | ||||||
| Commodity derivatives (Note 6) |
447 | — | ||||||
| Asset retirement obligations |
6,349 | 6,132 | ||||||
| Other noncurrent liabilities |
4 | 221 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
136,013 | 114,905 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 9) |
||||||||
| Redeemable Management Incentive Units (Note 10) |
7,386 | 4,831 | ||||||
| Members’ Equity—common units—450,000 units outstanding |
505,345 | 494,392 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable units, and members’ equity |
$ | 648,744 | $ | 614,128 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | (0.60 | ) | $ | (0.41 | ) | |||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-5
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations (Unaudited)
| FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED |
||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share data) | AUGUST 31, 2022 |
AUGUST 31, 2021 |
||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 179,177 | $ | 106,986 | ||||
| Natural gas |
45,510 | 17,496 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total revenue |
224,687 | 124,482 | ||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||
| Production expense |
35,179 | 32,591 | ||||||
| Production taxes |
17,828 | 10,082 | ||||||
| General and administrative |
11,496 | 7,704 | ||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
46,310 | 45,476 | ||||||
| Unit-based compensation (Note 10) |
7,539 | 814 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total operating expenses |
118,352 | 96,667 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Operating Income |
106,335 | 27,815 | ||||||
| Other (Expense) Income |
||||||||
| Commodity derivative loss, net |
(47,990 | ) | (32,934 | ) | ||||
| Interest expense |
(2,847 | ) | (2,517 | ) | ||||
| Other income |
10 | 11 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total other (expense) income |
(50,827 | ) | (35,440 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 55,508 | $ | (7,625 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net income (loss) per unit—basic and diluted |
$ | 0.12 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net income (loss) per non-founder MIUs classified as temporary equity—basic and diluted |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Weighted average units outstanding—basic and diluted |
438,625 | 438,625 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-6
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Members’ Equity (Unaudited)
| (In thousands) | MEMBERS’ EQUITY |
|||
| Balance—December 1, 2020 |
$ | 489,808 | ||
| Net loss |
(7,625 | ) | ||
| Fair market value MIU adjustment (See Note 10) |
(1,601 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance—August 31, 2021 |
480,582 | |||
| Balance—December 1, 2021 |
494,392 | |||
| Net income |
55,508 | |||
| Distribution to common unit holders |
(42,000 | ) | ||
| Fair market value MIU adjustment (See Note 10) |
(2,555 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance—August 31, 2022 |
$ | 505,345 | ||
|
|
|
|||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-7
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (Unaudited)
| FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED |
||||||||
| (In thousands) | AUGUST 31, 2022 |
AUGUST 31, 2021 |
||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities |
||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 55,508 | $ | (7,625 | ) | |||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
46,310 | 45,476 | ||||||
| Unrealized loss on derivative instruments |
7,852 | 26,263 | ||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
7,539 | 814 | ||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs |
324 | 203 | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities that provided (used) cash: |
||||||||
| Revenue receivable |
(12,779 | ) | (9,890 | ) | ||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
13 | 1,990 | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
776 | (1,085 | ) | |||||
| Accrued liabilities |
2,867 | 1,675 | ||||||
| Other |
7 | (19 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
108,417 | 57,802 | ||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities |
||||||||
| Acquisition of oil and gas properties |
(20,283 | ) | (2,738 | ) | ||||
| Development of oil and gas properties |
(37,023 | ) | (28,652 | ) | ||||
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(11 | ) | (114 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(57,317 | ) | (31,504 | ) | ||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities |
||||||||
| Proceeds from revolving credit facility |
16,000 | — | ||||||
| Repayments of revolving credit facility |
(18,000 | ) | (23,500 | ) | ||||
| Distributions |
(42,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Debt issuance costs |
(1,816 | ) | (27 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(45,816 | ) | (23,527 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash |
5,284 | 2,771 | ||||||
| Cash—Beginning of year |
2,801 | 1,734 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash—End of year |
$ | 8,085 | $ | 4,505 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information—Cash paid for interest |
$ | 2,493 | $ | 2,297 | ||||
| Supplemental Disclosure of Noncash Activity |
||||||||
| Oil and gas property included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ | 20,779 | $ | 11,624 | ||||
| Unit-based compensation liability transferred to redeemable management incentive units |
— | 333 | ||||||
| $ | (0.31 | ) | $ | (0.10 | ) | |||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-8
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
Note 1—Nature of Business
Vitesse Energy, LLC (the “Company”), a Delaware limited liability company, was formed on April 29, 2014 and is currently governed by the Second Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vitesse Energy, LLC dated July 1, 2018, as amended by the First Amendment to the Second Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vitesse Energy, LLC dated February 18, 2020. The membership interests in the Company are held approximately 97.5% by affiliates of Jefferies Financial Group (“JFG”) and approximately 2.5% by 3B Energy, LLC (“3B”), an entity whose members are comprised of certain executives of the Company. JFG is currently contemplating a contribution of the Company to a newly formed entity controlled by an affiliate of JFG (“SpinCo”), whereby the securities of SpinCo held by JFG or its affiliates would be distributed pro rata to the shareholders of JFG. If the distribution is consummated, SpinCo would become an independent, publicly traded entity.
The business purpose of the Company is to acquire, own, explore, develop, manage, produce, exploit, and dispose of oil and gas properties. The Company is focused on acquiring nonoperated working interest and royalty interest ownership primarily in the core of the Bakken Field in North Dakota and Montana. The Company also owns nonoperated interests in oil and gas properties in Colorado and Wyoming.
Note 2—Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries, Vitesse Management Company LLC (“Vitesse Management”) and Vitesse Oil, Inc. Intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Basis of Presentation
The condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“GAAP”). Conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the condensed consolidated financial statements and notes. Although these estimates are based on management’s best available knowledge of current and expected future events, actual results could differ from these estimates, which may be significantly impacted by various factors, including those outside of our control, such as the impact of a sustained deterioration in commodity prices and volumes, which would negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
These unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial statements have been prepared pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). Accordingly, these condensed consolidated financial statements reflect all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, that are, in the opinion of management, necessary to present fairly the financial position and results of operations for the respective interim periods. Certain information and note disclosures normally included in our annual financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP have been condensed or omitted from these interim financial statements pursuant to such rules and regulations, although we believe the disclosures made are adequate to make the information presented not misleading. These unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended November 30, 2021.
The results of operations for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year.
The Company operates in a single reportable segment. All of the Company’s operations are conducted in the continental United States.
Oil and Gas Properties
During nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company recorded depletion expense of $46.0 million and $45.2 million, respectively. The Company’s depletion rate for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021 was $16.71 and $16.76 per Boe, respectively.
F-9
The Company reviews its oil and gas properties for impairment whenever events and circumstances indicate a decline in the recoverability of their carrying value. The Company estimates the expected future cash flows of its oil and gas properties and compares such cash flows to the carrying amount of the proved oil and gas properties to determine if the amount is recoverable. If the carrying amount exceeds the estimated undiscounted future cash flows, the Company will adjust its proved oil and gas properties to estimated fair value. The factors used to estimate fair value include estimates of reserves, future commodity prices adjusted for basis differentials, future production estimates, anticipated capital expenditures, and a discount rate commensurate with the risk associated with realizing the projected cash flows. The discount rate is a rate that management believes is representative of current market conditions and includes estimates for a risk premium and other operational risks. There were no proved oil and gas property impairments during the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021.
Unit-based Compensation
In 2018, the Company amended the Limited Liability Company Agreement (the “Company Agreement”) which modified certain terms and conditions related to management incentive units (“MIUs”) (see Note 10) and common units held by the founding members of management. The Company is accounting for MIUs granted to employees (which excludes the founding members of management) as liability instruments under accounting guidance related to share-based compensation, whereby vested awards are recognized as liabilities, with changes in the estimated value of the awards recorded in earnings, until the holders have borne the risk of unit ownership, at which point the liability associated with the employee MIUs is reclassified to temporary equity, and changes in the estimated value of the employee MIUs are recorded as an adjustment to members’ equity.
Incentive compensation is also recognized for in-substance call options granted to the founding members of management which are classified as liabilities, recorded at estimated fair market value at each period end. Changes in the estimated fair value are recorded in earnings. As the Company is a private entity whose units are not traded, we consider the average volatility of comparable entities to develop an estimate of expected volatility for our awards of unit-based compensation which results in a reasonable estimate of fair value. Refer to Note 10 for further information regarding these awards.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue is derived from the sale of its produced oil and natural gas from wells in which the Company has nonoperated revenue or royalty interests. The Company’s oil and natural gas are produced and sold primarily in the core of the Bakken Field in North Dakota and Montana.
The sales of produced oil and natural gas are made under contracts that the operators of the wells have negotiated with customers, which typically include variable consideration based on monthly pricing tied to local indices and volumes delivered. Revenue is recorded at the point in time when control of the produced oil and natural gas transfers to the customer. Statements and payment may not be received via the operator of the wells for one to three months after the date the produced oil and natural gas is delivered, and, as a result, the amount of production delivered to the customer and the price that will be received for the sale of the product is estimated utilizing production reports, market indices, and estimated differentials. At the end of each month when the performance obligation is satisfied, the variable consideration can be reasonably estimated, and revenue due to the Company is recorded within revenue receivable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet until payment is received. Differences between the estimated amounts and the actual amounts received from the sale of the produced oil and natural gas are recorded when known, which is generally when statements and payment are received. Such differences have historically been immaterial.
For the oil and natural gas produced from wells in which the Company has nonoperated revenue or royalty interests, the Company recognizes revenue based on the details included in the statements received from the operator. Any gathering, transportation, production taxes, and other deductions included on the statements are recorded based on the information provided by the operator. The Company does not disclose the value of unsatisfied performance obligations as it applies the practical exemption which applies to variable consideration that is recognized as control of the product is transferred to the customer. Since each unit of product represents a separate performance obligation, future volumes are wholly unsatisfied, and disclosure of the transaction price allocated to remaining performance obligations is not required.
F-10
Concentrations of Credit Risk
For the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021, four and two operator(s) accounted for 48 percent and 25 percent of oil and natural gas revenue, respectively. As of August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021, two and four operators accounted for 31 percent and 52 percent, respectively, of oil and natural gas revenue receivable.
The Company’s oil and natural gas revenue receivable is generated from the sale of oil and natural gas by operators on its behalf. The Company monitors the financial condition of its operators.
Deferred Finance Charges
Costs associated with the revolving credit facility are deferred and amortized to interest expense over the term of the related financing. During the nine months ended August 31, 2022, the Company incurred $1.8 million in deferred financing costs. During the nine months ended August 31, 2021, the Company incurred immaterial deferred financing costs.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, Disclosure Framework—Changes to Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement. ASU No. 2018-13 modifies the disclosure requirements on fair value measurements in Topic 820, Fair Value Measurement. The Company adopted ASU 2018-13 on December 1, 2021. The guidance did not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements or notes accompanying the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses: Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. The ASU includes changes to the accounting and measurement of financial assets, including the Company’s accounts receivable, by requiring the Company to recognize an allowance for all expected credit related losses over the life of the financial asset at origination. This is different from the current practice, where an allowance is not recognized until the losses are considered probable. The new guidance will be effective for the Company’s year ending November 30, 2024. Upon adoption, the ASU will be applied using a modified retrospective transition method to the beginning of the earliest period in which the new guidance is effective. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is evaluating the impact the new guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Subsequent Events
The condensed consolidated interim financial statements and related disclosures include evaluation of events up through October 12, 2022, which is the date the consolidated interim financial statements were issued.
Note 3—Asset Acquisitions
During the nine months ended August 31, 2022, the Company purchased a number of proved oil and gas properties and proved leaseholds for an aggregate purchase price of $20.3 million. The transactions qualified as asset acquisitions; therefore, the oil and gas properties were recorded based on the fair value of the total consideration transferred on the acquisition dates, and transaction costs were capitalized as a component of the assets acquired. Transaction costs during the nine months ended August 31, 2022 were immaterial. The purpose of the acquisitions was to acquire proved developed and proved undeveloped oil and gas properties that were proximate and complementary to existing properties and leases for strategic purposes.
Note 4—Fair Value Measurements
Accounting standards require certain assets and liabilities be reported at fair value in the consolidated financial statements and provide a framework for establishing that fair value. The framework for determining fair value is based on a hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs and valuation techniques used to measure fair value.
Fair values determined by Level 1 inputs use quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Company has the ability to access.
Fair values determined by Level 2 inputs use other inputs that are observable, either directly or indirectly. These Level 2 inputs include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets and other inputs, such as interest rates, yield curves, and forward commodity price curves, that are observable at commonly quoted intervals.
F-11
Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs, including inputs that are available in situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the related asset or liability. These Level 3 fair value measurements are based primarily on management’s own estimates using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques taking into account the characteristics of the asset or liability. Significant Level 3 inputs include estimated future cash flows used in determining the fair value of purchased oil and gas properties.
In instances where inputs used to measure fair value fall into different levels in the above fair value hierarchy, fair value measurements in their entirety are categorized based on the lowest level input that is significant to the valuation. The Company’s assessment of the significance of particular inputs to these fair value measurements requires judgment and considers factors specific to each asset or liability.
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
As of August 31, 2022, the Company’s derivative financial instruments are composed of commodity swaps. The fair value of the swap agreements is determined under the income valuation technique using a discounted cash flow model, which requires a variety of inputs, including contractual terms, published forward commodity prices, and discount rates, as appropriate. The Company’s estimates of fair value of derivatives include consideration of the counterparty’s creditworthiness, the Company’s creditworthiness, and the time value of money. The consideration of these factors results in an estimated exit price for each derivative asset or liability under a marketplace participant’s view. All of the significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly; therefore, the Company’s commodity derivative instruments are included within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy (see Note 6).
Financial Instruments Not Measured at Fair Value
The carrying amounts of the majority of the Company’s financial instruments, namely cash, receivables, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities, approximate their fair values due to the short-term nature of these instruments. The Company’s credit facility (see Note 5) has a recorded value that approximates fair market value, as it bears interest at a floating rate that approximates a current market rate. The fair values of derivative instruments are estimated based on market conditions in effect at the end of each reporting period.
Note 5—Credit Facility
In May 2015, the Company entered into a credit facility (the “Credit Facility”) with a syndicate of banks (the “Lenders”) led by Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. (the “Administrative Agent”) with the Company as the borrower (the “Borrower”), which originally matured in May 2020. The Credit Facility has been subsequently amended, and the maturity date has been extended to April 2026. The most recent amendment was executed in April 2022. The Credit Facility specifies an aggregate maximum credit amount equal to $500.0 million and a maximum borrowing base, as determined by the Lenders. The determination of the borrowing base takes into consideration the estimated value of the Company’s oil and gas properties in accordance with the Lenders’ customary practices for oil and gas loans. The borrowing base is subject to scheduled redeterminations on a semiannual basis. The amount available for borrowing could be increased or decreased as a result of such redeterminations. Under certain circumstances, the Borrower and the Lenders shall each have the option to request one unscheduled borrowing base redetermination per fiscal year. As of August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021, the Company’s borrowing base was $200.0 million and $140.0 million, respectively, of which $66.0 million and $68.0 million, respectively, was outstanding.
At the Company’s option, borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest at either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the Administrative Agent’s prime rate, the Federal Funds rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day SOFR rate plus 1.0%), plus a spread ranging from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the borrowing base utilization percentage. Additionally, the Company incurs an unused credit facility fee of 0.500 percent regardless of the borrowing base utilization percentage. As of August 31, 2022, the interest rate on the outstanding balance under the Credit Facility was 5.56 percent.
The Credit Facility includes customary terms and covenants that place limitations on certain types of activities, including the payment of dividends and distributions, and requires satisfaction of certain financial covenants, such as minimum leverage and current ratios. The Credit Facility also requires excess cash at any point in time over $10.0 million to be repaid to the Borrowers, subject to the terms in the Credit Facility. The Company was in
F-12
compliance with all financial covenants of the Credit Facility at August 31, 2022. The Credit Facility is guaranteed by the Company’s subsidiaries and is collateralized with a minimum of 85 percent of the proved PV10 reserve value of the Company’s oil and gas properties.
In addition, the Credit Facility places additional conditions on the ability of the founding members of management to put their common units back to the Company (see Note 10). These conditions include the establishment of maximum percentages of debt outstanding relative to the existing borrowing base and pro forma debt to earnings before interest, taxes, depletion, depreciation, amortization, and exploration expense (“EBITDAX”) ratios, as defined in the Credit Facility, at the date of the permitted exercise.
Note 6—Derivative Instruments
The Company periodically enters into various commodity hedging instruments to mitigate a portion of the effect of oil and natural gas price fluctuations. The Company classifies the fair value amounts of commodity derivative assets and liabilities as current or noncurrent commodity derivative assets or current or noncurrent commodity derivative liabilities, whichever the case may be.
The following table summarizes the location and fair value amounts of commodity derivative instruments in the consolidated balance sheet as of August 31, 2022, as well as the gross recognized derivative assets, liabilities, and amounts offset in the condensed consolidated balance sheet:
| (In thousands) | GROSS RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ (LIABILITIES) |
GROSS AMOUNTS OFFSET |
NET RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ (LIABILITIES) |
|||||||||
| Commodity derivative assets: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative assets |
$ | 790 | $ | (790 | ) | $ | — | |||||
| Noncurrent derivative assets |
$ | 1,846 | $ | (1,846 | ) | $ | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 2,635 | $ | (2,635 | ) | $ | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Commodity derivative liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative liabilities |
$ | (15,355 | ) | $ | 790 | $ | (14,565 | ) | ||||
| Noncurrent derivative liabilities |
$ | (2,292 | ) | $ | 1,846 | $ | (447 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | (17,647 | ) | $ | 2,635 | $ | (15,012 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following table summarizes the location and fair value amounts of commodity derivative instruments in the consolidated balance sheet as of November 30, 2021, as well as the gross recognized derivative assets, liabilities, and amounts offset in the consolidated balance sheet:
| (In thousands) | GROSS RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ (LIABILITIES) |
GROSS AMOUNTS OFFSET |
NET RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ (LIABILITIES) |
|||||||||
| Commodity derivative assets: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative assets |
$ | 1,513 | $ | — | $ | 1,513 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,513 | $ | — | $ | 1,513 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Commodity derivative liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative liabilities |
$ | (8,672 | ) | $ | — | $ | (8,672 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | (8,672 | ) | $ | — | $ | (8,672 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-13
As of August 31, 2022, the Company had the following crude oil swaps:
| CONTRACT | TYPE |
TERM |
VOLUME HEDGED (Bbls) |
INDEX |
ROUNDED FIXED PRICE ($/Bbl) |
|||||||||
| 1 | Swap | September 2022 - November 2022 | 75,000 | WTI-NYMEX | $ | 51 | ||||||||
| 2 | Swap | September 2022 - November 2022 | 90,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 49 | |||||||||
| 3 | Swap | September 2022 - November 2022 | 90,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 65 | |||||||||
| 4 | Swap | September 2022 - November 2022 | 90,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 71 | |||||||||
| 5 | Swap | December 2022 - November 2023 | 360,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 70 | |||||||||
| 6 | Swap | December 2022 - November 2023 | 360,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 78 | |||||||||
| 7 | Swap | December 2022 - November 2023 | 180,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 86 | |||||||||
| 8 | Swap | December 2022 - November 2023 | 180,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 88 | |||||||||
| 9 | Swap | December 2023 - November 2024 | 360,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 72 | |||||||||
| 10 | Swap | December 2023 - November 2024 | 180,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 79 | |||||||||
| 11 | Swap | December 2023 - November 2024 | 180,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 81 | |||||||||
Due to the volatility of oil prices, the estimated fair values of the Company’s commodity derivative instruments are subject to large fluctuations from period to period.
The counterparties in the Company’s derivative instruments also participate in the Company’s Credit Facility; accordingly, the Company is not required to post collateral, as the counterparties have the right of offset for any derivative liabilities, and the Credit Facility is secured by the Company’s oil and gas assets. For further discussion related to the fair value of the Company’s derivatives, see Note 4.
Note 7—Accrued Liabilities
Accrued liabilities at August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021 are summarized as follows:
| (In thousands) | 31-AUG-22 | 30-NOV-21 | ||||||
| Accrued capital expenditures |
$ | 14,000 | $ | 11,500 | ||||
| Accrued lease operating expenses, net |
1,982 | 1,270 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation |
2,285 | 2,714 | ||||||
| Accrued derivative settlement |
3,701 | 2,450 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
2,016 | 683 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 23,984 | $ | 18,617 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 8—Related Party Transactions
3B acquired common units in the Company which were funded by two Initial Loans with related parties (see Note 13). As part of the funding of the Company, 3B entered into two different promissory notes with VE Holding LLC, an entity owned by JFG. The promissory notes allowed 3B to borrow up to $7.875 million and $3.5 million, initially accruing interest at 10.0 percent and 3.5 percent, respectively, and had maturity dates of May 7, 2021 (the “Initial Loans”). Initially, repayment of the $3.5 million promissory note was fully guaranteed by one of the members of 3B. Each of the two Initial Loans are collateralized by all of the common units held by 3B. In 2020 the $3.5 million promissory note was amended to remove the guarantee, change the interest rate to 10.0 percent and extend the maturity date to December 31, 2023. At the same time the $7.875 million promissory note was amended to extend the maturity date to December 31, 2023. The Initial Loans between 3B and VE Holding LLC are held outside of the Company and are not a liability of the Company. During 2021, a $12.0 million ratable distribution was made to the common unit holders. The 3B distribution of $0.3 million was used to pay down a pro rata portion of the outstanding interest on the Initial Loans.
F-14
In connection with the Company Agreement, in July 2018 certain executives entered into two separate promissory notes aggregating to $10.0 million with VE Holding LLC (the “2018 Notes”), which are collateralized by the MIUs granted to the respective executive. The 2018 Notes accrue interest at 3.0 percent per annum payable annually on December 31 and mature the earlier of July 1, 2024, an MIU exchange, or an acceleration event (as defined). The 2018 Notes may be prepaid at any time but are subject to mandatory prepayment upon the issuance of any distributions from the Company related to the MIUs held by such executives. Additionally, the 2018 Notes were considered full recourse to each respective executive for a limited time, with such recourse reduced by one-third each December 31 through 2020. As the 2018 Notes are between VE Holding LLC and the executives, they do not represent liabilities of the Company.
The Company has entered into an amended and restated services agreement (the “Services Agreement”) by and between the Company, Vitesse Management, and Vitesse Oil, LLC (“Vitesse Oil”) on May 7, 2014. Vitesse Oil is an entity with management common to that of the Company. Per the Services Agreement, costs incurred by Vitesse Management was to be allocable between the Company and Vitesse Oil initially at 50 percent each and adjusted automatically each quarter, such that the Company’s share of allocable costs shall be the greater of 50 percent or the quotient of the total contributed capital to the Company made by its members and the sum of the total contributed capital to the Company and Vitesse Oil by their respective members. As such, the Company incurred 90 percent of the Vitesse Management costs for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2020. The amount of costs reimbursed from Vitesse Oil to the Company for management services was $0.9 million for each of the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021. The amount due to the Company from Vitesse Oil as of August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021 was immaterial.
On July 1, 2016, the Company entered into a separate services agreement between Vitesse Management and JETX Energy, LLC (“JETX”), formerly known as Juneau Energy, LLC, another entity owned by JFG with common management. Per this services agreement, Vitesse Management is to provide JETX certain administrative services and supervise, administer, and manage the business affairs and operations of JETX and its subsidiaries for a service provider fee of $0.2 million per month. The term of this service agreement extends for an unlimited amount of time; however, it is subject to termination by either Vitesse Management or JETX if provided written consent following the first anniversary or a final exit event. During each of the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company received its net share of fees from JETX of approximately $1.8 million, which is classified as a reduction to general and administrative expenses on the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of operations.
Note 9—Commitments and Contingencies
Litigation
From time to time, the Company may be involved in litigation relating to claims arising out of its operations in the normal course of business. As of the date of this report, management of the Company was unaware of any material legal proceedings against the Company. The Company maintains insurance to cover certain actions.
Note 10—Members’ Equity and Unit-Based Compensation
The Company has two classes of membership units, with the following units authorized, issued, and outstanding as of August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021:
| AUTHORIZED | ISSUED AND OUTSTANDING |
|||||||
| Common units |
450,000,000 | 450,000,000 | ||||||
| Management incentive units |
1,000,000 | 953,750 | ||||||
Common Units
Common units issued to date have been issued at $1 per unit, with an aggregate capital commitment from all common members of $450 million. There initially shall be five managers on the board of managers, with three managers designated by JFG (such designated managers are each a “Jefferies Manager”) and two managers designated by 3B. For voting purposes, each manager is entitled to one vote, and the affirmative vote of a majority of
F-15
the board of managers, including at least one Jefferies Manager, is required to ratify any significant decisions of the Company.
Certain executives of the Company, as a result of their ownership of 3B, were granted the right to put all of their common units back to the Company in exchange for their pro rata share of the oil and gas interests then owned by the Company beginning in May 2017 (the “Common Unit Exchange Option”). In connection with the Company Agreement, the terms of the Common Unit Exchange Option were modified, where it may only be exercised on January 1, 2021 or on the annual anniversary thereafter and subject to additional conditions. Such conditions include, but are not limited to, that the Company is not in the process of an initial public offering; common unit holders have either received distributions resulting in, or the fair value of the Company’s net assets are such that the Company would achieve, a specified rate of return (“Flip Threshold”); and 3B reimburses the common unit holders for its pro rata share of liabilities in excess of cash balances at the time of exercise. Further, 3B must discharge any principal and interest outstanding related to the Initial Loans. As a result of the Common Unit Exchange Option resulting in the transfer of a portion of the oil and gas interests in proportion to 3B’s percentage holding of the common units, the Common Unit Exchange Option is considered to be a transaction that does not occur at fair market value. Through the issuance date of these financial statements the Common Unit Exchange Option has not been exercised.
In addition to the Common Unit Exchange Option, in the event of termination of any or both of the executives that hold common units, the Company has the option to repurchase the common units held by 3B in exchange for cash (the “Common Unit Call Option”). The Common Unit Call Option would be executed at fair market value on the date of the transaction.
As a result of 3B’s receipt of in-substance nonrecourse notes (the “Initial Loans”) that are each collateralized by all of the common units held by 3B, for accounting purposes the Company has granted 3B an in-substance call option that is within the scope of accounting guidance related to share-based compensation (the “Common Unit Option Grant”), which was fully vested on the date of grant in 2014. Due to the nature and terms of the Common Unit Exchange Option described above, the Common Unit Option Grant is classified as a liability award, remeasured at fair market value at each reporting date with the change in fair market value recorded to earnings. As of August 31, 2022, the aggregate intrinsic value of the Common Unit Option Grant, which is both outstanding and exercisable, is $0.7 million.
Management Incentive Units
Management incentive units may be issued by the Company to eligible employees and/or consultants. All MIUs are nonvoting and provide the MIU holders the opportunity to participate in distributions after the common unit holders have received a return equal to the Flip Threshold (as defined). In connection with the Company Agreement, the terms and conditions of the MIUs were modified from the Company’s original LLC agreement. Such modifications included, but were not limited to, a reset and change in the Flip Threshold, as well as changes to specific terms and conditions of MIU holder put rights and Company call rights.
MIUs have been granted to the founding members of management (“Founder MIUs”) and certain other employees of the Company (“Non-Founder MIUs”). Holders of Non-Founder MIUs may put at least 25 percent of their vested MIUs to the Company for cash at estimated fair market value as of the date of the transaction, on or after January 1, 2022, subject to conditions that include, but are not limited to, continued employment and no pending initial public offering (the “Non-Founder MIU Put Option”). Holders of the Founder MIUs may put at least 10 percent of their vested MIUs to the Company on or after January 1, 2021 for either (1) cash at estimated fair market value as of the date of the transaction or (2) interests in the Company’s oil and gas properties with a fair market value equal to the fair market value of the MIU as of the date of the transaction, subject to conditions that include, but are not limited to, the Company is not in the process of an initial public offering; common unit holders have either received distributions resulting in, or the fair value of the Company’s net assets are such that the common unit holders would achieve the Flip Threshold, and the 2018 Notes have been repaid or are to be repaid out of proceeds from the exercise of the put option (the “Founder MIU Put Option”). In addition, the Company has the right to repurchase Founder MIUs and Non-Founder MIUs at fair market value upon the termination of employment for any reason (the “MIU Call Option”). With respect to the Flip Threshold, as of April 2018 management determined that the achievement of the Flip Threshold was probable. Through the issuance date of these financial statements none of the Founder MIU Put Options, the Non-Founder MIU Put Options, or the MIU Call Option have been exercised.
F-16
All MIUs are subject to vesting requirements and forfeiture provisions specific to the Founder MIUs and Non-Founder MIUs, as outlined in the Company Agreement, employment agreement, grant letters, and other supporting MIU documentation. All unvested MIUs vest upon a final exit event (as defined), and are cancelled in the event of termination of the grantee. In the event of termination for Cause (as defined) all vested MIUs are forfeited for no consideration.
The Company accounts for Non-Founder MIUs as liability-based awards until the respective holder has borne the risk of unit ownership, at which point the value of the liability is reclassified outside of permanent equity. While the awards are classified as liabilities, compensation expense is recorded through the vesting period, and changes in the estimated fair market value of the liability, are recorded in earnings. Once reclassified outside of permanent equity increases in the estimated fair market value of the award are recorded through members’ equity. During the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company recorded a reduction of $2.6 million and $1.6 million respectively, through members’ equity to adjust the Non-Founder MIUs to fair market value.
A summary of the Company’s activity related to Non-Founder MIUs for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021 is presented below:
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Nonvested at period end |
28,750 | 45,000 | ||||||
| Granted during the period |
— | — | ||||||
| Vested during the period |
16,250 | 37,000 | ||||||
| Forfeited during the period |
— | — | ||||||
| Fair value of MIUs vested during the period |
$ | 0.5 million | $ | 0.8 million | ||||
As of August 31, 2022, there was $0.9 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested unit-based compensation arrangements. That cost is expected to be recognized through June 2024, over a weighted-average period of 1.2 years.
As a result of each of the management founders’ receipt of an in-substance nonrecourse note (the 2018 Notes) that are each collateralized by all of Founder MIUs held by the respective executive, for accounting purposes the Company has granted each of the management founders an in-substance call option that is within the scope of accounting guidance related to share-based compensation (the “Founder MIU Option Grant”). Due to the nature and terms of the Founder MIU Put Option described above, the Founder MIU Option Grant is classified as a liability award, remeasured at fair market value at each reporting date with the change in fair market value recorded to earnings. As of August 31, 2022, the aggregate intrinsic value of the Founder MIU Option Grant, which is both outstanding and exercisable, is $11.4 million.
Total compensation cost recognized in the condensed consolidated statements of operations within Unit-based compensation for the nine months ended August 31, 2022 and 2021 is as follows:
| FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED AUGUST 31, |
||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||
| Common Unit Option Grant |
$ | 1,494 | $ | (426 | ) | |||
| Founder MIU Option Grant |
5,609 | 1,219 | ||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs |
436 | 21 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 7,539 | $ | 814 | ||||
F-17
The liability recorded in the consolidated balance sheets within Unit-based compensation as of August 31, 2022 and November 30, 2021 is as follows:
| (In thousands) | 31-AUG-22 | 30-NOV-21 | ||||||
| Common Unit Option Grant |
$ | 3,200 | $ | 1,706 | ||||
| Founder MIU Option Grant |
12,119 | 6,510 | ||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs |
572 | 136 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 15,891 | $ | 8,352 | ||||
Measurement of unit-based compensation
The Company records the Non-founder MIUs, Founder MIU Option Grant, and Common Unit Option Grant at fair value at the date of grant and at each balance sheet date, which results in compensation cost being measured at fair value. As noted above, vested Non-founder MIUs, where the respective holder has borne the risk of ownership, are recorded within temporary equity, with changes in fair value recorded within members’ equity.
The fair value of each of the Founder MIU Option Grant and the Common Unit Option Grant (collectively “the Options”) are estimated using a Black Scholes Model that uses the assumptions noted in the following tables. As the Company doesn’t have publicly-traded equity we incorporated data from a group of publicly-traded peer companies when estimating fair value, and because when estimating fair value management incorporates ranges of assumptions for inputs, those ranges are disclosed. Expected volatilities are based on the historical volatility of our identified peer group of companies. The expected term of the Options is determined based on the time to exit/liquidity event. The risk-free rate for periods within the expected life of the option is interpolated from the US constant maturity treasury rate, for a term corresponding to the expected term.
| Founder MIU Option Grant | 31-AUG-22 | 30-NOV-21 | ||
| Expected volatility |
155% | 125% - 170% | ||
| Weighted-average volatility |
155% | 150% | ||
| Expected dividends/distributions |
0% | 0% | ||
| Expected term (in years) |
0.4 | 1 | ||
| Risk-free rate |
3.20% | 0.24% |
| Common Unit Option Grant | 31-AUG-22 | 30-NOV-21 | ||
| Expected volatility |
50% | 50% | ||
| Weighted-average volatility |
50% | 50% | ||
| Expected dividends/distributions |
0% | 0% | ||
| Expected term (in years) |
0.4 | 1 | ||
| Risk-free rate |
3.20% | 0.24% |
Distributions
Distributions of funds associated with common units follow a prescribed framework, which is outlined in detail in the Company Agreement. In general, distributions are first allocated to those unitholders based on their allocable share, as defined in the Company Agreement. Each unitholder will then receive a distribution in accordance with the tiered waterfall, as defined in the Company Agreement. The Company made $42.0 million of distributions on common units during the nine months ended August 31, 2022.
F-18
Earnings Per Unit
We have two classes of equity in the form of common units and MIUs that are vested and where the holder has borne the risks and rewards of ownership at which point the MIU is reclassified from liabilities to outside of permanent equity. Both common units and temporary equity classified MIUs are considered common units, and distributions are made in accordance with the Company Agreement. As such, we present earnings per unit (“EPU”) for both classes of equity. In calculating EPU we apply the two-class method. Under the two-class method net income (loss) attributable to common units is allocated to common units and other participating securities in proportion to the claim on earnings of each participating security after giving effect to distributions declared during the period, if any.
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net income (loss) per unit:
| FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED |
||||||||
| AUGUST 31, 2022 |
AUGUST 31, 2021 |
|||||||
| Common Units |
||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 55,508 | $ | (7,625 | ) | |||
| less: income allocable to participating securities |
||||||||
| In-substance options on common units (Common Unit Option Grant) |
(1,403 | ) | — | |||||
| In-substance options on Founder MIUs (Founder MIU Option Grant) |
— | — | ||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs classified as temporary equity |
— | — | ||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs classified as liabilities |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common unitholders |
$ | 54,105 | $ | (7,625 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding (in 000s) |
450,000 | 450,000 | ||||||
| less: Common Units accounted for as in-substance options |
(11,375 | ) | (11,375 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding (in 000s) |
438,625 | 438,625 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Basic and Diluted EPU |
$ | 0.12 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||
| Temporary Equity Classified MIUs |
||||||||
| Income allocable to Non-Founder MIUs classified as temporary equity |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
| MIUs classified in temporary equity (in 000s) |
250 | 234 | ||||||
| Basic and Diluted EPU |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
F-19
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors of Vitesse Energy, LLC
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Vitesse Energy, LLC and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of November 30, 2021 and 2020, the related consolidated statements of operations, members’ equity, and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended November 30, 2021, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of November 30, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended November 30, 2021, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB and in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Denver, Colorado
August 29, 2022
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2021.
F-20
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
| NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
| Assets |
| |||||||
| Current Assets |
||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 2,801 | $ | 1,734 | ||||
| Revenue receivable |
31,959 | 15,999 | ||||||
| Commodity derivatives (Note 6) |
1,513 | 9,223 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
148 | 2,176 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
36,421 | 29,132 | ||||||
| Oil and Gas Properties—Using the successful efforts method of accounting (Note 2) |
||||||||
| Proved oil and gas properties |
890,788 | 847,809 | ||||||
| Less accumulated DD&A and impairment |
(314,292 | ) | (253,851 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total oil and gas properties |
576,496 | 593,958 | ||||||
| Other Property and Equipment—Net |
223 | 233 | ||||||
| Other Assets |
||||||||
| Commodity derivatives (Note 6) |
— | 2,305 | ||||||
| Other noncurrent assets |
988 | 1,502 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total other assets |
988 | 3,807 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 614,128 | $ | 627,130 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities, Redeemable Units, and Members’ Equity |
| |||||||
| Current Liabilities |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 4,593 | $ | 9,305 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities (Note 7) |
18,617 | 12,717 | ||||||
| Commodity derivatives (Note 6) |
8,672 | — | ||||||
| Other current liabilities |
318 | 351 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
32,200 | 22,373 | ||||||
| Long-term Liabilities |
||||||||
| Revolving credit facility (Note 5) |
68,000 | 98,500 | ||||||
| Unit-based compensation (Note 13) |
8,352 | 7,579 | ||||||
| Asset retirement obligations (Note 8) |
6,132 | 5,666 | ||||||
| Other noncurrent liabilities |
221 | 539 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
114,905 | 134,657 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) |
||||||||
| Redeemable Management Incentive Units (Note 13) |
4,831 | 2,665 | ||||||
| Members’ Equity—common units—450,000 units outstanding |
494,392 | 489,808 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable units, and members’ equity |
$ | 614,128 | $ | 627,130 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-21
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Consolidated Statements of Operations
| FOR THE YEARS ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share data) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||
| Oil |
$ | 151,838 | $ | 91,542 | $ | 157,112 | ||||||
| Natural gas |
33,340 | 5,688 | 14,189 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenue |
185,178 | 97,230 | 171,301 | |||||||||
| Operating Expenses |
||||||||||||
| Production expense |
43,910 | 41,732 | 42,875 | |||||||||
| Production taxes |
14,535 | 9,173 | 15,572 | |||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,581 | 9,196 | 7,957 | |||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
60,846 | 58,307 | 64,721 | |||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties (Note 2) |
— | 13,200 | — | |||||||||
| Unit-based compensation (Note 13) |
1,409 | (544 | ) | 3,295 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
131,281 | 131,063 | 134,420 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) |
53,897 | (33,833 | ) | 36,881 | ||||||||
| Other (Expense) Income |
||||||||||||
| Commodity derivative (loss) gain, net |
(32,590 | ) | 29,633 | 3,778 | ||||||||
| Interest expense |
(3,207 | ) | (4,679 | ) | (4,825 | ) | ||||||
| Other income |
14 | 22 | 54 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total other (expense) income |
(35,783 | ) | 24,976 | (993 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 18,114 | $ | (8,857 | ) | $ | 35,888 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) per common unit—basic and diluted |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | 0.08 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) per non-founder MIUs classified as temporary equity—basic and diluted |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-22
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Consolidated Statements of Members’ Equity
| (In thousands) | MEMBERS’ EQUITY |
|||
| Balance—December 1, 2018 |
$ | 487,015 | ||
| Net income |
35,888 | |||
| Distribution to common unit holders |
(25,000 | ) | ||
| Fair market value MIU adjustment (Note 13) |
(271 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance—November 30, 2019 |
497,632 | |||
| Net loss |
(8,857 | ) | ||
| Fair market value MIU adjustment (Note 13) |
1,033 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance—November 30, 2020 |
489,808 | |||
| Net income |
18,114 | |||
| Distribution to common unit holders |
(12,000 | ) | ||
| Fair market value MIU adjustment (Note 13) |
(1,530 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance—November 30, 2021 |
$ | 494,392 | ||
|
|
|
|||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-23
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| FOR THE YEARS ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 18,114 | $ | (8,857 | ) | $ | 35,888 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depletion, depreciation, amortization, and accretion |
60,846 | 58,307 | 64,721 | |||||||||
| Unrealized loss (gain) on derivative instruments |
18,687 | (2,472 | ) | 280 | ||||||||
| Realized gain on derivative instruments related to early settlement of contract |
— | — | (591 | ) | ||||||||
| Unit-based compensation |
1,409 | (544 | ) | 3,295 | ||||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs |
276 | 362 | 281 | |||||||||
| Impairment of proved oil and gas properties |
— | 13,200 | — | |||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities that provided (used) cash: |
||||||||||||
| Revenue receivable |
(15,959 | ) | 18,663 | (4,116 | ) | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
1,921 | (1,303 | ) | (605 | ) | |||||||
| Accounts payable |
(997 | ) | (524 | ) | 2,405 | |||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
2,700 | (548 | ) | (373 | ) | |||||||
| Other |
(26 | ) | 25 | 9 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by Operating Activities |
86,971 | 76,309 | 101,194 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities |
||||||||||||
| Acquisition of oil and gas properties |
(6,210 | ) | (9,234 | ) | (5,094 | ) | ||||||
| Development of oil and gas properties |
(36,986 | ) | (61,486 | ) | (99,143 | ) | ||||||
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(121 | ) | (113 | ) | (183 | ) | ||||||
| Other |
— | 25 | 53 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in Investing Activities |
(43,317 | ) | (70,808 | ) | (104,367 | ) | ||||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from revolving credit facility |
1,000 | 10,000 | 33,000 | |||||||||
| Repayments of revolving credit facility |
(31,500 | ) | (15,500 | ) | (8,000 | ) | ||||||
| Distributions |
(12,000 | ) | — | (25,000 | ) | |||||||
| Debt issuance costs |
(87 | ) | (28 | ) | (41 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in Financing Activities |
(42,587 | ) | (5,528 | ) | (41 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash |
1,067 | (27 | ) | (3,214 | ) | |||||||
| Cash—Beginning of year |
1,734 | 1,761 | 4,975 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash—End of year |
$ | 2,801 | $ | 1,734 | $ | 1,761 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information—Cash paid for interest |
$ | 2,896 | $ | 4,376 | $ | 4,504 | ||||||
| Supplemental Disclosure of Noncash Activity |
||||||||||||
| Oil and gas properties included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ | 15,174 | $ | 15,690 | $ | 41,452 | ||||||
| Asset retirement obligations capitalized to oil and gas properties |
192 | 338 | 324 | |||||||||
| Unit-based compensation liability transferred to redeemable management incentive units |
636 | 655 | 2,773 | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-24
VITESSE ENERGY, LLC
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1—Nature of Business
Vitesse Energy, LLC (the “Company”), a Delaware limited liability company, was formed on April 29, 2014 and is currently governed by the Second Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vitesse Energy, LLC dated July 1, 2018, as amended by the First Amendment to the Second Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vitesse Energy, LLC dated February 18, 2020. The membership interests in the Company are held approximately 97.5% by affiliates of Jefferies Financial Group (“JFG”) and approximately 2.5% by 3B Energy, LLC (“3B”), an entity whose members are comprised of certain executives of the Company. JFG is currently contemplating a contribution of the Company to a newly formed entity controlled by an affiliate of JFG (“SpinCo”), whereby the securities of SpinCo held by JFG or its affiliates would be distributed pro rata to the shareholders of JFG. If the distribution is consummated, SpinCo would become an independent, publicly traded entity.
The business purpose of the Company is to acquire, own, explore, develop, manage, produce, exploit, and dispose of oil and gas properties. The Company is focused on acquiring nonoperated working interest and royalty interest ownership primarily in the core of the Bakken Field in North Dakota and Montana. The Company also owns nonoperated interests in oil and gas properties in Colorado and Wyoming.
Note 2—Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries, Vitesse Management Company LLC (“Vitesse Management”) and Vitesse Oil, Inc. Intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Segment and Geographic Information
The Company operates in a single reportable segment. The Company’s chief operating decision maker is the Chief Executive Officer. All of the Company’s operations are conducted in the continental United States.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Depletion, depreciation, and amortization (“DD&A”) and the evaluation of proved oil and gas properties for impairment are determined using estimates of oil and gas reserves. There are numerous uncertainties in estimating the quantity of reserves and in projecting the future rates of production and timing of development expenditures, which includes lack of control over future development plans as a non-operator. Oil and gas reserve engineering is a subjective process of estimating underground accumulations of oil and gas that cannot be measured in an exact way. In addition, significant estimates include, but are not limited to, estimates relating to certain crude oil and natural gas revenues and expenses, fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed under business combinations, valuation of unit-based compensation, and valuation of commodity derivative instruments. Further, these estimates and other factors, including those outside of the Company’s control, such as the impact of lower commodity prices, may have a significant adverse impact to the Company’s business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. As of the consolidated balance sheet date and periodically throughout the year, balances of cash exceeded the federally insured limit. As of November 30, 2021 and 2020 the Company held no cash equivalents.
F-25
Oil and Gas Properties
The Company follows the successful efforts method of accounting for oil and gas activities. Under this method of accounting, costs associated with the acquisition, drilling, and equipping of successful exploratory wells and costs of successful and unsuccessful development wells are capitalized and depleted, net of estimated salvage values, using the units-of-production method on the basis of a reasonable aggregation of properties within a common geological structural feature or stratigraphic condition, such as a reservoir or field. The Company’s proved oil and gas reserve information was computed by applying the average first-day-of-the-month oil and gas price during the 12-month period ended on the balance sheet date. During the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, the Company recorded depletion expense of $60.4 million, $58.0 million and $64.4 million, respectively. The Company’s depletion rate for the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 was $16.73, $16.40 and $16.45 per Boe, respectively.
Exploration, geological and geophysical costs, delay rentals, and drilling costs of unsuccessful exploratory wells are charged to expense as incurred. The sale of a partial interest in a proved property is accounted for as a cost recovery, and no gain or loss is recognized as long as this treatment does not significantly affect the units-of-production amortization rate. A gain or loss is recognized for all other sales of proved properties.
Costs associated with unevaluated exploratory wells are excluded from the depletable basis until the determination of proved reserves, at which time those costs are reclassified to proved oil and gas properties and subject to depletion. If it is determined that the exploratory well costs were not successful in establishing proved reserves, such costs are expensed at the time of such determination.
The Company reviews its oil and gas properties for impairment whenever events and circumstances indicate a decline in the recoverability of their carrying value. The Company estimates the expected future cash flows of its oil and gas properties and compares such cash flows to the carrying amount of the proved oil and gas properties to determine if the amount is recoverable. If the carrying amount exceeds the estimated undiscounted future cash flows, the Company will adjust its proved oil and gas properties to estimated fair value. The factors used to estimate fair value include estimates of reserves, future commodity prices adjusted for basis differentials, future production estimates, anticipated capital expenditures, and a discount rate commensurate with the risk associated with realizing the projected cash flows. The discount rate is a rate that management believes is representative of current market conditions and includes estimates for a risk premium and other operational risks. There were no proved oil and gas property impairments during the years ended November 30, 2021 and 2019. Proved oil and gas property impairments during the year ended November 30, 2020 were $13.2 million and were related to the Company’s Wyoming properties.
Asset Retirement Obligations (AROs)
AROs relate to estimated plugging and abandonment costs of oil and gas properties, including facilities, and the reclamation of the Company’s well locations. The Company records the fair value of an ARO in the period in which it is incurred. When the liability is initially recorded, the Company capitalizes an estimated cost by increasing the carrying amount of proved oil and gas properties. Over time, the liability is accreted each period toward an estimated future cost, and the capitalized cost is depleted. The Company uses the income valuation technique to estimate the fair value of AROs using the amounts and timing of expected future dismantlement costs, credit-adjusted risk-free rates, and the time value of money. For business combinations, the valuation utilizes a discount rate commensurate with what a market participant would use for AROs recorded. Revisions to the liability could occur due to changes in estimated abandonment costs or well economic lives or if federal or state regulators enact new requirements regarding the abandonment of wells. Adjustments to the liability are made as these estimates change. Upon settlement of the liability, the Company reports a gain or loss to the extent the actual costs differ from the recorded liability.
Unit-based Compensation
In 2018, the Company amended the Limited Liability Company Agreement (the “Company Agreement”) which modified certain terms and conditions related to management incentive units (“MIUs”) (see Note 13) and common units held by the founding members of management. The Company is accounting for MIUs granted to employees (which excludes the founding members of management) as liability instruments under accounting guidance related to share-based compensation, whereby vested awards are recognized as liabilities, with changes in the estimated
F-26
value of the awards recorded in earnings, until the holders have borne the risk of unit ownership, at which point the liability associated with the employee MIUs is reclassified to temporary equity, and changes in the estimated value of the employee MIUs are recorded as an adjustment to members’ equity.
Incentive compensation is also recognized for in-substance call options granted to the founding members of management which are classified as liabilities, recorded at estimated fair market value at each period end. Changes in the estimated fair value are recorded in earnings. As the Company is a private entity whose units are not traded, we consider the average volatility of comparable entities to develop an estimate of expected volatility for our awards of unit-based compensation which results in a reasonable estimate of fair value. Refer to Note 13 for further information regarding these awards.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue is derived from the sale of its produced oil and natural gas from wells in which the Company has nonoperated revenue or royalty interests. The Company’s oil and natural gas are produced and sold primarily in the core of the Bakken Field in North Dakota and Montana.
The sales of produced oil and natural gas are made under contracts that the operators of the wells have negotiated with customers, which typically include variable consideration based on monthly pricing tied to local indices and volumes delivered. Revenue is recorded at the point in time when control of the produced oil and natural gas transfers to the customer. Statements and payment may not be received via the operator of the wells for one to three months after the date the produced oil and natural gas is delivered, and, as a result, the amount of production delivered to the customer and the price that will be received for the sale of the product is estimated utilizing production reports, market indices, and estimated differentials. At the end of each month when the performance obligation is satisfied, the variable consideration can be reasonably estimated, and revenue due to the Company is recorded within revenue receivable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet until payment is received. Differences between the estimated amounts and the actual amounts received from the sale of the produced oil and natural gas are recorded when known, which is generally when statements and payment are received. Such differences have historically been immaterial.
For the oil and natural gas produced from wells in which the Company has nonoperated revenue or royalty interests, the Company recognizes revenue based on the details included in the statements received from the operator. Any gathering, transportation, production taxes, and other deductions included on the statements are recorded based on the information provided by the operator. The Company does not disclose the value of unsatisfied performance obligations as it applies the practical exemption which applies to variable consideration that is recognized as control of the product is transferred to the customer. Since each unit of product represents a separate performance obligation, future volumes are wholly unsatisfied, and disclosure of the transaction price allocated to remaining performance obligations is not required.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
For the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 three, two and three operators accounted for 37 percent, 30 percent and 40 percent of oil and natural gas revenue, respectively. As of November 30, 2021 and 2020 four and three operators accounted for 52 percent and 36 percent, respectively, of oil and natural gas revenue receivable.
The Company’s oil and natural gas revenue receivable is generated from the sale of oil and natural gas by operators on its behalf. The Company monitors the financial condition of its operators.
Income Taxes
The Company is a limited liability company (“LLC”). Accordingly, no provision for income taxes has been recorded, as the income, deductions, expenses, and credits of the Company are reported on the income tax returns of the Company’s members.
The Company accounts for uncertainty in income taxes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, which prescribe a comprehensive model for recognizing, measuring, presenting, and disclosing in the consolidated financial statements tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return, including a decision on whether to file in a particular jurisdiction. Only tax positions that meet a more-likely- than-not recognition threshold at the effective date may be recognized or continue to be recognized. If taxing authorities were to disallow any tax positions
F-27
taken by the Company, the additional income taxes, if any, would be imposed on the members rather than the Company, subject to IRS rules, which provide that adjustments resulting from IRS audit of the LLC will be assessed at the LLC level.
Deferred Finance Charges
Costs associated with the revolving credit facility are deferred and amortized to interest expense over the term of the related financing. The amount of deferred financing costs incurred, and the amortization of deferred financing costs, was immaterial for all periods presented.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company enters into derivative contracts to manage its exposure to oil and gas price volatility. Commodity derivative contracts may take the form of swaps, puts, calls, or collars. Cash settlements from the Company’s commodity price risk management activities are recorded in the month the contracts mature. Any realized gains and losses on settled derivatives, as well as mark-to-market gains or losses, are aggregated and recorded to Commodity derivative (loss) gain, net on the consolidated statements of operations.
Generally accepted accounting principles require recognition of all derivative instruments on the consolidated balance sheets as either assets or liabilities measured at fair value. Subsequent changes in the derivatives’ fair value are recognized currently in earnings unless specific hedge accounting criteria are met. Gains and losses on derivative hedging instruments must be recorded in either other comprehensive income or current earnings, depending on the nature and designation of the instrument. The Company has elected to not designate any derivative instruments as accounting hedges, and therefore marks all commodity derivative instruments to fair value and records changes in fair value in earnings. Amounts associated with deferred premiums on derivative instruments are recorded as a component of the derivatives’ fair values (see Note 6).
New Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, Disclosure Framework—Changes to Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement. ASU No. 2018-13 modifies the disclosure requirements on fair value measurements in Topic 820, Fair Value Measurement. The Company adopted ASU 2018-13 on December 1, 2021. The guidance did not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements or notes accompanying the consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses: Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. The ASU includes changes to the accounting and measurement of financial assets, including the Company’s accounts receivable, by requiring the Company to recognize an allowance for all expected credit related losses over the life of the financial asset at origination. This is different from the current practice, where an allowance is not recognized until the losses are considered probable. The new guidance will be effective for the Company’s year ending November 30, 2024. Upon adoption, the ASU will be applied using a modified retrospective transition method to the beginning of the earliest period in which the new guidance is effective. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is evaluating the impact the new guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Subsequent Events
The consolidated financial statements and related disclosures include evaluation of events through August 29, 2022, which is the date the consolidated financial statements were issued.
Note 3—Asset Acquisitions
During the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, the Company purchased a number of proved oil and gas properties and proved leaseholds for an aggregate purchase price of $6.2 million, $9.2 million and $5.1 million, respectively. The transactions qualified as asset acquisitions; therefore, the oil and gas properties were recorded based on the fair value of the total consideration transferred on the acquisition dates, and transaction costs were capitalized as a component of the assets acquired. Transaction costs during 2021, 2020 and 2019 were immaterial. The purpose of the acquisitions was to acquire proved developed and proved undeveloped oil and gas properties that were proximate and complementary to existing properties and leases for strategic purposes.
F-28
Note 4—Fair Value Measurements
Accounting standards require certain assets and liabilities be reported at fair value in the consolidated financial statements and provide a framework for establishing that fair value. The framework for determining fair value is based on a hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs and valuation techniques used to measure fair value.
Fair values determined by Level 1 inputs use quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Company has the ability to access.
Fair values determined by Level 2 inputs use other inputs that are observable, either directly or indirectly. These Level 2 inputs include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets and other inputs, such as interest rates, yield curves, and forward commodity price curves, that are observable at commonly quoted intervals.
Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs, including inputs that are available in situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the related asset or liability. These Level 3 fair value measurements are based primarily on management’s own estimates using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques taking into account the characteristics of the asset or liability. Significant Level 3 inputs include estimated future cash flows used in determining the fair value of purchased oil and gas properties.
In instances where inputs used to measure fair value fall into different levels in the above fair value hierarchy, fair value measurements in their entirety are categorized based on the lowest level input that is significant to the valuation. The Company’s assessment of the significance of particular inputs to these fair value measurements requires judgment and considers factors specific to each asset or liability.
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
As of November 30, 2021, the Company’s derivative financial instruments are composed of commodity swaps. The fair value of the swap agreements is determined under the income valuation technique using a discounted cash flow model. The fair values of options are determined under the income valuation technique using an option pricing model along with the stated amount of deferred premiums if applicable. The valuation models require a variety of inputs, including contractual terms, published forward commodity prices, volatilities for options, and discount rates, as appropriate. The Company’s estimates of fair value of derivatives include consideration of the counterparty’s creditworthiness, the Company’s creditworthiness, and the time value of money. The consideration of these factors results in an estimated exit price for each derivative asset or liability under a marketplace participant’s view. All of the significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly; therefore, the Company’s commodity derivative instruments are included within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy (see Note 6).
Nonrecurring Fair Value Measurements
Nonrecurring measurements include the fair value of impaired proved oil and gas properties. The Company determines the estimated fair value of the impaired proved oil and gas properties by using a discounted cash flow approach with unobservable Level 3 inputs (see Note 2) at the time of impairment. Significant inputs utilized in determining the fair value of its Wyoming proved oil and gas properties of $26.9 million during the year ended November 30, 2020 included commodity futures prices adjusted for basis differentials, wellbore-only reserves, and a discount rate commensurate with the risk associated with realizing the projected cash flows of 10 percent.
The Company uses the income valuation technique to estimate the fair value of asset retirement obligations, at initial recognition, arising from the development of proved properties using the amounts and timing of expected future dismantlement costs and credit-adjusted risk-free rates. Accordingly, the fair value is based on unobservable inputs and, therefore, is included within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The significant unobservable inputs include the gross cost of abandoning oil and gas wells; the economic lives of the properties; the inflation rate; and the credit-adjusted risk-free rate of the Company.
Financial Instruments Not Measured at Fair Value
The carrying amounts of the majority of the Company’s financial instruments, namely cash, receivables, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities, approximate their fair values due to the short-term nature of these instruments. The Company’s credit facility (see Note 5) has a recorded value that approximates fair market value, as it bears interest at a floating rate that approximates a current market rate. The fair values of derivative instruments are estimated based on market conditions in effect at the end of each reporting period.
F-29
Note 5—Credit Facility
In May 2015, the Company entered into a credit facility (the “Credit Facility”) with a syndicate of banks (the “Lenders”) led by Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. (the “Administrative Agent”) with the Company as the borrower (the “Borrower”), which originally matured in May 2020. The Credit Facility has been subsequently amended, and the maturity date has been extended to April 2023. The most recent amendment was executed in November 2021. The Credit Facility specifies an aggregate maximum credit amount equal to $500.0 million and a maximum borrowing base, as determined by the Lenders. The determination of the borrowing base takes into consideration the estimated value of the Company’s oil and gas properties in accordance with the Lenders’ customary practices for oil and gas loans. The borrowing base is subject to scheduled redeterminations on a semiannual basis. The amount available for borrowing could be increased or decreased as a result of such redeterminations. Under certain circumstances, the Borrower and the Lenders shall each have the option to request one unscheduled borrowing base redetermination per fiscal year. As of November 30, 2021 and 2020, the Company’s borrowing base was $140.0 million and $120.0 million, respectively, of which $68.0 million and $98.5 million, respectively, was outstanding.
The Company has the option to request borrowings under either a eurodollar loan or an Alternative Base Rate loan. Eurodollar loans bear interest at the adjusted LIBOR plus an applicable margin ranging from 2.75 percent to 3.75 percent depending on the borrowing base utilization percentage. Alternative Base Rate loans bear interest at the higher of (a) the prime rate in effect on such day, (b) the federal funds effective rate in effect on such day plus 0.5 percent, or (c) the adjusted LIBOR for a one-month interest period on such day plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.75 percent to 2.75 percent depending on the borrowing base utilization percentage. Interest is calculated and paid monthly in arrears. Additionally, the Company incurs an unused credit facility fee of 0.500 percent regardless of the borrowing base utilization percentage. As of November 30, 2021, the interest rate on the outstanding balance under the Credit Facility was 3.10 percent.
The Credit Facility includes customary terms and covenants that place limitations on certain types of activities, including the payment of dividends and distributions, and requires satisfaction of certain financial covenants, such as minimum leverage and current ratios. The Credit Facility also requires excess cash at any point in time over $10.0 million to be repaid to the Borrowers, subject to the terms in the Credit Facility. The Company was in compliance with all financial covenants of the Credit Facility at November 30, 2021 and 2020. The Credit Facility is guaranteed by the Company’s subsidiaries and is collateralized with a minimum of 85 percent of the proved PV10 reserve value of the Company’s oil and gas properties.
In addition, the Credit Facility places additional conditions on the ability of the founding members of management to put their common units back to the Company (see Note 13). These conditions include the establishment of maximum percentages of debt outstanding relative to the existing borrowing base and pro forma debt to earnings before interest, taxes, depletion, depreciation, amortization, and exploration expense (“EBITDAX”) ratios, as defined in the Credit Facility, at the date of the permitted exercise.
In April 2022, the Company amended its Credit Facility with a syndicate of banks. The Credit Facility will mature in April 2026. The Credit Facility permits borrowing on a revolving credit basis with availability equal to the lesser of the aggregate elected commitments of $170 million and the current borrowing base of $200 million. At the Company’s option, borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest at either an adjusted forward-looking term rate based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) or an adjusted base rate (“Base Rate”) (the highest of the Administrative Agent’s prime rate, the Federal Funds rate plus 0.50% or the 30-day SOFR rate plus 1.0%), plus a spread ranging from 1.75% to 2.75% with respect to Base Rate borrowings and 2.75% to 3.75% with respect to SOFR borrowings, in each case based on the borrowing base utilization percentage.
Note 6—Derivative Instruments
The Company periodically enters into various commodity hedging instruments to mitigate a portion of the effect of oil and natural gas price fluctuations. The Company classifies the fair value amounts of commodity derivative assets and liabilities as current or noncurrent commodity derivative assets or current or noncurrent commodity derivative liabilities, whichever the case may be.
F-30
The following table summarizes the location and fair value amounts of commodity derivative instruments in the consolidated balance sheet as of November 30, 2021, as well as the gross recognized derivative assets, liabilities, and amounts offset in the consolidated balance sheet:
| (In thousands) | GROSS RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ LIABILITIES |
GROSS AMOUNTS OFFSET |
NET RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ LIABILITIES |
|||||||||
| Commodity derivative assets: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative assets |
$ | 1,513 | $ | — | $ | 1,513 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,513 | $ | — | $ | 1,513 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Commodity derivative liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative liabilities |
$ | 8,672 | $ | — | $ | 8,672 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 8,672 | $ | — | $ | 8,672 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following table summarizes the location and fair value amounts of all commodity derivative instruments in the consolidated balance sheet as of November 30, 2020, as well as the gross recognized derivative assets, liabilities, and amounts offset in the consolidated balance sheet:
| (In thousands) | GROSS RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ LIABILITIES |
GROSS AMOUNTS OFFSET |
NET RECOGNIZED FAIR VALUE ASSETS/ LIABILITIES |
|||||||||
| Commodity derivative assets: |
||||||||||||
| Current derivative assets |
$ |
9,299 |
|
$ | (76 | ) | $ | 9,223 | ||||
| Noncurrent derivative assets |
2,305 | — | 2,305 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 11,604 | $ | (76 | ) | $ | 11,528 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Commodity derivative liabilities—Current deferred option premiums |
$ | 76 | $ | (76 | ) | $ | — | |||||
As of November 30, 2021, the Company had the following crude oil swaps:
| CONTRACT | TYPE |
TERM |
VOLUME HEDGED (Bbls) |
INDEX | ROUNDED FIXED PRICE |
|||||||||
| 1 | Swap | December 2021 - December 2021 | 25,000 | WTI-NYMEX | $ | 52 | ||||||||
| 2 | Swap | December 2021 - December 2021 | 25,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 52 | |||||||||
| 3 | Swap | December 2021 - December 2021 | 35,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 53 | |||||||||
| 4 | Swap | December 2021 - November 2022 | 360,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 71 | |||||||||
| 5 | Swap | January 2022 - November 2022 | 330,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 49 | |||||||||
| 6 | Swap | January 2022 - November 2022 | 330,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 65 | |||||||||
| 7 | Swap | January 2022 - November 2022 | 275,000 | WTI-NYMEX | 51 | |||||||||
As of November 30, 2021, the Company had the following natural gas swap:
| CONTRACT |
TYPE |
TERM |
VOLUME HEDGED (Mcfs) |
INDEX | ROUNDED FIXED PRICE ($/Mcf) |
|||||||||||
| 8 | Swap | January 2022 - April 2022 | 600,000 | HHUB-NYMEX | $ | 4 | ||||||||||
F-31
Due to the volatility of oil prices, the estimated fair values of the Company’s commodity derivative instruments are subject to large fluctuations from period to period.
The counterparties in the Company’s derivative instruments also participate in the Company’s Credit Facility; accordingly, the Company is not required to post collateral, as the counterparties have the right of offset for any derivative liabilities, and the Credit Facility is secured by the Company’s oil and gas assets. For further discussion related to the fair value of the Company’s derivatives, see Note 4.
Note 7—Accrued Liabilities
Accrued liabilities at November 30, 2021 and 2020 are summarized as follows:
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
| Accrued capital expenditures |
$ | 11,500 | $ | 8,300 | ||||
| Accrued lease operating expenses, net |
1,270 | 2,332 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation |
2,714 | 1,674 | ||||||
| Accrued derivative settlement |
2,450 | — | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
683 | 411 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 18,617 | $ | 12,717 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 8—Asset Retirement Obligations
A rollforward of AROs for the years ended November 30, 2021 and 2020 are presented below.
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
| Balance—Beginning of year |
$ | 5,666 | $ | 5,079 | ||||
| Liabilities incurred |
123 | 338 | ||||||
| Accretion expense |
274 | 249 | ||||||
| Revisions |
69 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Balance—End of year |
$ | 6,132 | $ | 5,666 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 9—Related Party Transactions
3B acquired common units in the Company which were funded by two Initial Loans with related parties (see Note 13). As part of the funding of the Company, 3B entered into two different promissory notes with VE Holding LLC, an entity owned by JFG. The promissory notes allowed 3B to borrow up to $7.875 million and $3.5 million, initially accruing interest at 10.0 percent and 3.5 percent, respectively, and had maturity dates of May 7, 2021 (the “Initial Loans”). Initially, repayment of the $3.5 million promissory note was fully guaranteed by one of the members of 3B. Each of the two Initial Loans are collateralized by all of the common units held by 3B. In 2020 the $3.5 million promissory note was amended to remove the guarantee, change the interest rate to 10.0 percent and extend the maturity date to December 31, 2023. At the same time the $7.875 million promissory note was amended to extend the maturity date to December 31, 2023. The Initial Loans between 3B and VE Holding LLC are held outside of the Company and are not a liability of the Company. During 2021, a $12.0 million ratable distribution was made to the common unit holders. The 3B distribution of $0.3 million was used to pay down a pro rata portion of the outstanding interest on the Initial Loans.
In connection with the Company Agreement, in July 2018 certain executives entered into two separate promissory notes aggregating to $10.0 million with VE Holding LLC (the “2018 Notes”), which are collateralized by the MIUs granted to the respective executive. The 2018 Notes accrue interest at 3.0 percent per annum payable annually on December 31 and mature the earlier of July 1, 2024, an MIU exchange, or an acceleration event (as defined). The 2018 Notes may be prepaid at any time but are subject to mandatory prepayment upon the issuance of any
F-32
distributions from the Company related to the MIUs held by such executives. Additionally, the 2018 Notes were considered full recourse to each respective executive for a limited time, with such recourse reduced by one-third each December 31 through 2020. As the 2018 Notes are between VE Holding LLC and the executives, they do not represent liabilities of the Company.
The Company has entered into an amended and restated services agreement (the “Services Agreement”) by and between the Company, Vitesse Management, and Vitesse Oil, LLC (“Vitesse Oil”) on May 7, 2014. Vitesse Oil is an entity with management common to that of the Company. Per the Services Agreement, costs incurred by Vitesse Management was to be allocable between the Company and Vitesse Oil initially at 50 percent each and adjusted automatically each quarter, such that the Company’s share of allocable costs shall be the greater of 50 percent or the quotient of the total contributed capital to the Company made by its members and the sum of the total contributed capital to the Company and Vitesse Oil by their respective members. As such, the Company incurred 90 percent of the Vitesse Management costs for the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019. The amount of costs reimbursed from Vitesse Oil to the Company for management services was $1.1 million, $1.0 million, and $0.9 million for each of the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The amount due to the Company from Vitesse Oil as of November 30, 2021 and 2020 was immaterial.
On July 1, 2016, the Company entered into a separate services agreement between Vitesse Management and JETX Energy, LLC (“JETX”), formerly known as Juneau Energy, LLC, another entity owned by JFG with common management. Per this services agreement, Vitesse Management is to provide JETX certain administrative services and supervise, administer, and manage the business affairs and operations of JETX and its subsidiaries for a service provider fee of $0.2 million per month. The term of this service agreement extends for an unlimited amount of time; however, it is subject to termination by either Vitesse Management or JETX if provided written consent following the first anniversary or a final exit event. During each of the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, the Company received its net share of fees from JETX of approximately $2.4 million, which is classified as a reduction to general and administrative expenses on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
On July 1, 2016, the Company implemented the Employee Participation Plan (“EPP”) pursuant to which employees, consultants, or independent contractors of the Company may be invited to personally acquire a working interest in new oil and gas wells in which the Company elects to participate. The EPP was subsequently amended on January 1, 2018. The tranches are not to exceed a maximum of $2.0 million of capital expenditures in the aggregate for each year. Participants in the EPP are required to fund their proportion of development costs and ongoing operating expenses of those specific wellbores. Compensation expense is measured by the allocable amount of the value of the assigned wellbore leasehold costs which has historically been immaterial.
In 2018, the Company authorized a $2.0 million retention bonus, of which $1.5 million is paid by funding participants’ development and operating expenses under the EPP. Participants vest ratably in their interests in the underlying wells at December 31, 2018, 2019, and 2020 if still employed; thus, the Company recognized compensation expense of $0.4 million and $0.5 million in 2020 and 2019, respectively, as the interests of the remaining participants vested or were deemed to vest.
Note 10—Employment Agreements
The Company has executed employment agreements with two executives. The term of each agreement is through December 31, 2023, with an automatic renewal clause on a year-to-year basis. Both executives and Vitesse Management had the right to terminate the agreement effective December 31, 2022 if notice was given prior to December 31, 2021. Such notice was not given. Under the employment agreements, the executives have rights to minimum salaries and certain compensation agreements upon termination of employment, including executive base salary, accrued vacation pay earned, and unreimbursed expenses incurred up to the date of termination. In addition, for fiscal 2019 and thereafter, the executives qualify for defined minimum annual bonuses. Under the terms of the employment agreements, the executives also are subject to noncompetition and nonsolicitation agreements.
Also, as part of amendments to the respective employment agreements made in July 2018, the previously vested Founder MIUs (Note 13) were subjected to forfeiture if the executive were to terminate employment for any reason other than Good Reason (as defined). However, the forfeiture provision were reduced over time such that if the executive remained employed through December 31, 2020 the Founder MIUs are no longer subject to forfeiture.
F-33
Note 11—Leases
The Company is obligated under noncancelable leases primarily for facilities and equipment. Total expense under these operating leases was $0.4 million, $0.4 million and $0.3 million for the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019.
Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company’s lease agreements do not provide an implicit borrowing rate; therefore, an internal incremental borrowing rate is determined based on information available at the lease commencement date for the purpose of determining the present value of lease payments. The right-of-use assets of $0.5 million and $0.9 million as of November 30, 2021 and 2020, respectively, are recorded within Other noncurrent assets on the consolidated balance sheets. The related lease obligations of $0.5 million and $0.9 million as of November 30, 2021 and 2020, respectively, are recorded within Other current liabilities and Other noncurrent liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets.
Note 12—Commitments and Contingencies
Litigation
From time to time, the Company may be involved in litigation relating to claims arising out of its operations in the normal course of business. As of the date of this report, management of the Company was unaware of any material legal proceedings against the Company. The Company maintains insurance to cover certain actions.
Note 13—Members’ Equity and Unit-Based Compensation
The Company has two classes of membership units, with the following units authorized, issued, and outstanding as of November 30, 2021 and 2020:
| AUTHORIZED | ISSUED AND OUTSTANDING |
|||||||
| Common units |
450,000,000 | 450,000,000 | ||||||
| Management incentive units |
1,000,000 | 953,750 | ||||||
Common Units
Common units issued to date have been issued at $1 per unit, with an aggregate capital commitment from all common members of $450 million. There initially shall be five managers on the board of managers, with three managers designated by JFG (such designated managers are each a “Jefferies Manager”) and two managers designated by 3B. For voting purposes, each manager is entitled to one vote, and the affirmative vote of a majority of the board of managers, including at least one Jefferies Manager, is required to ratify any significant decisions of the Company.
Certain executives of the Company, as a result of their ownership of 3B, were granted the right to put all of their common units back to the Company in exchange for their pro rata share of the oil and gas interests then owned by the Company beginning in May 2017 (the “Common Unit Exchange Option”). In connection with the Company Agreement, the terms of the Common Unit Exchange Option were modified, where it may only be exercised on January 1, 2021 or on the annual anniversary thereafter and subject to additional conditions. Such conditions include, but are not limited to, that the Company is not in the process of an initial public offering; common unit holders have either received distributions resulting in, or the fair value of the Company’s net assets are such that the Company would achieve, a specified rate of return (“Flip Threshold”); and 3B reimburses the common unit holders for its pro rata share of liabilities in excess of cash balances at the time of exercise. Further, 3B must discharge any principal and interest outstanding related to the Initial Loans. As a result of the Common Unit Exchange Option resulting in the transfer of a portion of the oil and gas interests in proportion to 3B’s percentage holding of the common units, the Common Unit Exchange Option is considered to be a transaction that does not occur at fair market value. Through the issuance date of these financial statements the Common Unit Exchange Option has not been exercised.
F-34
In addition to the Common Unit Exchange Option, in the event of termination of any or both of the executives that hold common units, the Company has the option to repurchase the common units held by 3B in exchange for cash (the “Common Unit Call Option”). The Common Unit Call Option would be executed at fair market value on the date of the transaction.
As a result of 3B’s receipt of in-substance nonrecourse notes (the “Initial Loans”) that are each collateralized by all of the common units held by 3B, for accounting purposes the Company has granted 3B an in-substance call option that is within the scope of accounting guidance related to share-based compensation (the “Common Unit Option Grant”), which was fully vested on the date of grant in 2014. Due to the nature and terms of the Common Unit Exchange Option described above, the Common Unit Option Grant is classified as a liability award, remeasured at fair market value at each reporting date with the change in fair market value recorded to earnings. As of November 30, 2021, the aggregate intrinsic value of the Common Unit Option Grant, which is both outstanding and exercisable, was negative as the fair value of the common unit is less than the deemed exercise price.
Management Incentive Units
Management incentive units may be issued by the Company to eligible employees and/or consultants. All MIUs are nonvoting and provide the MIU holders the opportunity to participate in distributions after the common unit holders have received a return equal to the Flip Threshold (as defined). In connection with the Company Agreement, the terms and conditions of the MIUs were modified from the Company’s original LLC agreement. Such modifications included, but were not limited to, a reset and change in the Flip Threshold, as well as changes to specific terms and conditions of MIU holder put rights and Company call rights.
MIUs have been granted to the founding members of management (“Founder MIUs”) and certain other employees of the Company (“Non-Founder MIUs”). Holders of Non-Founder MIUs may put at least 25 percent of their vested MIUs to the Company for cash at estimated fair market value as of the date of the transaction, on or after January 1, 2022, subject to conditions that include, but are not limited to, continued employment and no pending initial public offering (the “Non-Founder MIU Put Option”). Holders of the Founder MIUs may put at least 10 percent of their vested MIUs to the Company on or after January 1, 2021 for either (1) cash at estimated fair market value as of the date of the transaction or (2) interests in the Company’s oil and gas properties with a fair market value equal to the fair market value of the MIU as of the date of the transaction, subject to conditions that include, but are not limited to, the Company is not in the process of an initial public offering; common unit holders have either received distributions resulting in, or the fair value of the Company’s net assets are such that the common unit holders would achieve the Flip Threshold, and the 2018 Notes have been repaid or are to be repaid out of proceeds from the exercise of the put option (the “Founder MIU Put Option”). In addition, the Company has the right to repurchase Founder MIUs and Non-Founder MIUs at fair market value upon the termination of employment for any reason (the “MIU Call Option”). With respect to the Flip Threshold, as of April 2018 management determined that the achievement of the Flip Threshold was probable. Through the issuance date of these financial statements none of the Founder MIU Put Options, the Non-Founder MIU Put Options, or the MIU Call Option have been exercised.
All MIUs are subject to vesting requirements and forfeiture provisions specific to the Founder MIUs and Non-Founder MIUs, as outlined in the Company Agreement, employment agreement, grant letters, and other supporting MIU documentation. All unvested MIUs vest upon a final exit event (as defined), and are cancelled in the event of termination of the grantee. In the event of termination for Cause (as defined) all vested MIUs are forfeited for no consideration.
The Company accounts for Non-Founder MIUs as liability-based awards until the respective holder has borne the risk of unit ownership, at which point the value of the liability is reclassified outside of permanent equity. While the awards are classified as liabilities, compensation expense is recorded through the vesting period, and changes in the estimated fair market value of the liability, are recorded in earnings. Once reclassified outside of permanent equity increases in the estimated fair market value of the award are recorded through members’ equity. During the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, the Company recorded a reduction of $1.5 million, an increase of $1.0 million and a reduction of $0.3 million respectively, through members’ equity to adjust the Non-Founder MIUs to fair market value.
F-35
A summary of the Company’s activity related to Non-Founder MIUs for the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019, is presented below:
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Nonvested at period end |
45,000 | 82,500 | 82,500 | |||||||||
| Granted during the period |
— | 50,000 | 15,000 | |||||||||
| Vested during the period |
37,500 | 50,000 | 58,750 | |||||||||
| Forfeited during the period |
— | — | 12,500 | |||||||||
| Fair value of MIUs vested during the period |
$ | 0.7 million | $ | 0.7 million | $ | 1.3 million | ||||||
As of November 30, 2021, there was $1.0 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested unit-based compensation arrangements. That cost is expected to be recognized through June 2024, over a weighted-average period of 1.4 years.
As a result of each of the management founders’ receipt of an in-substance nonrecourse note (the “2018 Notes”) that are each collateralized by all of Founder MIUs held by the respective executive, for accounting purposes the Company has granted each of the management founders an in-substance call option that is within the scope of accounting guidance related to share-based compensation (the “Founder MIU Option Grant”). Due to the nature and terms of the Founder MIU Put Option described above, the Founder MIU Option Grant is classified as a liability award, remeasured at fair market value at each reporting date with the change in fair market value recorded to earnings. As of November 30, 2021, the aggregate intrinsic value of the Founder MIU Option Grant, which is both outstanding and exercisable, is $5.0 million.
Total compensation cost (income) recognized in the consolidated statements of operations within Unit-based compensation for each of the years ended November 30, 2021, 2020 and 2019 is as follows:
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Common Unit Option Grant |
$ | (569 | ) | $ | (1,308 | ) | $ | (28 | ) | |||
| Founder MIU Option Grant |
1,625 | 700 | 2,213 | |||||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs |
353 | 64 | 1,110 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,409 | $ | (544 | ) | $ | 3,295 | |||||
The liability recorded in the consolidated balance sheets within Unit-based compensation as of November 30, 2021 and 2020 is as follows:
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
| Common Unit Option Grant |
$ | 1,706 | $ | 2,275 | ||||
| Founder MIU Option Grant |
6,510 | 4,885 | ||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs |
136 | 419 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 8,352 | $ | 7,579 | ||||
Measurement of unit-based compensation
The Company records the Non-founder MIUs, Founder MIU Option Grant, and Common Unit Option Grant at fair value at the date of grant and at each balance sheet date, which results in compensation cost being measured at fair value. As noted above, vested Non-founder MIUs, where the respective holder has borne the risk of ownership, are recorded within temporary equity, with changes in fair value recorded within members’ equity.
F-36
The fair value of each of the Founder MIU Option Grant and the Common Unit Option Grant (collectively “the Options”) are estimated using a Black Scholes Model that uses the assumptions noted in the following tables. As the Company doesn’t have publicly-traded equity we incorporated data from a group of publicly-traded peer companies when estimating fair value, and because when estimating fair value management incorporates ranges of assumptions for inputs, those ranges are disclosed. Expected volatilities are based on the historical volatility of our identified peer group of companies. The expected term of the Options is determined based on the Time to Exit/Liquidity Event. The risk-free rate for periods within the expected life of the option is interpolated from the US constant maturity treasury rate, for a term corresponding to the expected term.
| Founder MIU Option Grant | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||
| Expected volatility |
125% - 170% | 130% - 145% | 125% - 160% | |||||
| Weighted-average volatility |
150% | 137.5% | 142.5% | |||||
| Expected dividends/distributions |
0% | 0% | 0% | |||||
| Expected term (in years) |
1 | 2 | 2.1 | |||||
| Risk-free rate |
0.24% | 0.16% | 1.61% | |||||
| Common Unit Option Grant | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||
| Expected volatility |
50% | 60% - 65% | 45% | |||
| Weighted-average volatility |
50% | 62.5% | 45% | |||
| Expected dividends/distributions |
0% | 0% | 0% | |||
| Expected term (in years) |
1 | 2 | 2.1 | |||
| Risk-free rate |
0.24% | 0.16% | 1.61% |
Distributions
Distributions of funds associated with common units follow a prescribed framework, which is outlined in detail in the Company Agreement. In general, distributions are first allocated to those unitholders based on their allocable share, as defined in the Company Agreement. Each unitholder will then receive a distribution in accordance with the tiered waterfall, as defined in the Company Agreement. The Company made $12.0 million and $25.0 million of distributions on common units during the years ended November 30, 2021 and 2019, respectively.
F-37
Earnings Per Unit
We have two classes of equity in the form of common units and MIUs that are vested and where the holder has borne the risks and rewards of ownership at which point the MIU is reclassified from liabilities to outside of permanent equity. Both common units and temporary equity classified MIUs are considered common units, and distributions are made in accordance with the Company Agreement. As such, we present earnings per unit (“EPU”) for both classes of equity. In calculating EPU we apply the two-class method. Under the two-class method net income (loss) attributable to common units is allocated to common units and other participating securities in proportion to the claim on earnings of each participating security after giving effect to distributions declared during the period, if any. The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net income (loss) per unit:
| FOR THE YEARS ENDED NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Common Units |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
18,114 | (8,857 | ) | 35,888 | ||||||||
| less: income allocable to participating securities |
||||||||||||
| In-substance options on common units (Common Unit Option Grant) |
(458 | ) | — | (907 | ) | |||||||
| In-substance options on Founder MIUs (Founder MIU Option Grant) |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs classified as temporary equity |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Non-Founder MIUs classified as liabilities |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common unitholders |
17,656 | (8,857 | ) | 34,981 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding (in 000s) |
450,000 | 450,000 | 450,000 | |||||||||
| less: Common Units accounted for as in-substance options |
(11,375 | ) | (11,375 | ) | (11,375 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding (in 000s) |
438,625 | 438,625 | 438,625 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic and Diluted EPU |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | 0.08 | |||||
| Temporary Equity Classified MIUs |
||||||||||||
| Income allocable to Non-Founder MIUs classified as temporary equity |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| MIUs classified in temporary equity (in 000s) |
234 | 196 | 146 | |||||||||
| Basic and Diluted EPU |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
F-38
Supplemental Oil and Gas Information (Unaudited)
Oil and Natural Gas Exploration and Production Activities
Oil and natural gas sales reflect the market prices of net production sold or transferred with appropriate adjustments for any contractual provisions. Production expenses include lifting costs incurred to operate and maintain productive wells and related equipment including such costs as operating labor, repairs and maintenance, materials, supplies and fuel consumed. Production taxes include ad valorem and severance taxes. Depletion of crude oil and natural gas properties relates to capitalized costs incurred in acquisition, exploration, and development activities. Results of operations do not include interest expense and general corporate amounts. The results of operations for the Company’s crude oil and natural gas production activities are provided in the Company’s related consolidated statements of operations. Capitalized costs relating the Company’s oil and natural gas producing activities as of
November 30, 2021 and 2020 are provided in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
Costs Incurred
The costs incurred in crude oil and natural gas acquisition, exploration and development activities are highlighted in the table below.
| NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Costs Incurred for the Year: |
||||||||||||
| Proved Property Acquisition and Other |
$ | 6,210 | $ | 9,234 | $ | 5,094 | ||||||
| Development |
36,769 | 36,859 | 111,913 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 42,979 | $ | 46,093 | $ | 117,007 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Oil and Natural Gas Reserve Data
The following tables present the Company’s net proved crude oil and natural gas reserves as prepared by Cawley, and include changes as estimated by the Company’s engineering staff. The Company emphasizes that reserves are approximations and are expected to change as additional information becomes available. Reservoir engineering is a subjective process of estimating underground accumulations of crude oil and natural gas that cannot be measured in an exact way, and the accuracy of any reserve estimate is a function of the quality of available data and of engineering and geological interpretation and judgment.
| NATURAL GAS (MMcf) |
OIL (MBbl) |
MBoe | ||||||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2018 |
73,353 | 37,898 | 50,124 | |||||||||
| Revisions of Previous Estimates |
12,413 | 3,612 | 5,681 | |||||||||
| Extensions, Discoveries and Other Additions |
4,478 | 1,427 | 2,173 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of Reserves |
2,185 | 1,397 | 1,761 | |||||||||
| Production |
(5,105 | ) | (3,063 | ) | (3,914 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2019 |
87,324 | 41,271 | 55,825 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Revisions of Previous Estimates |
(5,723 | ) | (8,094 | ) | (9,048 | ) | ||||||
| Extensions, Discoveries and Other Additions |
2,199 | 729 | 1,096 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of Reserves |
6,638 | 1,799 | 2,905 | |||||||||
| Production |
(5,609 | ) | (2,599 | ) | (3,534 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2020 |
84,829 | 33,106 | 47,244 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Revisions of Previous Estimates |
(4,181 | ) | (2,998 | ) | (3,694 | ) | ||||||
| Extensions, Discoveries and Other Additions |
2,648 | 899 | 1,340 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of Reserves |
1,793 | 959 | 1,258 | |||||||||
| Production |
(7,065 | ) | (2,436 | ) | (3,614 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves at November 30, 2021 |
78,024 | 29,530 | 42,534 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-39
| NATURAL GAS (MMcf) |
OIL (MBbl) |
MBoe | ||||||||||
| Proved Developed Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2018 |
33,663 | 17,513 | 23,124 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2019 |
39,059 | 18,928 | 25,438 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
47,418 | 17,841 | 25,744 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
58,437 | 17,764 | 27,504 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Proved Undeveloped Reserves: |
||||||||||||
| November 30, 2018 |
39,690 | 20,385 | 27,000 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2019 |
48,264 | 22,342 | 30,386 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2020 |
37,410 | 15,265 | 21,500 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
19,586 | 11,765 | 15,030 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Proved reserves are estimated quantities of crude oil and natural gas, which geological and engineering data indicate with reasonable certainty to be recoverable in future years from known reservoirs under existing economic and operating conditions. Proved developed reserves are proved reserves that can be expected to be recovered through existing wells with existing equipment and operating methods. Proved undeveloped reserves are included for reserves for which there is a high degree of confidence in their recoverability and they are scheduled to be drilled within the next five years.
Notable changes in proved reserves for the year ended November 30, 2021 included the following:
| ∎ | Revisions to previous estimates. In 2021, revisions to previous estimates increased proved developed and decreased proved undeveloped reserves by a net amount of 3.7 MMBoe. Included in these revisions were 4.3 MMBoe of upward adjustments caused by higher crude oil and natural gas prices and 6.9 MMBoe of downward adjustments related to the removal of undeveloped drilling locations due to a slower recovery of rig activity than expected in the Williston Basin, 0.5 MMBoe of downward adjustments related to the removal of drilled uncompleted wells in the Central Rockies related to the SEC 5-year development rule and 0.6 MMBoe of downward adjustments attributable to well performance when comparing the Company’s reserve estimates at November 30, 2021 to November 30, 2020. |
| ∎ | Extensions and discoveries. In 2021, total extensions and discoveries of 1.3 MMBoe were attributable to additions of proved undeveloped locations in the Williston Basin. |
Notable changes in proved reserves for the year ended November 30, 2020 included the following:
| ∎ | Revisions to previous estimates. In 2020, revisions to previous estimates decreased proved developed and undeveloped reserves by a net amount of 9.0 MMBoe. Included in these revisions were 9.7 MMBoe of downward adjustments caused by lower crude oil and natural gas prices largely attributable to the impacts of the global coronavirus pandemic, a 1.2 MMBoe upward adjustment attributable to well performance when comparing the Company’s reserve estimates at November 30, 2020 to November 30, 2019 and 0.6 MMBoe of downward adjustments related to the removal of undeveloped drilling locations related to the SEC 5-year development rule. |
| ∎ | Extensions and discoveries. In 2020, total extensions and discoveries of 1.0 MMBoe were attributable to additions of proved undeveloped locations in the Williston Basin. |
Notable changes in proved reserves for the year ended November 30, 2019 included the following:
| ∎ | Revisions to previous estimates. In 2019, revisions to previous estimates increased proved reserves by a net amount of 5.7 MMBoe. Included in these revisions were 0.8 MMBoe of downward adjustments caused by lower crude oil and natural gas prices and 5.8 MMBoe of upward adjustments attributable to upward |
F-40
| revisions of undeveloped and proved non-producing locations due to current year drilling results and 0.7 MMBoe of upward adjustments attributable to well performance when comparing the Company’s reserve estimates at November 30, 2019 to November 30, 2018. |
| ∎ | Extensions and discoveries. In 2019, total extensions and discoveries of 2.2 MMBoe were attributable to additions of proved undeveloped locations in the Williston Basin. |
Standardized Measure of Discounted Future Net Cash Inflows and Changes Therein
The following table presents a standardized measure of discounted future net cash flows relating to proved crude oil and natural gas reserves, and the changes in standardized measure of discounted future net cash flows relating to proved crude oil and natural gas were prepared in accordance with the provisions of ASC 932 Extractive Activities—Oil and Gas. Future cash inflows were computed by applying average prices of crude oil and natural gas for the last 12 months to estimated future production. Future production and development costs were computed by estimating the expenditures to be incurred in developing and producing the proved crude oil and natural gas reserves at the end of the year (including asset retirement costs), based on year-end costs and assuming continuation of existing economic conditions. Future income tax expenses were calculated by applying appropriate year-end tax rates to future pretax cash flows relating to proved crude oil and natural gas reserves, less the tax basis of properties involved and tax credits and loss carry forwards relating to crude oil and natural gas producing activities. Income taxes for the Company are zero due to the Company’s tax status as a pass-through entity. Future net cash flows are then discounted at the rate of 10%. Actual future cash inflows may vary considerably, and the standardized measure does not represent the fair value of the Company’s crude oil and natural gas reserves.
| NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Future Cash Inflows |
$ | 2,151,098 | $ | 1,405,418 | $ | 2,448,491 | ||||||
| Future Production Costs |
(816,329 | ) | (713,495 | ) | (947,883 | ) | ||||||
| Future Development Costs |
(230,101 | ) | (245,128 | ) | (368,894 | ) | ||||||
| Future Income Tax Expense |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Future Net Cash Inflows |
$ | 1,104,668 | $ | 446,795 | $ | 1,131,714 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 10% Annual Discount for Estimated Timing of Cash Flows |
(503,055 | ) | (255,617 | ) | (627,685 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Standardized Measure of Discounted Future Net Cash Flows |
$ | 601,613 | $ | 191,178 | $ | 504,029 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The twelve-month average prices were adjusted to reflect applicable transportation and quality differentials on a well-by-well basis to arrive at realized sales prices used to estimate the Company’s reserves. The price of other liquids is included in natural gas. The prices for the Company’s reserve estimates were as follows:
| NATURAL GAS $/Mcf |
OIL $/Bbl |
|||||||
| November 30, 2021 |
$ | 3.46 | $ | 64.81 | ||||
| November 30, 2020 |
$ | 1.94 | $ | 40.45 | ||||
| November 30, 2019 |
$ | 2.76 | $ | 55.34 | ||||
F-41
Changes in the Standardized Measure of Discounted Future Net Cash Flows at 10% per annum follow:
| NOVEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
| Beginning of Period |
$ | 191,178 | $ | 504,029 | $ | 647,156 | ||||||
| Sales of Oil and Natural Gas Produced, Net of Production Costs |
(126,733 | ) | (49,948 | ) | (112,854 | ) | ||||||
| Extensions and Discoveries |
17,911 | 2,332 | 12,326 | |||||||||
| Previously Estimated Development Cost Incurred During the Period |
16,924 | 22,308 | 39,714 | |||||||||
| Net Change of Prices and Production Costs |
415,685 | (322,506 | ) | (227,520 | ) | |||||||
| Change in Future Development Costs |
22,606 | 79,816 | 3,167 | |||||||||
| Revisions of Quantity and Timing Estimates |
(17,833 | ) | (115,228 | ) | 79,830 | |||||||
| Accretion of Discount |
19,118 | 50,403 | 64,716 | |||||||||
| Change in Income Taxes |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Purchases of Minerals in Place |
23,272 | 17,304 | 26,408 | |||||||||
| Other |
39,485 | 2,668 | (28,914 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| End of Period |
$ | 601,613 | $ | 191,178 | $ | 504,029 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-42